Initiatives to Transition to a Circular Economy
Basic Policy
The JFE Group views transition to a circular economy as indispensable for realizing a sustainable society, and we are taking action to shift the overall economic system of society from a conventional linear economy to a circular economy. In these efforts, we are using digital technologies and collaborating with government, municipalities, and customers throughout the value chain, extending beyond the Group’s framework. We are promoting initiatives from three perspectives: converting byproducts and waste into resources, developing eco-product/eco-solution technologies with high resource efficiency, and expanding the use and sales of recycled resources. These activities will also contribute to addressing environmental issues such as climate change and biodiversity conservation and nature positive.
Circular Economy Concept and Initiatives
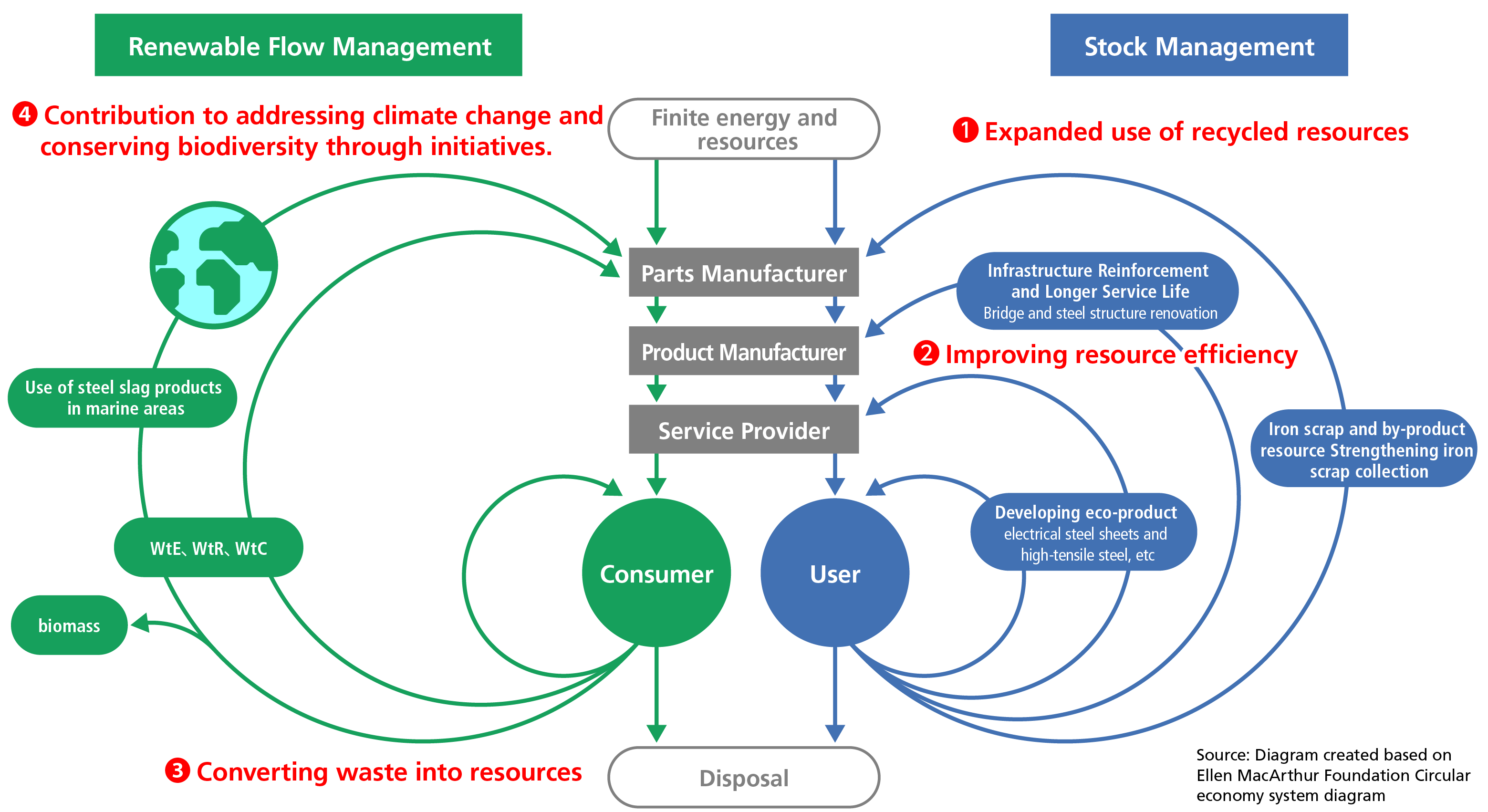
Iron is easily recovered, highly recyclable, and can be infinitely recycled as raw material for the same steel products. The JFE Group is also recovering and using steel scrap as well as developing initiatives for transitioning to a circular economy.
Our steel business using recycled resources by effectively using byproduct resources such as dust, sludge, and slag generated in the steelmaking process and using waste plastics as blast furnace raw materials. We are also improving resource efficiency by providing high-quality, high-performance steel products.
Our engineering business is delivering solutions for resource circulation by constructing plant and infrastructure facilities such as biomass fuel plants for food waste and sewage sludge, and waste-to-energy plants, as well as operating and managing these facilities on consignment. In addition, we are promoting a circular economy through recycling businesses for PET bottles and plastics, and energy supply businesses.
Our trading business is procuring environmentally sound materials such as biomass fuel by drawing upon our supply chain management network.
Since the steelmaking process consumes large volumes of fresh water for cooling and cleaning products and facilities, the efficient use of water resources, taking into account the impact on water sources and surrounding stakeholders, is a key issue. In response, we are reducing water intake by building systems to purify and recycle used water as much as possible at steelworks. In addition, we are raising employee awareness of water conservation and continuously minimizing environmental impact through reduced and more efficient water use. Furthermore, we place priority on maintaining a safe and sanitary water environment in the areas surrounding our manufacturing sites, implementing measures to protect water quality to have the least possible impact on local water resources, and actively preserving the living environment of local residents.
For details on the recycling businesses of JFE Steel and JFE Engineering, please see:
Governance
The JFE Group Environmental Committee, chaired by the president of JFE Holdings and operating under the JFE Group Sustainability Council, sets goals for environmental protection, monitors, and works to improve the Group’s overall environmental performance. Key issues for corporate management are deliberated at the Group Management Strategy Committee as well and reported to the Board of Directors. The board oversees environmental challenges by discussing the reports. Additionally, specialized committees set up by JFE Group operating companies and affiliates implement specific activities.
JFE Group Initiatives to Transition to a Circular Economy
Conversion of Byproducts and Waste into Resources
The JFE Group incorporates the circular economy concept into its business activities to ensure the responsible use of limited resources, reduce environmental impact, and realize a sustainable society. In particular, we are reusing byproducts and waste as new resources as ways to circulate resources and minimize waste.
EN Building a Recycling Value Chain
As one of Japan’s leading companies capable of providing one-stop solutions from the collection and transportation of waste to the intermediate treatment and recycling of recovered products, JFE Engineering is striving to establish a recycling value chain, including collaboration with partner companies and municipalities.
Recycling Value Chain
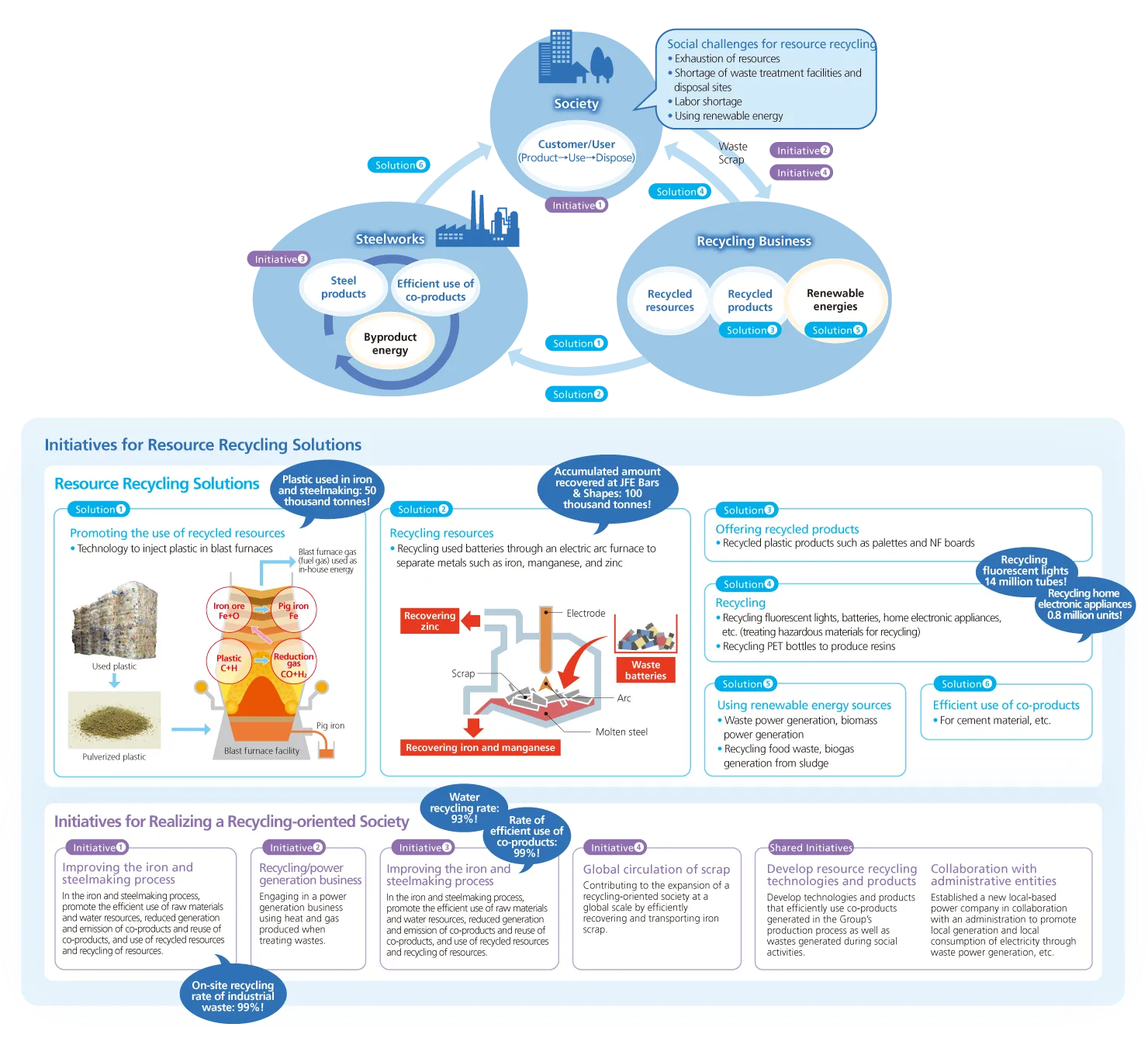
In addition, JFE Engineering is constructing and operating waste-to-energy facilities and waste treatment facilities overseas in alignment with the Ministry of the Environment’s National Action Plan for Marine Plastic Litter, formulated in 2019.
Furthermore, J&T Recycling Corporation, a Group company of JFE Engineering, supports the activities of the Japan Clean Ocean Material Alliance (CLOMA) , which was established to support activities that address the problem of marine plastic litter. As a member of CLOMA, the company is recycling PET bottles and plastics.
EN Promoting Plastic Recycling
J&T Recycling Corporation joined the recycling plan formulated by Sendai City under the Plastic Resource Circulation Act in September 2022 and, for the first time in Japan, obtained certification from both the Minister of the Environment and the Minister of Economy, Trade and Industry. Following this, in April 2023, the company launched the integrated collection of plastic products. In Sendai, product plastics that had previously been incinerated can now be collected with plastic containers and packaging for more efficient recycling.
In July 2023, J&T Recycling Corporation and the JR East Group jointly established J Circular System Corporation in Kawasaki, Kanagawa Prefecture to promote plastic recycling in Japan. This facility, one of the largest in Japan, is able to process 200 tonnes of used plastics per day and is set up to handle the entire process, from sorting to recycling into new products. The plant began full-scale operation in April 2025 and can directly accept unsorted used plastics collected by municipalities and businesses. This makes it possible to recycle used plastics that had previously been incinerated because they were difficult to sort. The collected used plastics are subjected to advanced sorting, and depending on their characteristics, they are recycled as material recycling or chemical recycling in collaboration with nearby recycling businesses, thereby enhancing resource circulation.
At present, recycling plans formulated under the Plastic Resource Circulation Act by Kawasaki City, Fujisawa City, and Ota Ward have received ministerial certification, and this is the first case in Japan where certification has been obtained through the collaboration of multiple municipalities and recycling businesses. With this certification, a large portion of the used plastics separated and collected as household waste from municipalities and citizens can now be recycled at this facility.
With its unprecedented recycling system, J Circular Systems aspires to become a forerunner in advanced plastic resource circulation and in promoting decarbonization while contributing to the realization of a sustainable, recycling-oriented society.
Ministerial Certification of the Recycling Plan in Sendai City

Scope of Municipal Recycling Plans Related to J Circular Systems

- Japan’s First! J&T Recycling Corporation Participates in Sendai City's Plastic Waste Recycling Project
- J&T Recycling Corporation Establishes J Circular System Corporation—Its Plastic Recycling Facilities on the Kawasaki Waterfront Have the Largest Scale in the Tokyo Metropolitan Area (Japanese only)
EN Horizontal Recycling of PET Bottles

Kyoei J&T Recycling Corporation*1, a subsidiary of J&T Recycling Corporation*2, launched its flake manufacturing plant in October 2021 and completed its pellet production line in April 2022 to begin full-scale commercial operation. Its bottle-to-bottle (B-to-B) technology facilitates repeated recycling (closed-loop/horizontal recycling) an unlimited number of times, achieving a 63% reduction in CO2 compared to the production of PET bottles from crude oil (calculated by Mitsubishi UFJ Research and Consulting Co., Ltd .), and was included as an example*3 of addressing resource and environmental constraints in the White Paper on Manufacturing Industries (Monozukuri) 2010, published by the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry.
Beverage manufacturers and retailers are pursuing a variety of ways to boost the recycling rate of PET bottles (B-to-B). In response to these needs, the B-to-B business of Kyoei J&T Recycling significantly contributes to realizing a circular economy and reducing CO2 emissions by curbing the use of natural resources.
- *1A joint venture of J&T Recycling Corporation and Kyoei Sangyo Co., Ltd
- *2A Group company of JFE Engineering
- *3By Kyoei Sangyo Co., Ltd.
Horizontal Recycling Flow of PET Bottles
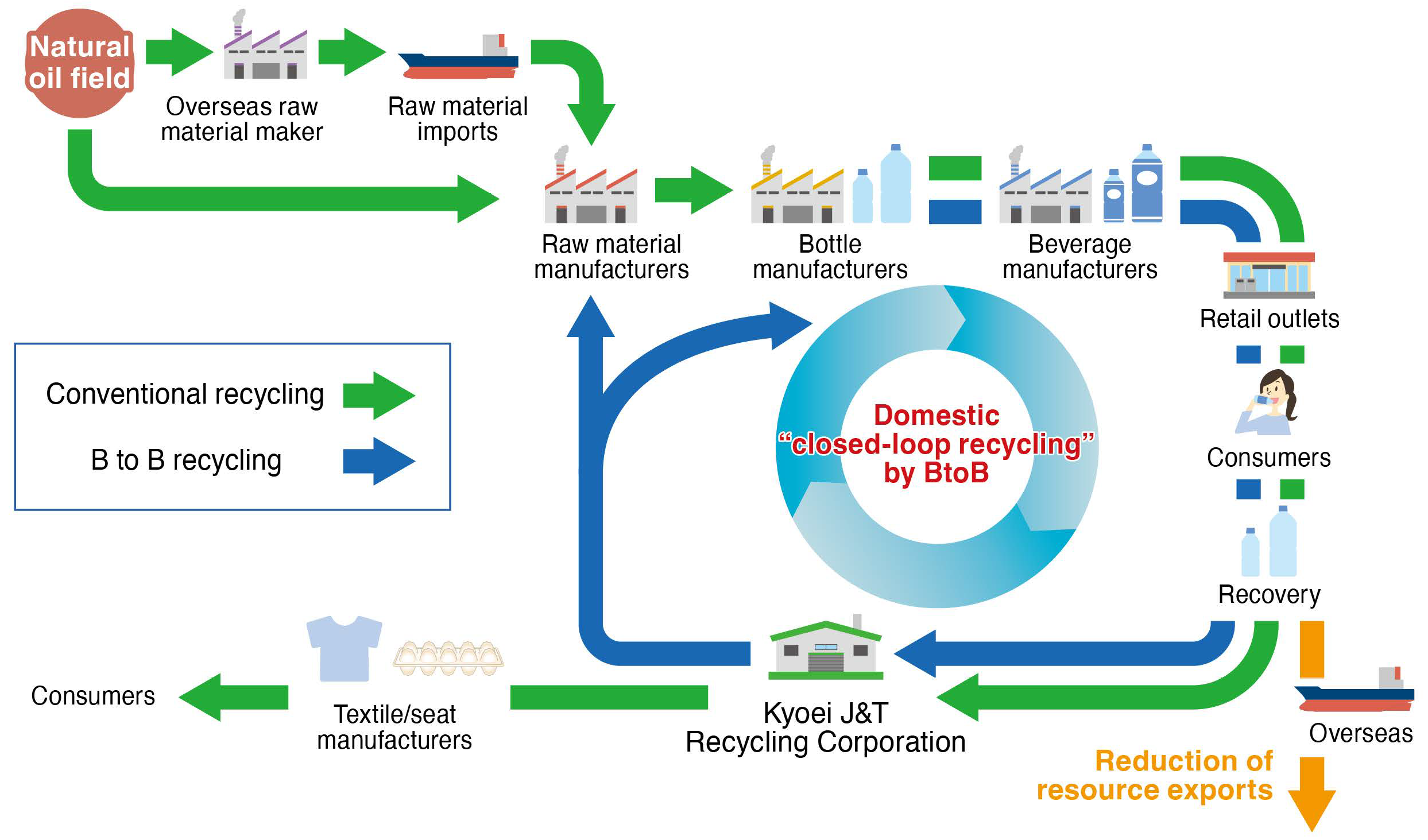
- Kyoei J&T Recycling Corporation’s West Japan PET Bottle MR Center Begins Full Commercial Operations
- Establishment of Joint Venture between J&T Recycling Corporation and Kyoei Sangyo Co., Ltd. — Construction of Japan’s Largest PET Bottle Recycling Resin Plant Contributing to the Shift to B-to-B (Japanese only)
EN Recycling Food Waste
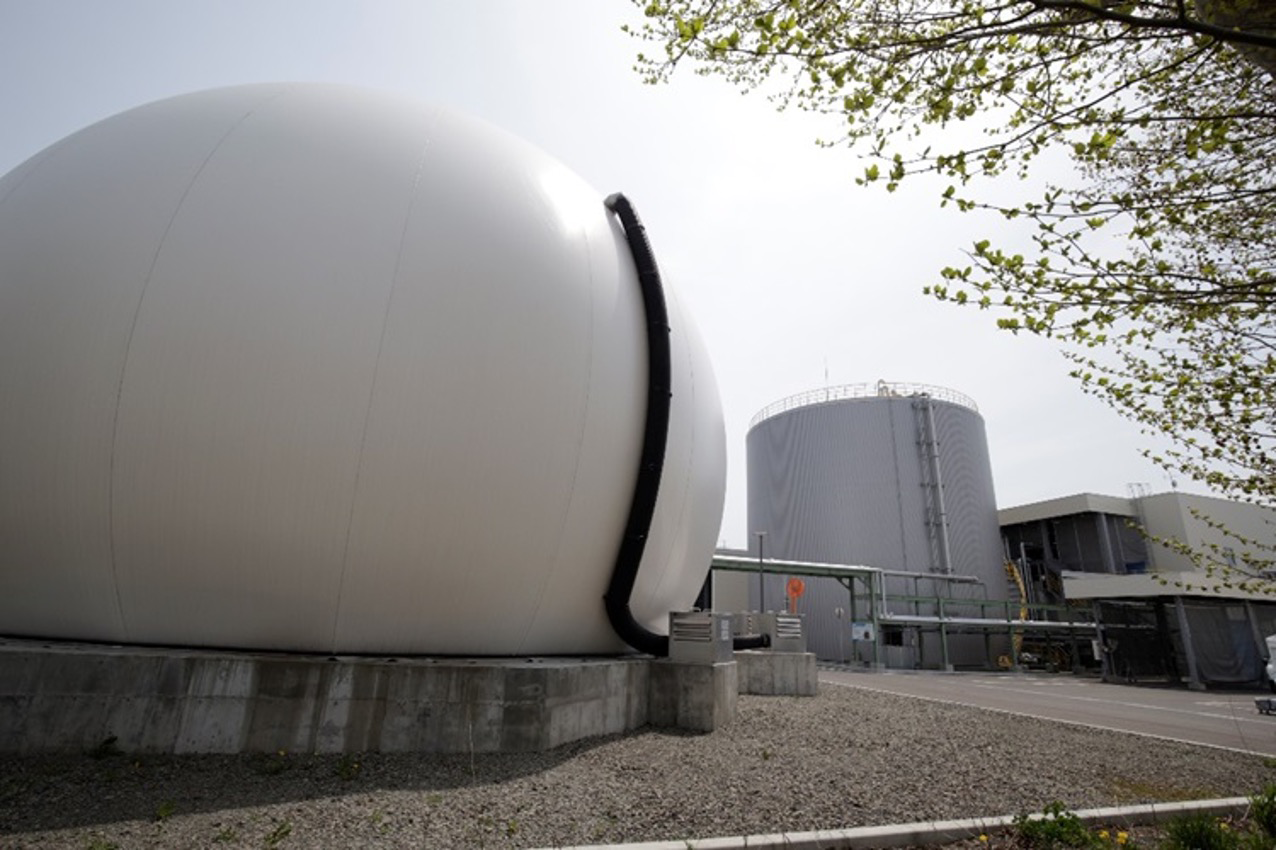
Sapporo Bio Food Recycling Corporation of the J&T Recycling Corporation Group has constructed a new plant to update and expand the capacity of its food recycling power generation plant in Sapporo City, and the plant started operation in November 2024. It is Hokkaido’s largest food biogas power generation facility*1, and J&T Recycling operates food recycling power generation businesses*2 at six locations nationwide, including this site.
In 2018, Sapporo City formulated the “2nd Sapporo City Basic Environmental Plan” and has been actively promoting waste reduction and resource recycling initiatives toward achieving zero carbon city status by 2050. While the progress of the plan shows significant reduction in both “household waste” and “business waste” over the past decade, the volume and utilization rate of food waste remained a challenge. To address this issue, Sapporo Bio Food Recycling has renovated its existing plant in the Sapporo Recycling Complex and significantly strengthened its processing capacity. The new plant will be capable of processing up to 100 tons per day, handling not only the existing 68 tons per day of municipal food waste from Sapporo City school meal centers but also industrial food waste from food manufacturing plants in and around Sapporo City.
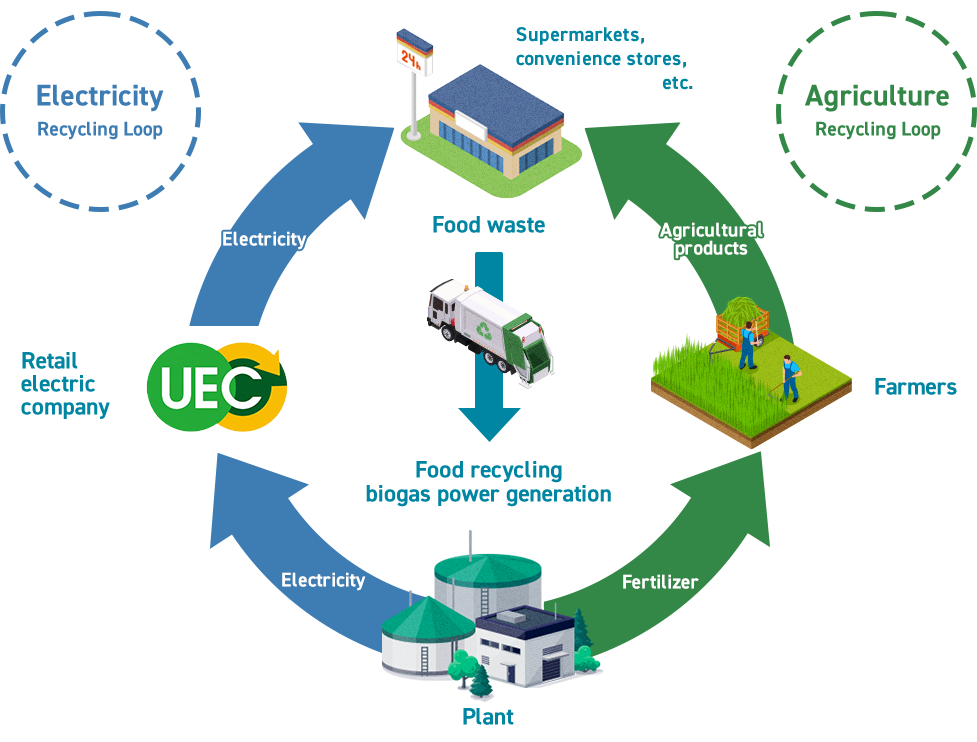
The new facility generates electricity by fermenting food waste using microorganisms and using the produced methane gas as fuel. The power output is 1,980kW, with an expected annual power generation of approximately 16,420 MWh (equivalent to the annual electricity consumption of about 4,560 households). The generated electricity will be sold through the “Feed-in Tariff” system and through Urban Energy Corporation (UEC), JFE Engineering's retail electricity subsidiary, aiming to promote local production and consumption of renewable energy. Furthermore, the fermentation residue produced during the treatment process will be entirely converted into fertilizer. This will realize a local so-called “double recycling loop” that converts food waste into both clean power and fertilizer.
The JFE Engineering Group will continue to work with local communities to promote improved food recycling rates and local production and consumption of renewable energy, contributing to the realization of a recycling-based society.
- *1Largest biogas power generation facility using food waste as raw material in Hokkaido (according to our research)
- *2Food recycling business of the J&T Recycling Group
Double Recycling Loop: Creating Renewable Energy and Fertilizer from Food Waste

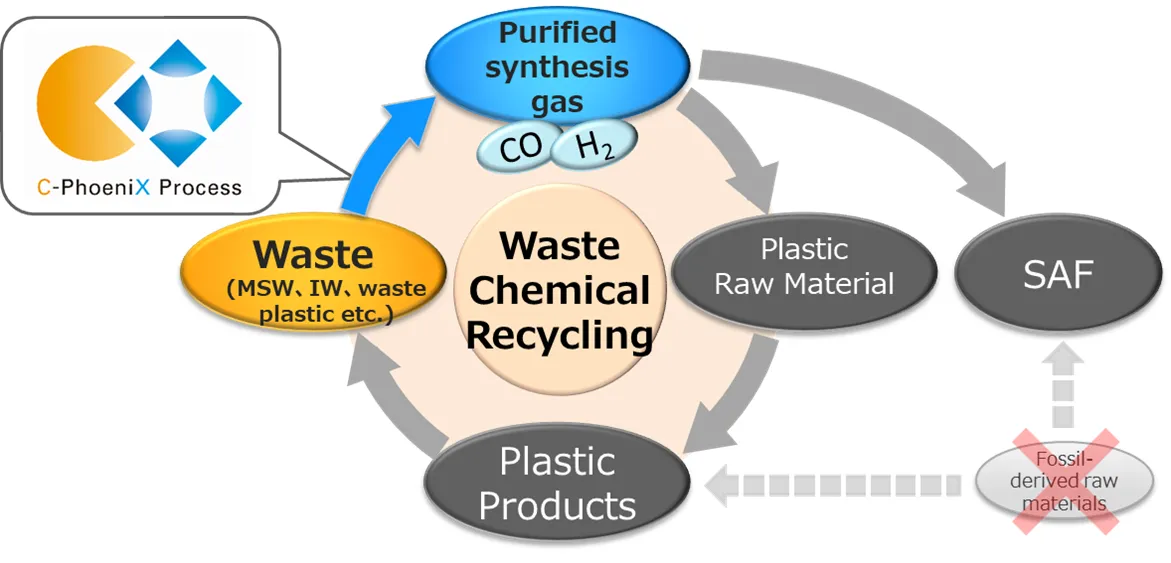
EN Development of a Waste Chemical Recycling Technology (C-PhoeniX Process™) through the Use of the Green Innovation Fund
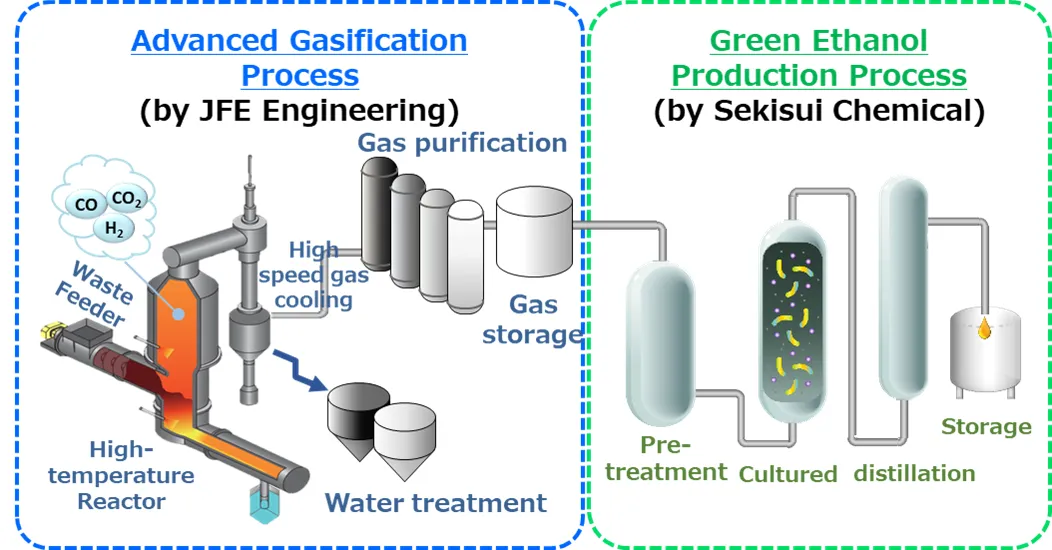
JFE Engineering responded to a public invitation to participate in the “Green Innovation Fund Project/Achieving Carbon Neutrality in Waste and Resource Circulation” project of the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO) in February 2024 and was selected*. Following more than two decades of trial and error, JFE Engineering established a technology to convert domestic and other kinds of waste into processable gases. The company’s unique gasification furnace has the longest running record in the world. The company is currently developing a new gasification technology, C-PhoeniX Process™ (or CX Process™), to improve and ultimately replace the current technology for carbon neutrality.
The C-PhoeniX Process™, based on the company’s accumulated technological expertise, exhibits an advanced capability to constantly produce high-quality, purified synthesis gases, consisting primarily of hydrogen and carbon monoxide, from a wide range of waste materials. Once established, this technology will be applicable to the waste-to-chemical (WtC) process, enabling many types of waste to be recycled for different purposes, including the production of plastic, sustainable aviation fuel (SAF), and hydrogen.
Through the use of the national Green Innovation Fund, JFE Engineering is set to develop a waste chemical recycling technology in cooperation with SEKISUI CHEMICAL Co., Ltd., which owns a technology for converting waste-originated purified synthesis gases into ethanol. In the meantime, JFE Engineering will accelerate the development of its C-PhoeniX Process™ for the advancement and social implementation of WtC. Development under the Green Innovation Projects is scheduled to be completed by the end of FY2030. JFE Engineering will deploy these two technologies, once established, overseas as well as in Japan, and will thereby contribute to the achievement of carbon neutrality by 2050.
Overview of Waste Chemical Recycling
Entire Process and Development Domains
- Developing the Advanced Waste-to-Chemical Gasification Process, the “C-PhoeniX Process” Toward Practical Use in Society
- “Waste-to-Chemical Technology Development for Green Ethanol Production by Integrating Advanced Gasification and Biochemical Conversion Technologies” adopted for the NEDO Green Innovation Fund project
EN Support for New Regional Electricity Projects
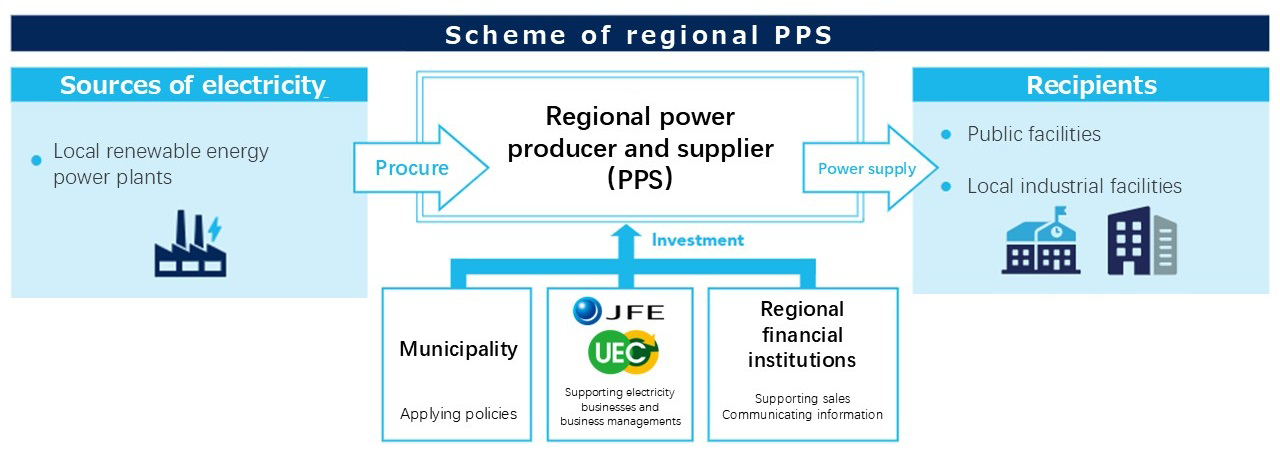
JFE Engineering is creating mechanisms for effectively using regional renewable energy sources such as wind and geothermal power and supplying electricity to local public facilities from renewable energy plants constructed by JFE Engineering, including waste-to-energy plants. These efforts support local production and consumption of energy.
Urban Energy Corporation (UEC), a subsidiary of JFE Engineering, provides consistent support for new regional electricity projects, from establishment to operation, with the goal of achieving regional decarbonization and stabilizing energy costs. Drawing on its extensive experience and expertise cultivated in the retail power business, UEC ensures stable and efficient operations, thereby contributing to the creation of sustainable communities.
New Regional Electricity Scheme Diagram
Record of Support for New Regional Electricity Projects
EN Construction and Operation of Waste-to-Energy Plants Overseas
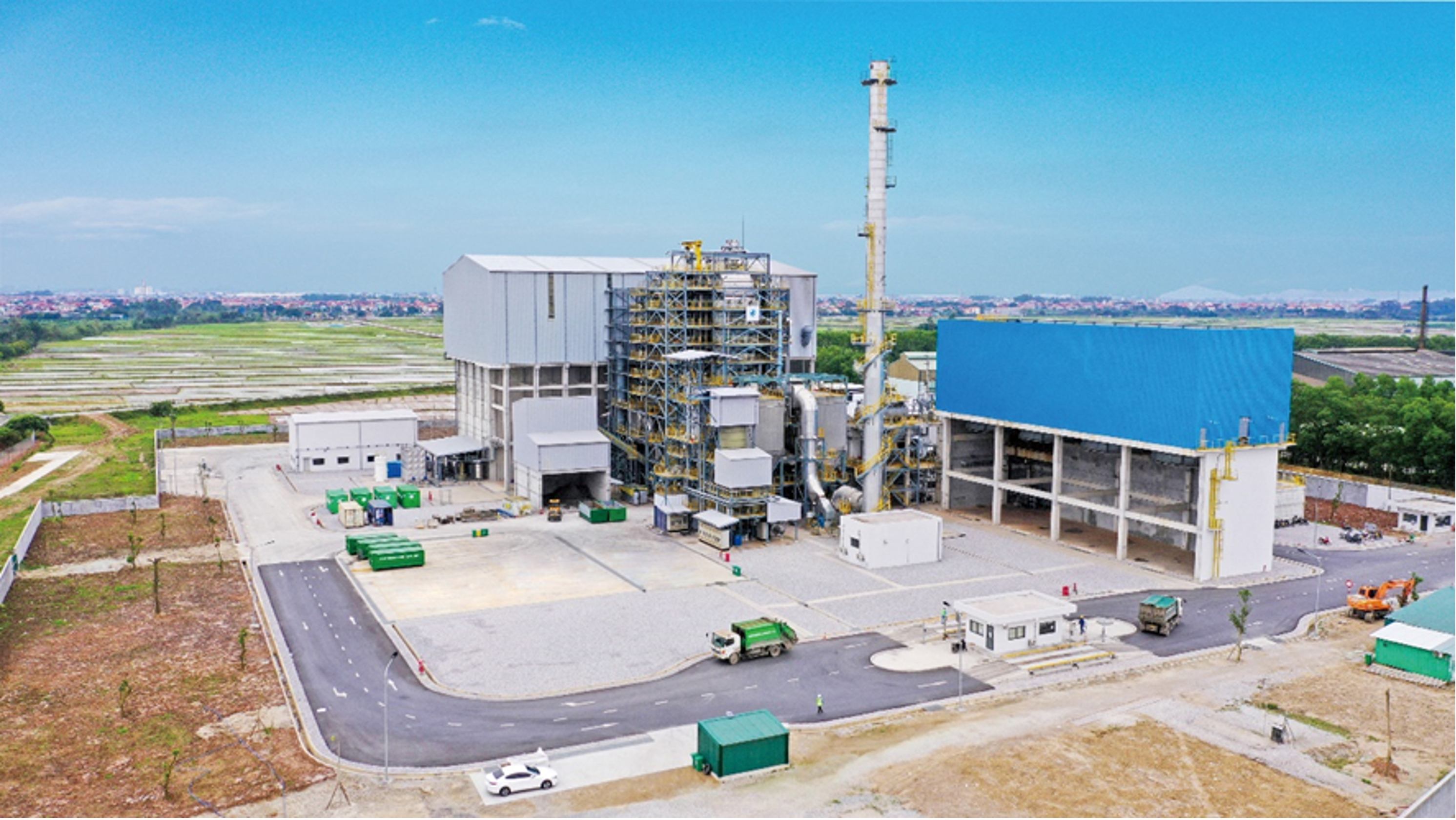
JFE Engineering and the Thuan Thanh Environment Joint Stock Company *1 (TT) jointly established T&J Green Energy Company Limited (T&J) to conduct a waste-to-energy business in Bac Ninh Province, Vietnam.
After the establishment of T&J, JFE Engineering was responsible for plant design, construction, and operation, while TT handled the obtaining of permits and approvals, securing the plant site, collecting and transporting waste for incineration, and treating incineration ash. The waste-to-energy plant began selling electricity in January 2024. The facility incinerates 500 tonnes per day of municipal and industrial waste with an output of 11.6 MW and an expected annual power generation of 91,872 MWh. The generated electricity is sold to Vietnam Electricity Corporation under the feed-in tariff (FIT) system.
Funding for the construction and operation of the T&J plant was provided through the equipment subsidy program under the Japanese government’s Joint Crediting Mechanism (JCM),*2 together with loans from the International Finance Corporation (IFC) of the World Bank Group and the Finland−IFC Blended Finance for Climate Program. This financing package was based on recognizing the project’s proper waste treatment and an expected reduction of approximately 600,000 tonnes of GHG emissions over 15 years. The project was implemented in cooperation between the governments of Vietnam and Japan. Both companies plan to use this project as a pilot for launching similar efforts.
Drawing from the JFE Engineering Group's experience in the construction and operation of waste treatment plants, we will continue to contribute to the realization of a resource-recycling society by promoting business planning, construction, and operation in this field in Japan and overseas.
- *1A major recycling company in Vietnam is comprehensively engaged in waste incineration and other recycling businesses.
- *2Refinanced by a local bank at present.

ST Utilization of Byproducts Generated in the Steelmaking Process (Dust, Sludge, Slag)
JFE Steel carefully controls the generation and emission of iron and steelmaking slag (a co-product), iron dust from blast furnaces and converters, sludge from water treatment facilities, and other co-products by setting targets to improve recycling rates. Dust and sludge with high iron content are recycled as raw materials for steelmaking. Iron and steelmaking slag is effectively recycled for reuse in cement and other construction materials. The company is also promoting its use as environment recovery material such as Marine Stone™, which works effectively as a base for the adhesion of organisms and for improving the marine environment. As a result of these efforts, it achieved a 99.5% recycling rate for slag, dust, and sludge in FY2024, fulfilling the target of at least 99%, and it remains committed to consistently achieving the target.
For more quantitative data related to co-products, please refer to:
Contribution of Steel Slag Products
Many steel slag products are designated as specified procurement items (products that contribute to the reduction of environmental impact) for public works under the Act on Promotion of Procurement of Eco-Friendly Goods and Services by the State and Other Entities (Act on Promoting Green Procurement), which was enacted in 2001 to protect the natural environment.
To realize a circular economy, JFE Steel has set a target under the Eighth Medium-term Business Plan (FY2025-FY2027) for using a cumulative total of 320,000 tonnes of steel slag products for marine applications (with actual usage of 40,000 tonnes in FY2024), in order to contribute further to the conservation of natural resources (sand and stone). We will further expand this effort.
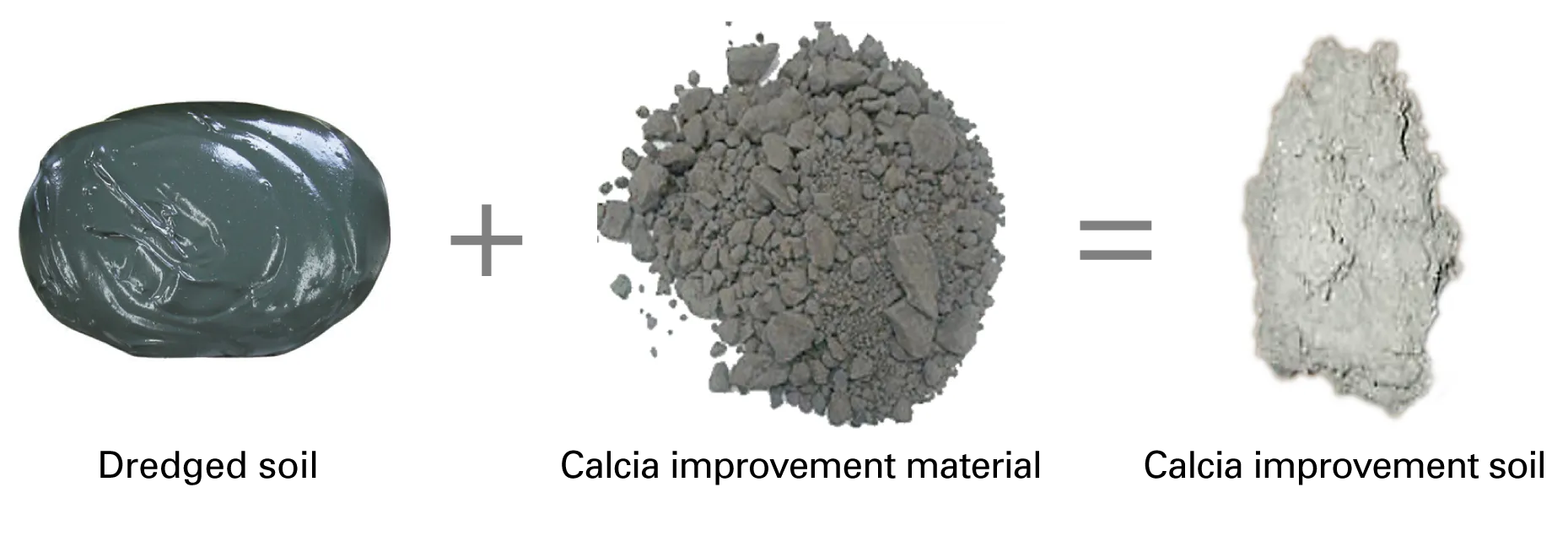
Calcia Improvement Material
Calcia improvement material is a slag product that uses converter-type steelmaking slag as raw material and is manufactured by controlling the composition and adjusting particle size. Dredged soil mixed with calcia improvement material is called calcia improved soil, which is stronger than the original weak dredged soil and is therefore able to prevent dredged soil from dissipating into the surrounding area and having a negative environmental impact placed in water. As a construction material for infrastructure development, it can be applied to landfill materials and other uses, enabling the effective use of dredged soil. Calcia improved soil has been used to construct a mid-section submerged breakwater*1 (Shin Honmoku Pier, Port of Yokohama), backfill material for earthquake-resistant quay walls (Fukuyama Port Minoshima District quay wall construction project), and soil for bank protection (Tokyo new landfill site development project).
Calcia-improved soil can also be used for creating shallow waters and tidal flats and backfilling deep excavated holes, as a technology that can restore marine environments*2.
- *1An embankment built under the water surface on the inside of a perimeter wall to divide the land into sections for reclamation
- *2Biodiversity Protection and Nature Positive
Calcia Improvement Material and Calcia Improvement Soil


Steel Slag Hydrated Matrix
Steel slag hydrated matrix is a steel slag product that can be used as a substitute for concrete but uses ground granulated blast furnace slag instead of cement, and steel slag instead of natural gravel and sand aggregate, as its ingredients. It effectively uses steel slag and does not rely on natural aggregate, thereby reducing environmental impact, and uses less cement, in turn reducing CO2 emissions.
There are many examples of blocks and artificial stones made from steel slag hydrated matrix being used as a substitute for concrete blocks and natural stones in harbor works, apart from the expected application for scour-prevention at the growing number of offshore wind-power stations to be constructed in the near future. In addition, we are conducting on-site monitoring in the Katsunan Central Zone of Chiba Port with the help of a local fishing association to assess the impact of these blocks on marine biodiversity.
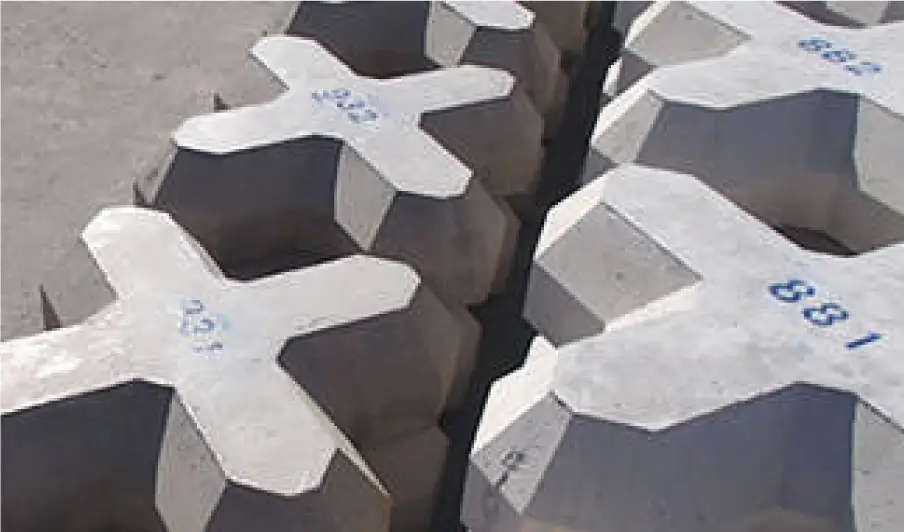


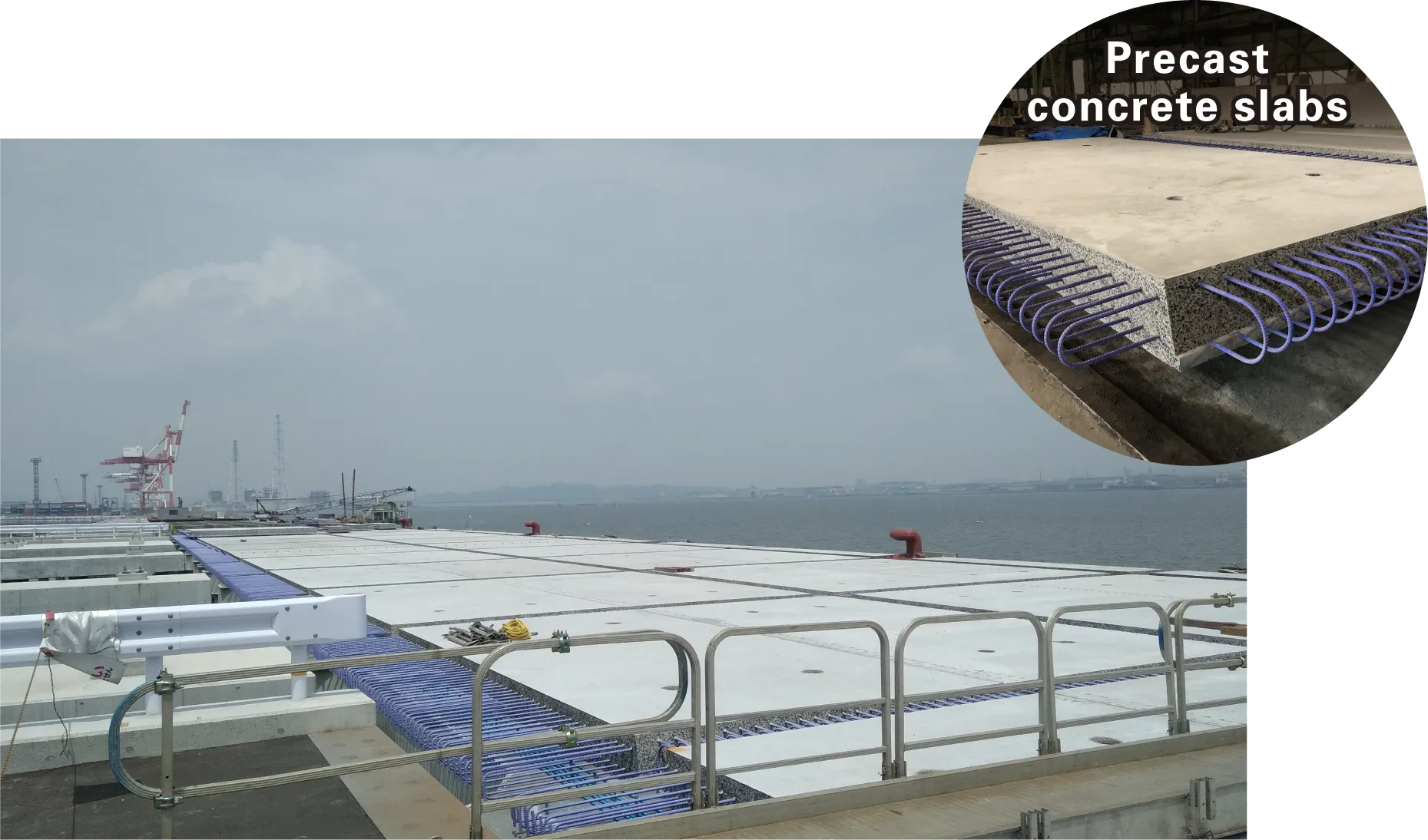
Precast Concrete Products Mixed with Finely Ground Blast Furnace Slag
Finely ground blast furnace slag can be used as a cementing material in concrete. This type of concrete exhibits significantly higher durability under harsh conditions such as applications in sewers and exposure to anti-freeze agents. Its effectiveness in reducing environmental impact is widely understood, although there has recently been growing interest in its practical applications for concrete constructions that require higher durability.
As one of the deliverables for the Japanese government’s Strategic Innovation Promotion Program, the Japan Society of Civil Engineers published a draft guideline in March 2019 on the application of finely ground blast furnace slag to precast concrete product, and its application now includes precast concrete slabs installed in highways and piers. With the application of finely ground blast furnace slag in concrete, the durability of precast products is expected to be greater and more consistent, allowing them to contribute to building national resilience.

Granulated Blast Furnace Slag
Granulated blast furnace slag, when ground to a fine powder and used to replace part of ordinary Portland cement, reduces the amount of limestone, crushed stone, and sand used, saves energy, and can also reduce CO2 generated in cement production. For example, blast furnace cement made by replacing 45% of ordinary Portland cement with granulated blast furnace slag reduces CO2 emissions per tonne of cement produced by 42%. In FY2024, JFE Steel supplied approximately 5.61 million tonnes of granulated blast furnace slag to cement production, equivalent to a reduction of about 3.98 million tonnes of CO2 emissions.
CO2 Emissions for Producing 1 Tonne of Cement (Unit: kg-CO2/tonne)
| CO2 Emissions Source | Regular Cement | Blast Furnace Slag Cement |
|---|---|---|
| Limestone | 476 | 270 |
| Electricity/energy | 283 | 170 |
| Total | 759 | 440 |
- *Source: Data published by the Japan Cement Association compiled from the actual FY2022 data
Initiatives for Realizing a Circular Economy in the Keihin Waterfront Area
Taking advantage of its proximity to Tokyo, the Mizue district is collaborating with Kawasaki City in expansion and development to create a major recycling hub for the metropolitan area. J&T Recycling Corporation, a group company of JFE Engineering, partnered with JR East and others to establish J Circular System Corporation in a pioneering project to construct the J Circular Systems Kawasaki Super Sorting Center as one of the largest plastic recycling facilities in the metropolitan area. Full-scale operations commenced in April 2025. Going forward, we will continue to promote businesses toward realizing a circular economy through the expansion and development of the recycling area.
Keihin District land business utilization (from materials of the Eighth Medium-term Business Plan)

Development of Resource-Efficient Eco-Products and Eco-Solutions
The JFE Group is developing and providing resource-efficient products and services to support the realization of a circular economy. We are deploying eco-products designed from the perspective of the entire life cycle and eco-solutions that create circular value to reduce environmental impact and effectively use resources.
EN Infrastructure Reinforcement and Longer Service Life
JFE Engineering is leveraging its diverse business portfolio to promote multifaceted efforts for transitioning to a circular economy. In the infrastructure field, we are helping to realize a sustainable society through projects that maximize the useful life of infrastructure through resource-saving and long-life design, energy- and labor-saving construction, and efficient operation through maintenance and renovation.
JFE Engineering Circular Economy
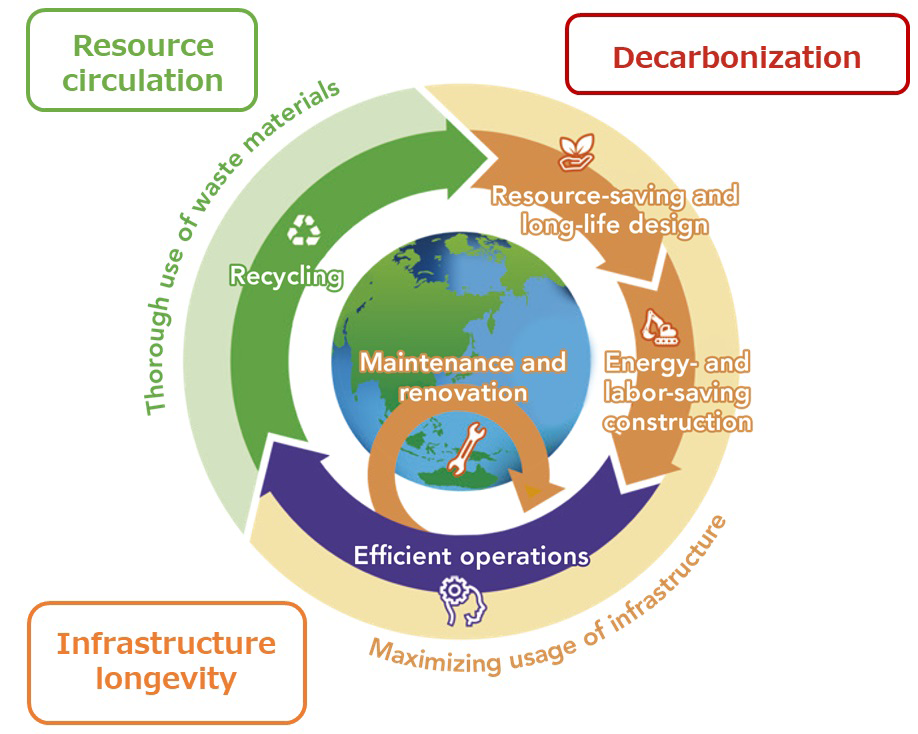
Toward Realizing Longer Service Life Bridges
Japan’s stock of social infrastructure is expected to age rapidly in the coming years. At the same time, declining birth rates, an aging society, and population decline are reducing the available labor force, making it increasingly difficult to secure engineers for infrastructure maintenance. To address this, JFE Engineering is working to lessen the burden of maintenance by using highly durable materials to construct bridges with longer service life.
Technology Allowing for Bridges with Longer Service Life
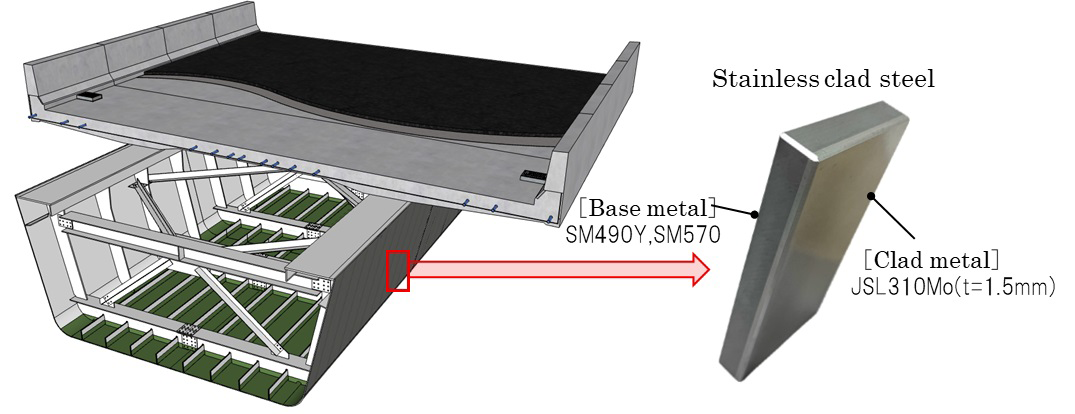
Conventional steel bridges suppress corrosion by using coatings such as paint that must be periodically reapplied. Using highly durable materials that do not need to be coated eliminates the need for reapplications, significantly reducing maintenance tasks associated with ordering, design, construction, and management. Moreover, these bridges demonstrate superior cost savings over a 100-year life cycle compared to painted bridges. We have thus pioneered in adopted stainless clad steel for constructing a road bridge.
Stainless clad steel is a steel plate with a two-layer structure, combining ordinary steel (carbon steel) and stainless steel. Stainless steel is placed on the outer surface, which is susceptible to salt damage, while painted carbon steel (base material) is used on the inner surface, which is less susceptible to corrosion. A stainless clad steel bridge is more economical than bridges made entirely of stainless steel or carbon steel, thereby combining economy and durability.
The clad steel selected for this project uses JSL310Mo, a stainless steel with extremely high corrosion resistance, to extend service life. This seawater-resistant stainless steel was uniquely developed by JFE Steel as a material for clad steel, positioning JFE Steel as a pioneer in fabrication and construction technology for steel structures using clad steel. This one-of-a-kind long-life bridge was possible through the combined strengths of the entire JFE Group.
The bridge is currently under construction as part of the replacement work for the Tedori River Bridge on the Hokuriku Expressway, commissioned by Central Nippon Expressway Company Limited.
Bridge using stainless clad steel
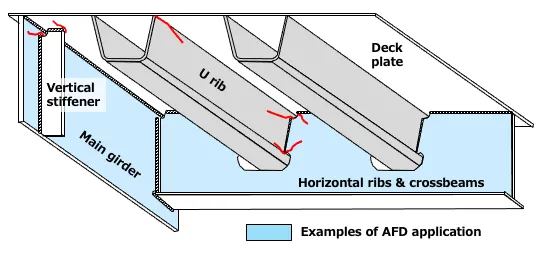
ST Anti-Fatigue-Damage Steel for Increased Bridge Safety (AFD™ Steel)
Extending the service life of steel structures conserves resources and reduces waste, although durability remains challenging. In particular, bridges contain many thin components that may develop fatigue cracks due to traffic load from automobiles and other vehicles, and cracks may propagate between inspections or repairs.
JFE Steel has developed a thin version of its anti-fatigue-damage steel (AFD™*1 steel) with improved fatigue resistance. The steel plate, produced by a plate mill at the East Japan Works (Keihin District) using the Super-RQ system with advanced cooling control, has a minimum thickness of 9 mm and retains the mechanical properties of conventional plates while offering improved fatigue resistance. Realization of thin-plate AFD™ steel allows for the application of highly durable materials across a wider range of structural members, such as thin bridge components prone to fatigue cracking. In addition, AFD™ steel suppresses fatigue crack propagation rate*2 to one-half or less compared to the upper limit of ordinary steel, and product life has been extended about twice the useful life of ordinary steel. This reduces life cycle costs accompanying the longer service life of components. The product received the Grand Prize in the Nikkei Superior Products and Services Awards 2023 in recognition of these features.
- *1Anti-fatigue damage
- *2Fatigue damage is caused by small, repeated forces that create cracks that gradually grow until the material fails. Since these cracks propagate incrementally with the repeated application of force, the length over which the cracks propagate per repetition is called the fatigue crack growth rate.
Examples of Thin AFD Steel Application
ST Electrical steel sheets
Electrical steel sheets* are popularly used as core materials for electrical equipment such as motors and transformers and therefore play a key role in determining their performance. JFE Steel contributes to global energy conservation and consequently to reducing CO2 emissions by supplying high-performance electrical steel sheets.
- *Electrical steel sheets are obtained by adding silicon to iron and are widely used as iron core materials in equipment such as motors and transformers.
Non-Oriented Electrical Steel Sheets Completion and Start-up of Phase I Expansion and Strengthened Production Capacity at the West Japan Works (Kurashiki District)
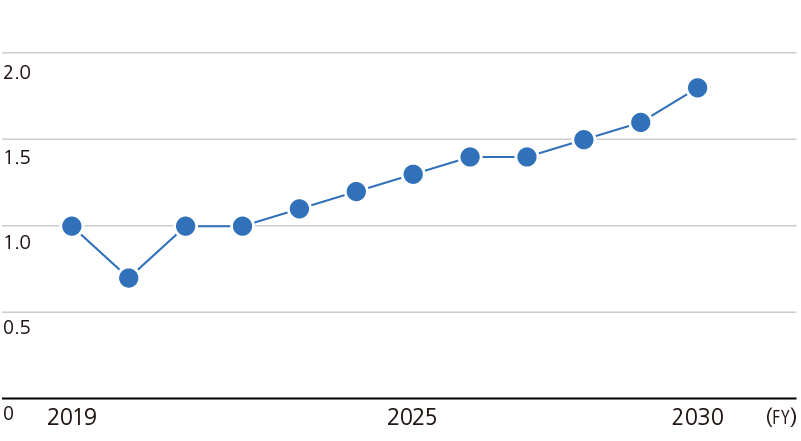
Transitioning to a carbon-neutral society requires a major transformation of the social structure, from fossil-fuel-based energy to primarily carbon-free sources. Highly efficient motors, constructed from high-performance, non-oriented electrical steel sheets, will be essential for transitioning to a society in which mobility depends on electric vehicles (xEVs) and zero-emission electricity is the primary source of energy.
JFE Steel’s high-grade non-oriented electrical steel sheets contribute to higher performance xEV drive motors through the improved efficiency of excellent low-iron-loss magnetic properties and reduced size made possible by high magnetic flux density. Recognizing the value of these characteristics has led many automobile manufacturers to incorporate these materials into their products, and demand for high-grade non-oriented electrical steel sheets is projected to expand rapidly. To keep pace with this demand, Phase I expansion work to increase capacity for electrical steel sheet production was completed as planned in July 2024, and line production began in September. The start-up of this facility had doubled JFE Steel’s production capacity for high-grade non-oriented electrical steel sheets (NO).
Since an even sharper surge in demand is expected for high-grade non-oriented electrical steel sheets essential for xEV drive motors, Phase II expansion work is now underway. This plan is projected to triple production capacity for top-grade non-oriented electrical steel sheets for main xEV motors by FY2026 compared to pre-Phase I levels.
Demand for Non-Oriented Electrical Steel Sheets (Calculated by JFE, 2020 results = 1.0)
Grain-Oriented Electrical Steel Sheets: Acquisition of Electrical Steel Sheet Manufacturing Company in India
The global demand for grain-oriented electrical steel sheets in transformers is expected to increase due to continuously growing demand for electric power and the expanding adoption of renewable energy. The demand for grain-oriented electrical steel sheets, particularly in India, is expected to increase by 1.8 times in 2030, compared to 2019.
In response, JFE Steel and JSW Steel Limited (JSW) established JSW JFE Electrical Steel Private Limited (hereafter J2ES), a joint venture company in India for grain-oriented electrical steel sheets, in 2023. Preparations, including equipment planning, are currently underway toward starting production in FY2027.
In addition, JFE Steel and JSW jointly acquired, through J2ES, thyssenkrupp Electrical Steel India Private Limited, an Indian manufacturer and distributor of electrical steel sheets in January 2025.
With this acquisition, J2ES will be able to enter the Indian market for grain-oriented electrical steel sheets earlier than planned, ahead of full-scale production in FY2027, thereby capturing medium- to long-term demand for these products. After the acquisition, we will quickly establish an integrated system covering manufacturing through sales to respond effectively to future growth in demand.
Demand for Grain-Oriented Electrical Steel Sheets in India (Calculated by JFE, 2019 results = 1.0)
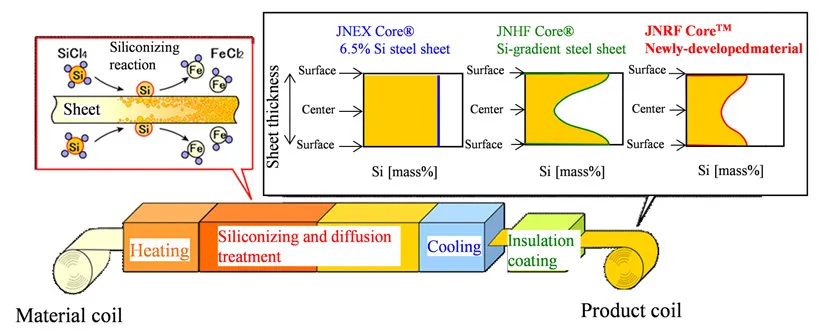
Resource-Saving Silicon-Gradient Steel Sheets
The recent trend toward increasing driving frequency due to the downsizing of electrical equipment has intensified the need to reduce iron loss* in the high-frequency range for electrical steel sheets, widely used as iron core material for electrical equipment such as motors and transformers. Meeting this demand depends upon increasing the concentration of silicon (Si), an element that strengthens electrical resistance. However, increasing concentration also causes magnetic flux density to decrease at the same time.
To overcome this, JFE Steel developed JNHF™, JNSF™, and JNRF™ using its proprietary chemical vapor deposition (CVD) continuous siliconizing process technology for controlling Si concentration distribution. These steel sheets offer low iron loss and high magnetic flux density in the high-frequency range, significantly contributing to higher efficiency and downsizing of electrical equipment. They are used as core materials for solar power reactors and high-speed motors.
In recognition of the positive social impact of this development, we received the 2022 Award for Science and Technology from the Minister of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology under the development category of the science and technology field. JFE Steel will continue to contribute to improving electrical equipment by raising efficiency, reducing size, and saving energy by providing high-performance, high-grade electrical steel sheets.
- *The loss of energy, primarily as heat, that occurs when the iron core is excited by an alternating current. The less iron lost, the higher the efficiency of electrical equipment.
CVD Continuous Siliconizing Process and Si Concentration Distribution Control
SH Further Expanding the Global Supply Chain for the Steel Sheets Business
The key factor in initiatives for countering climate change, including those for reducing CO2 emissions, is minimizing electricity loss and using generated electricity without loss. Motors found in places such as power plants, factories, and homes are responsible for 40−50% of all electricity consumed globally. In Japan, the ratio is approximately 55%. Improving the efficiency of motors by 1% in Japan would contribute to the equivalent of a 500,000 kW-class power generation plant in energy savings. Motors for electric vehicles, which are expected to become increasingly popular as we move toward a decarbonized society, and industrial motors essential for factory automation, need to become even more efficient and lighter through downsizing. In addition, continuous improvement in efficiency is required in transformers, which are essential for distributing electricity from source to factories and homes, in order to minimize energy loss in power transmission and distribution.
JFE Shoji has established a stable global supply chain that includes sourcing high-quality electrical steel sheets, which are essential for improving the efficiency of motors and transformers, from JFE Steel and other manufacturers and processing the products to meet customer needs. Since customers who depend on high-quality electrical steel sheets, such as manufacturers of motors and transformers, typically operate manufacturing facilities across the globe, the company has been expanding its electrical steel sheets supply chain in Japan, the Americas, China, ASEAN, India, and Europe. JFE Shoji will continue to build the world’s number-one global distribution and processing system for high-quality electrical steel sheets by further expanding its supply chain, enhancing processing functions, and expanding collaboration with alliance partners, to precisely respond to customer needs.
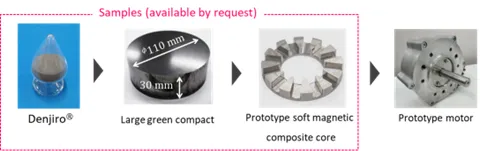
ST Verification of the Feasibility of Making Motors 48% Thinner Using Insulated Pure-Iron Powder Denjiro™
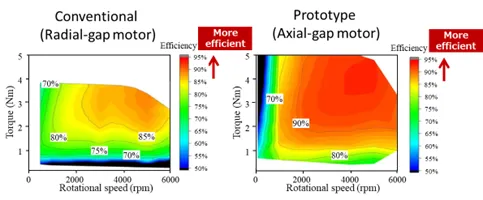
In a joint project with JFE Techno-Research Corporation and ARMIS CORPORATION, a venture company launched by Shizuoka University, JFE Steel designed and prototyped a motor using Denjiro™, the company’s insulated pure-iron powder, and demonstrated the feasibility of producing motors 48% thinner and 40% lighter than conventional models while maintaining the same output.
Demand continues to rise for smaller but higher-performing electric motors for industrial equipment and vehicles. Axial-gap motors, which are thinner than general radial-gap motors, can deliver high power (Figure 1). Unlike radial-gap motors, however, axial-gap motors pose a significant manufacturing challenge by requiring a three-dimensional magnetic core that cannot be made by laminating electrical steel sheets. In contrast, powder cores formed by pressing insulation-coated magnetic powder possesses uniform three-dimensional magnetic properties, can accommodate complex shapes, and provide flexibility in design. Furthermore, because these cores are easily crushed, copper wire can be readily separated and recovered from motors, improving recyclability. Efforts are underway to remanufacture crushed powder cores by reforming them for reuse. JFE Steel has developed and launched an insulation-coated pure iron powder Denjirou™ for powder cores. In this project, an axial gap motor incorporating powder cores made with Denjirou™ was designed, prototyped, and evaluated for performance (Figure 2). The results showed a 48% reduction in height and a 40% reduction in weight compared to conventional motors, at equal or greater efficiency (Table, Figure 3). Based on these results, JFE Steel and JFE Techno-Research Corporation have begun supporting customer design of components using powder cores while also supplying large powder compacts for machining and prototype powder cores processed into designed shapes to promote the use of powder cores for motors.
Going forward, JFE Steel will continue to develop products that meet customer needs while also encouraging technical exchanges, such as proposing the application of technologies and supporting prototype evaluation. These efforts will expand the supply of eco-products that contribute to a circular society and help realize a sustainable society.
Figure 1: Types of motors
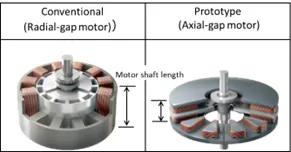
Figure 2: From powder to prototypes
Conventional vs. prototype motor (test results)
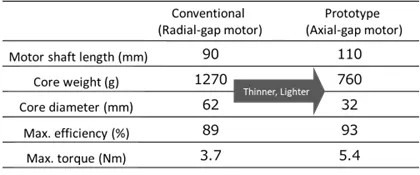
Figure 3: Efficiency of conventional vs. prototype motor
ST High-Tensile-Strength Steel Sheets (HITEN) for Automobiles
Applying high-tensile-strength steel sheets (HITEN) to automobile components helps reduce weight while maintaining crash safety performance. JFE Steel contributes to improved fuel efficiency and ultimately reducing CO2 emissions by supplying customers with ultra-high-tensile-strength steel sheets that meet needs for lighter car bodies. In addition to developing and producing these steel sheets for automobiles, JFE Steel develops application technologies. These include techniques for applying body design and forming/assembly technologies, which have been systematized to offer comprehensive solutions as JESOLVA™ (JFE Excellent SOLution for Vehicle Application), JFE Steel’s unique suite of application technologies for automotive steel sheets. To provide these solutions, JFE Steel is actively promoting early vendor involvement (EVI) activities, in which it collaborates with customers from the early stages of automobile development. By improving car body performance and reducing weight, JFE Steel is contributing to the development of next-generation automobiles and the realization of a sustainable society.
Construction of a Hot-Dip Galvanizing Line at West Japan Works (Fukuyama District)
The automotive industry is producing lighter and stronger car bodies to meet increasingly stringent environmental regulations and collision safety standards around the world, and demand is expected to grow for ultra-high-tensile sheets* with excellent processability. JFE Steel has therefore decided to construct a new hot-dip galvanizing line (CGL) at the West Japan Works (Fukuyama District), with an annual production capacity of 360,000 tonnes. The investment will total approximately 70 billion yen, with operations scheduled to commence in October 2028. The new line will enable JFE Steel to increase its production capacity for such sheets, including its JEFORMA™ series, to meet growing demand in the foreseeable future and respond to subsequent needs for even higher strength and functionality.
- *High-strength steel sheets with tensile strength ≥980 MPa (megapascals)
Wall Bending and Restrike Method to Suppress the Springback of Ultra-High Tensile Steel Sheets
JFE Steel’s Wall Bending and Restrike Method has been adopted and used to produce inner rockers, a body frame component, for use in vehicles manufactured and sold by a major Japanese automaker. The Wall Bending and Restrike Method, a press forming method, is applied to suppress the springback of 1,180 MPa class, ultra-high tensile steel sheets.
Since pressed steel sheets are subject to springback—that is, returning to their original shape when removed from a mold—springback conditions must be corrected. Press-formed ultra-high tensile steel sheets generate greater stress than ordinary steel sheets and are therefore more susceptible to higher levels of springback. The resulting challenge of controlling deformation from the intended shape and the increased difficulty of bonding with other components has been a bottleneck to the wider application of ultra-high tensile steel sheets.
The Wall Bending and Restrike Method provides a solution for reducing springback by applying an offsetting force to springback-induced stress, particularly through the optimization of sheet shape prior to press-forming. The inner rockers, a structural component at the bottom of a vehicle door, for which the Wall Bending and Restrike Method is used, are manufactured by Kyoho Machine Works, Ltd., and the application of this method to mass-production molds was achieved through a joint development by this company and JFE Steel.
Inner rocker made with the Wall Bending and Restrike Method

Forming Technologies for Ultra-High Tensile Steel Sheets—Inflow Control Method and Stress Reverse Forming™ Method
JFE Steel’s inflow control method and the Stress Reverse Forming™ Method were adopted and have been used for the production of three front bumper components for Suzuki Swift to reduce the formation of wrinkles at pressed areas of 980−1,180MPa class, ultra-high tensile steel sheets and reduce variation in dimensional accuracies.
When press-formed into a curvature shape, press wrinkles form on the steel sheets and the sheets tend to springback to their original shape; both conditions need to be corrected.
While contributing to vehicle weight reduction, ultra-high tensile steel sheets are susceptible to press wrinkles, mold damage, and shape variation, and all these issues are more likely to occur with thicker, stronger steel sheets, a factor that has inhibited the wider application of ultra-high tensile steel sheets. JFE Steel’s inflow control method is capable of reducing the formation of press wrinkles, particularly those around the flanges of pressed areas, by optimizing the inflow of materials at multiple press-forming processes.
The Stress Reverse Forming™ Method is designed to reduce variation in the scale of springback (or variation in dimensional accuracies), which increases as ultra-high tensile steel sheets have higher levels of strength. When press-formed, ultra-high tensile steel sheets are more susceptible to springback and to large variation in strength intensities than regular steel sheets. The Stress Reverse Forming™ Method uses the Bauschinger Effect, or the mechanical phenomenon in which deformation stress in steel sheets decreases immediately after the direction of the deformation is reversed. This method enables customers to stabilize their production of press components even if there are changes in the intensities of steel sheets.
The front bumper components for which these two methods are used are manufactured by Okamoto Press Industry, Co., Ltd. In fact, both the inflow control method and the Stress Reverse Forming™ Method were jointly developed by Okamoto and JFE Steel.
Ultra-High Tensile Steel Sheet Product Adopted for the First time as a Material for a Hybrid EV Battery Module Component
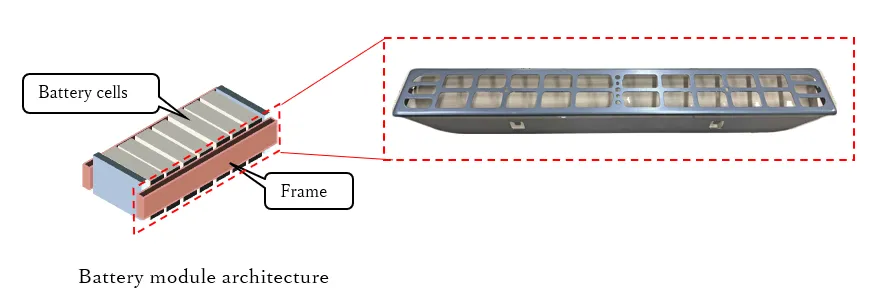
The 980 MPa class galvanized steel sheet was the first of JFE Steel’s ultra-high tensile steel sheet products to be selected and used as a material for a lithium-ion battery module frame used in hybrid EVs.
A vehicle battery pack is comprised of multiple battery cells and bound with a steel frame to achieve a high power output. The frame must have a high bonding force to prevent the battery from swelling and from losing performance due to heat during use, and thus there has been demand for a high strength steel sheet. However, high-strength steel sheets are known to be susceptible to fracture when formed by bending. This process is required to minimize the curvature of the folding area of the frame to almost a 90-degree angle and thereby shrink the size of the battery module.
This issue can now be resolved with the use of a press-forming method using CAE* and product specs developed by J-MAX Co., Ltd., both of which have enabled the use of JFE Steel’s 980 MPa class, galvanized steel sheet that has the high processability suitable for a battery module frame on hybrid EVs. This galvanized steel sheet is a product of the JEFORMA™ series, a lineup of steel sheets with high strength and high bending formability, properties achieved by optimizing the metallographic structure of the steel sheet through intricate temperature control at the continuous galvanizing facility of the West Japan Works (Fukuyama District).
- *Computer-Aided Engineering. A design tool using computer simulation.
Ultra-High Tensile Steel Sheet Product Adopted for a Hybrid EV Battery Module Component
Cold-Press Forming Technology for Integrated Auto-Frame Component
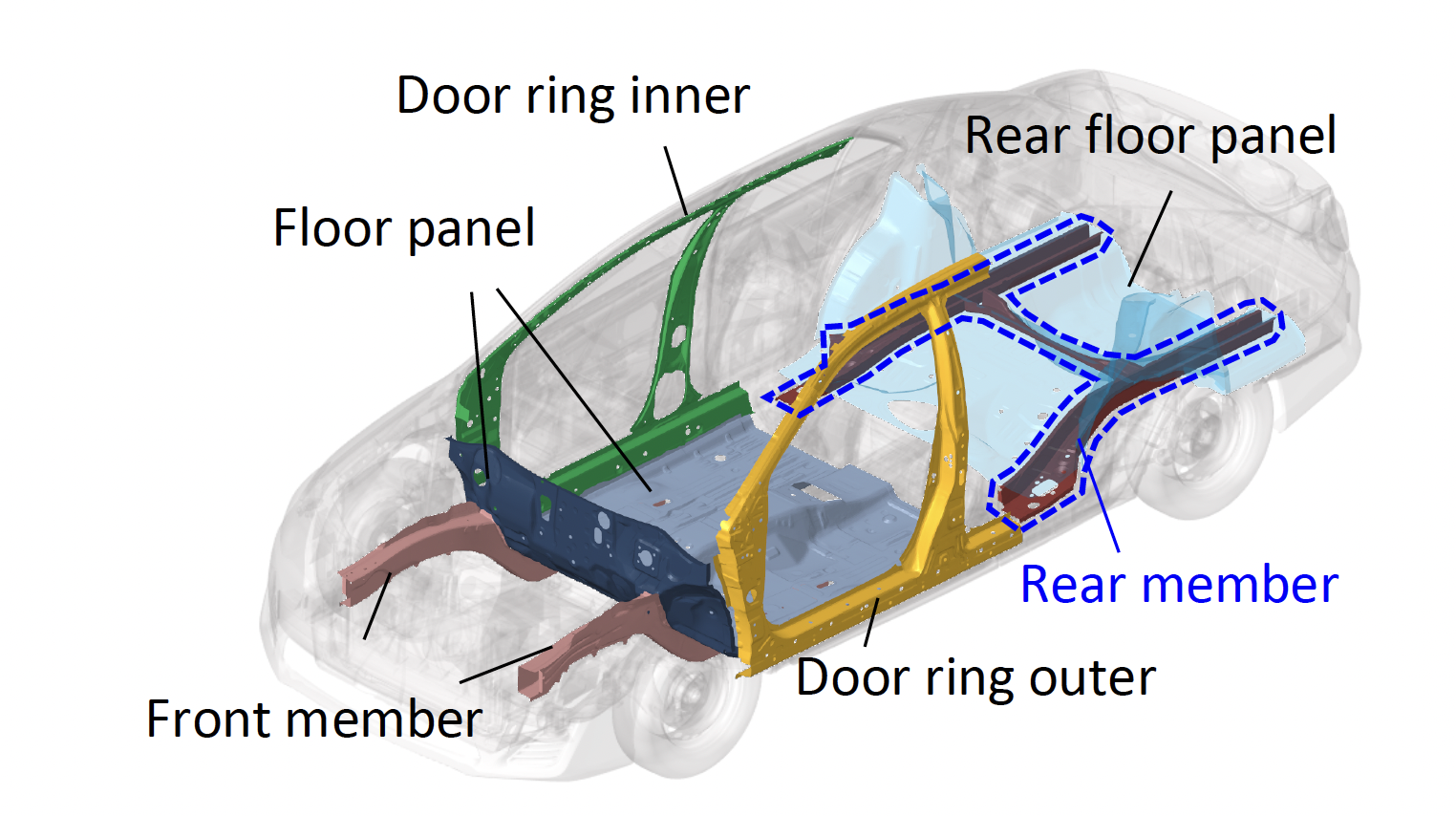
As a component integration solution using ultra-high-tensile-strength steel sheets and cold-press forming, JFE Steel has developed a technology for reducing the number of components in automobile body structures, targeting the rear member*1. Automakers have recently focused on large-scale component integration technologies such as giga casting, which uses aluminum casting technology, and medium-scale integration technologies such as hot stamping, which involves heating steel prior to press forming and simultaneously cooling and quenching in the die to achieve both formability and component strength. This technology falls into the same category of component integration technologies.
Component integration by cold-pressing presents challenges in formability. However, by utilizing JESOLVA™, JFE Steel’s unique systematized solution technology for automotive steel sheets, we have made it possible to form large components using ultra-high-tensile-strength steel sheets of up to 1,470 MPa class. Furthermore, to integrate components with different strengths, we applied Tailor Welded Blank (TWB)*2 and our proprietary Cold Patchwork Method*3, enabling designs with strength variations within a single component. The result is a reduced number of components, even for small-scale integrations, thereby increasing productivity and reducing the cost of auto-frame production.
Challenges arise as integrated components become larger, such as higher logistics costs and greater burdens on end users when damage requires extensive repairs. Limiting integration to appropriate ranges using this technology ensures portability and reduces repair burdens.
The rear member is a large part that protects the body from rear collisions and is composed of 11 spot-welded components. With this technology, the number of components can be reduced to as few as three while maintaining rear collision performance, thereby improving productivity and reducing costs in automobile body manufacturing.
- *1A structural component that supports a vehicle’s rear suspension and drivetrain and connects them to the body
- *2A processing technology that uses laser welding to join steel sheets of different thicknesses and strengths into a single sheet
- *3A technology for stacking and spot-welding together steel sheets for simultaneous press forming
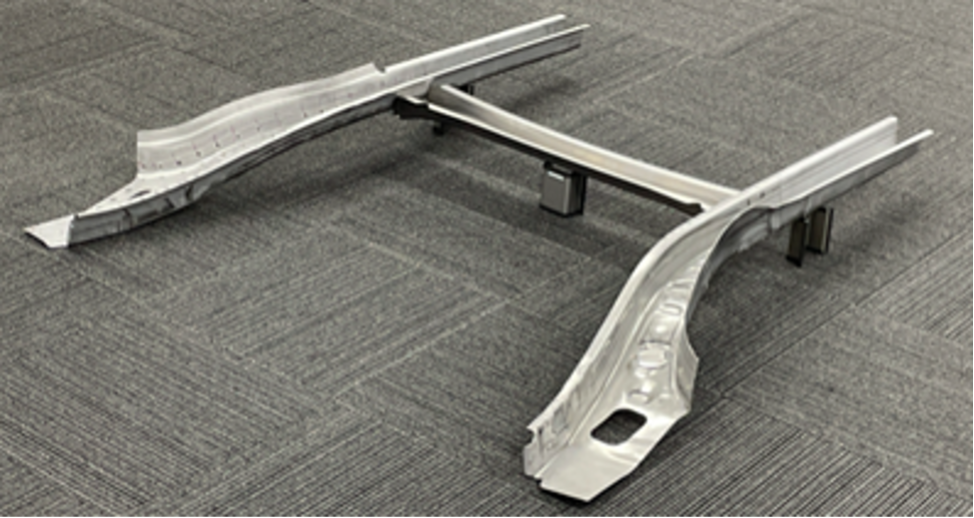
Cold-press integration target and rear member
Prototype rear member

ST Certification by SuMPO’s EcoLeaf Environmental Labeling Program

JFE Steel acquired SuMPO EPD certification for 36 product types under the SuMPO Environmental Label Program operated by the Sustainable Management Promotion Organization (SuMPO). These certifications cover three types of tinplate steel sheets for cans, nine flat steel products, nine construction steel products, three types of steel plates, four steel pipe products, and eight bar and wire rod products.
SuMPO EPD is a Type III EPD program managed by SuMPO for quantitatively disclosing the environmental impact of products and services throughout their life cycle, from raw material procurement to disposal and recycling in accordance with ISO 14025:2006 (environmental labels and declarations, Type III Environmental Declarations, Principles and Procedures). The environmental impact of our products is presented as graphic representations of data to increase transparency. The disclosure of environmental impact data with fairness and reliability assured by third-party review and verification enables customers to quantitatively and objectively evaluate the environmental impact of the products they use.
Going forward, JFE Steel will actively promote the acquisition and publication of SuMPO EPD for its products.
ST Extra-Thick, High-Strength Steel Plate for the Materialization of Large Container Ships
The world’s thickest crack arrest steel plate*1, developed by JFE Steel, is applicable to large container ships, with its 460 MPa class yield strength and a thickness of 100 mm. The technology is the first in the world to satisfy two different properties in the extra-thick steel plate: weldability and crack arrestability. Ensuring the safety of large container ships improves transport efficiency and fuel savings through lighter ship structures.
Container ships are characterized by large openings in the upper deck. Since their hulls are subjected to large wave loads at sea, extra-thick and high-strength steel must be used in the upper deck and hull sides (hatch side coamings). The trend toward building larger container ships for greater transport efficiency has required that steel plates be thickened from 50 to 100 mm and strengthened to the 460 MPa class in yield strength, while also providing high crack arrest properties to stop the propagation of brittle fractures in the steel. To ensure the safety of rapidly growing hull structures, the International Association of Classification Societies has mandated an arrest toughness value (Kca) of 8,000 N/mm3/2 or higher for steel plates of 80 mm and 100 mm thickness used in hatch side coamings. JFE Steel established a proprietary technology using Thermo-Mechanical Control Process (TMCP)*2 technology, which finely controls heating and rolling temperatures, to increase the ratio of crystal orientations in the central thickness of the plate that resist crack propagation. This ensures high crack arrest performance even in 100 mm extra-thick, high-strength steel plates, the world’s thickest.
The development of this technology received the 2023 Award for Science and Technology from the Minister of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology under the development category of the science and technology field for significantly contributing to the materialization of ultra-large container ships. It has been awarded many other prizes, including the 2018 Invention Prize of National Commendation for Invention and the 2019 Okochi Memorial Prize. We will continue to improve the economic efficiency, safety, and reliability of vessels by providing high-performance, high-quality steel material while meeting the diverse needs of customers and also addressing global environmental concerns and contributing to the realization of a sustainable society.
- *1A steel plate with outstanding ability to effectively confine hull damage to the minimum should weld cracking occur.
- *2A thermo-mechanical control process technology that improves the strength and toughness of steel material in an online process using controlled rolling and accelerated cooling systems
Expansion of the Use and Sales of Recycled Resources
The JFE Group is actively promoting the use of recycled resources to help realize a circular economy, and is expanding its market application through products and services that leverage these materials. By combining resource efficiency with waste reduction, we contribute to reducing environmental impact and achieving sustainable growth.
SH Initiatives to Strengthen the Handling of Environmentally Beneficial Products
Our trading business has strengthened the handling of environmentally beneficial products by setting KPIs for the handling volume of fuels for biomass power plants and steel scrap. Under the Eighth Medium-term Business Plan, JFE Shoji will lead in further expanding the lineup of environmentally beneficial products and promoting efforts toward realizing a circular economy.
Expanding Business in Biomass Fuels
JFE Shoji imports fuels such as palm kernel shells (PKS) to Japan from Malaysia and Indonesia and wood pellets from Southeast Asian countries as fuel supplies for domestic biomass power plants.
PKS and wood pellets are made from byproducts or waste materials generated during palm oil production and wood processing. Using these as fuel reduces waste and promotes effective resource use. These initiatives also contribute to realizing a circular economy.
Since these biomass fuels absorb CO2 during their growth process, they are regarded as carbon-neutral fuels, offsetting the CO2 emitted when burned. Furthermore, replanting and recultivation of the trees and crops used as raw materials support a more sustainable supply chain.
To encourage the shift away from coal-fired power, JFE Shoji is also developing and supplying alternative biomass fuels to reduce environmental impact and support energy transition through the use of waste as resources.


Expansion of Scrap Trading to Support the Development of a Recycling-Oriented Society
JFE Shoji engages in a recycling business for steel and aluminum scrap. Demand for steel scrap is particularly expected to grow in Japan and overseas as the global community advances toward carbon neutrality. JFE Shoji will contribute to building a recycling-oriented society by increasing scrap recycling across the globe.
ST Initiatives to Expand Scrap Collection and Use
Steel is highly recyclable because it can be separated and collected using magnetic force. Even after completing its role in society, it remains endlessly reusable as raw material for steel products while retaining its properties. Its recycling rate of 93.7% is extremely high compared to other materials. Steel is recycled through efficient separation and collection into high-quality, high-functionality products, reducing environmental impact across the entire life cycle.
JFE Steel uses steel scrap as raw material in blast furnaces, basic oxygen furnaces, and electric arc furnaces. We have traditionally collected and used “return scrap,” a term for scrap generated during production that is sold back by customers and Group factories. Under the Eighth Medium-term Business Plan, we have set a KPI for the expansion of this volume with associated action plans. For FY2025, we expect to achieve our target of doubling the volume of collected and used scrap compared to the average during the Seventh Medium-term Business Plan period. By expanding the collection and use of scrap toward the realization of a circular society, we will also contribute to addressing climate change.
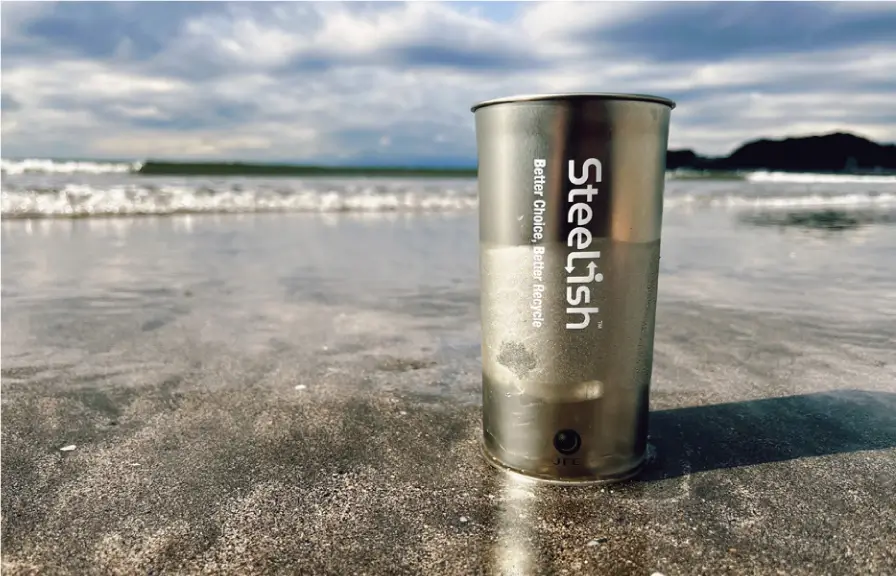
ST Reducing Plastic Waste by Manufacturing Cups from Highly Recyclable Steel
JFE Steel is proposing recyclable steel cups that take advantage of the properties of steel, featuring light weight, durability, thinness, and a pleasant feel and coolness when drinking. Steel cups can be repeatedly recycled into any type of steel product, taking advantage of steel’s high recyclability. Using easily recyclable steel cups also helps to solve the problem of disposable plastic waste. We are encouraging a recycling-based lifestyle by promoting the Steelish™ logo and developing activities that express the message of contributing stylishly to the global environment by leveraging the benefits of steel products.
As part of these activities, we have been promoting the BETTER RECYCLE Shonan Project since 2021. This project is a new attempt to approach the issue of disposable plastic cups with consumers and contribute to addressing the issue by proposing new lifestyles through the development of new products. The project team, made up of members from IBLC Co., Ltd. and Shonan Style (a magazine published by EDITORS, Inc.) as well as JFE Steel, sought advice and cooperation from local governments and disposable plastic cup suppliers in the Shonan area and created a prototype for an eco-friendly recyclable disposable steel cup. The prototype and the Steelish™ initiative were presented at Carnival Shonan 2022, an event held at the Kanagawa Municipal Tsujido Kaihin Park in November 2022 to explore turning the Shonan beaches into the first zero-waste beaches in Japan.
In March 2023, steel cups were used at Nakame Challenge Cup 2023, an event hosted by Asahi YOU. US, Ltd. and the Nakame Area Management Association to eliminate disposable plastic bottles discarded by people viewing cherry blossoms in Nakameguro and raise awareness of plastic pollution, food loss, and other sustainability issues.
JFE Steel is committed to playing its part in fostering public awareness about climate change and plastic pollution issues and to achieving the SDGs by developing steel solutions that meet the needs of customers and society as a whole.


Resource Recovery and Recycling Targets and Results
Recognizing that the efficient use of resources is a key environmental issue for the manufacturing industry, the JFE Group sets and manages progress against ambitious targets tailored to the respective business characteristics of Group companies. We will continue to pursue the following targets and advance initiatives that contribute to the transition to a circular economy.
The responsible use of water resources is also an important environmental concern for the manufacturing industry. Since the steel business consumes large volumes of water, we set ambitious targets for water recycling rates, manage progress, and strive to reduce water usage.
Targets and Results for FY2024 and Targets for FY2025
| Operating Company | FY2024 Targets | FY2024 Results and Initiatives | FY2025 Targets |
|---|---|---|---|
| JFE Steel | Recycling rate of co-products: 99% or higher | Resource recovery rate: 99.5% | Continue efforts to prevent and reduce the generation of dust and sludge in the recycling of co-products, to maintain the recycling rate of co-products at 99% or higher |
| Maintain efficient use of water Recirculated water usage rate: 90% or higher | Recirculated usage rate: 92.7% | Continue the water resource recycling effort to maintain the recirculated usage rate at 90% or higher | |
| JFE Engineering |
Recycling rate at construction sites
|
Recycling rate at construction sites
|
Recycling rate at construction sites
|
|
Recycling rate of office recyclable waste (Yokohama head office):
|
Recycling rate of office recyclable waste (Yokohama head office):
|
Recycling rate of office recyclable waste (Yokohama head office):
|
|
| JFE Shoji |
Global recycling of steel scrap
|
From FY2020: +5% Both domestic and overseas sales increased compared to previous year, achieving the target |
Global recycling of steel scrap: +10% from FY2020 Strengthen domestic and overseas procurement networks and expand sales to JFE Group and domestic and overseas customers |
JFE Steel Landfill of Co-Products and Recycling Rates
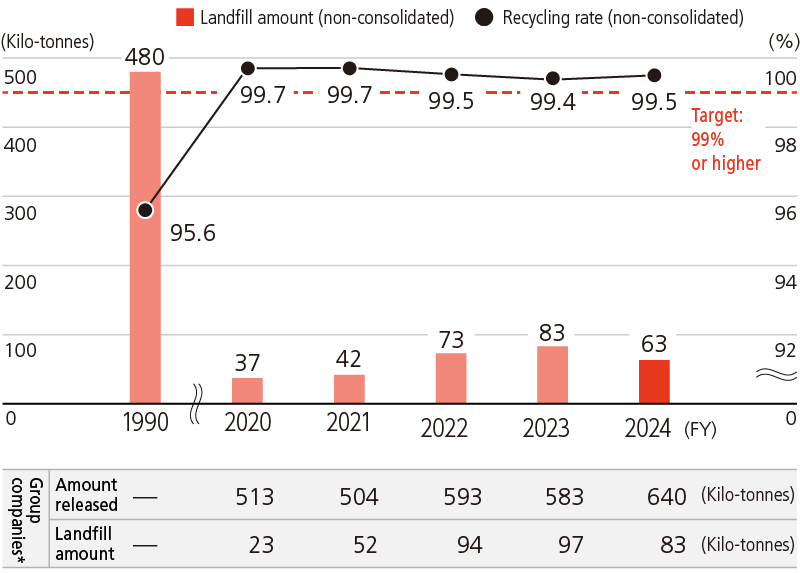
- *Twenty-two JFE Steel consolidated subsidiaries in Japan
JFE Engineering Waste Generated at Construction Sites
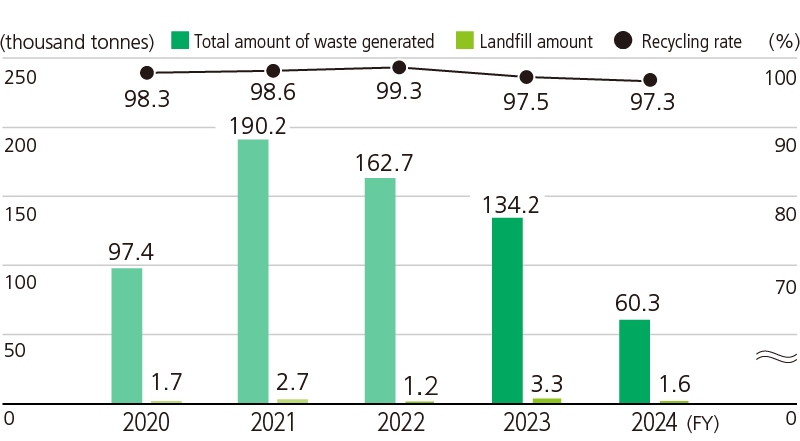
For more on waste generated at the steelworks, please refer to:
Efficient Use of Water Resources
ST Setting Targets for Water Recirculation
All of JFE Steel’s seven production sites in Japan developed a water management plan and monitored water usage in seeking to increase the recirculation rate of water in order to reduce the volume of water intake and drainage and efficiently use water resources. The target water recycling rate at JFE Steel, which uses a large volume of water for cooling and other processes, is 90% or more, which is extremely high considering the amount evaporated when water is used. We are striving to improve the recycling rate by adopting purification processes such as biological and chemical wastewater treatments, and we have been successfully achieving the target. Our recycling rate of industrial water in FY2024 maintained a high level of 92.4%.
JFE Steel Industrial Water Accepted and Circulated
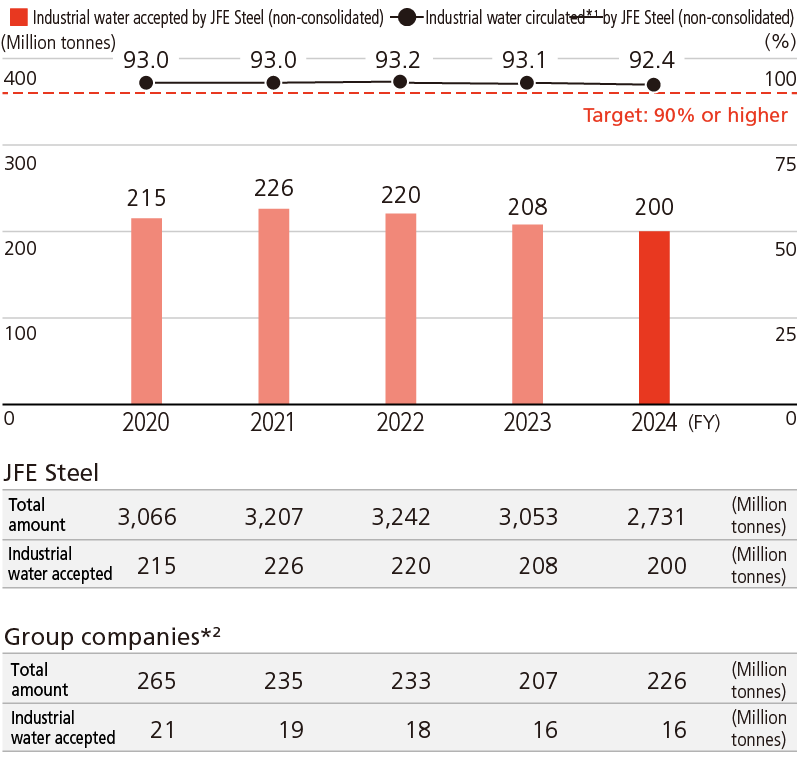
- *1Industrial water circulated (%) = (Total amount used - industrial water accepted)/total amount used ×100
- *2Twenty-two JFE Steel consolidated subsidiaries in Japan
EN Efficient Use of Water Resources
JFE Engineering and each Group company strive to use water efficiently at their business sites.
For more on quantitative data related to water, please refer to: