Addressing Climate Change Issues
JFE Group Environmental Management Strategy
In 2021, the JFE Group established the JFE Group Environmental Vision for 2050, which outlines our commitment to achieving carbon neutrality by 2050. Under our Eighth Medium-term Business Plan, we continue to position climate change initiatives as a top business priority and are accelerating our efforts toward this goal.
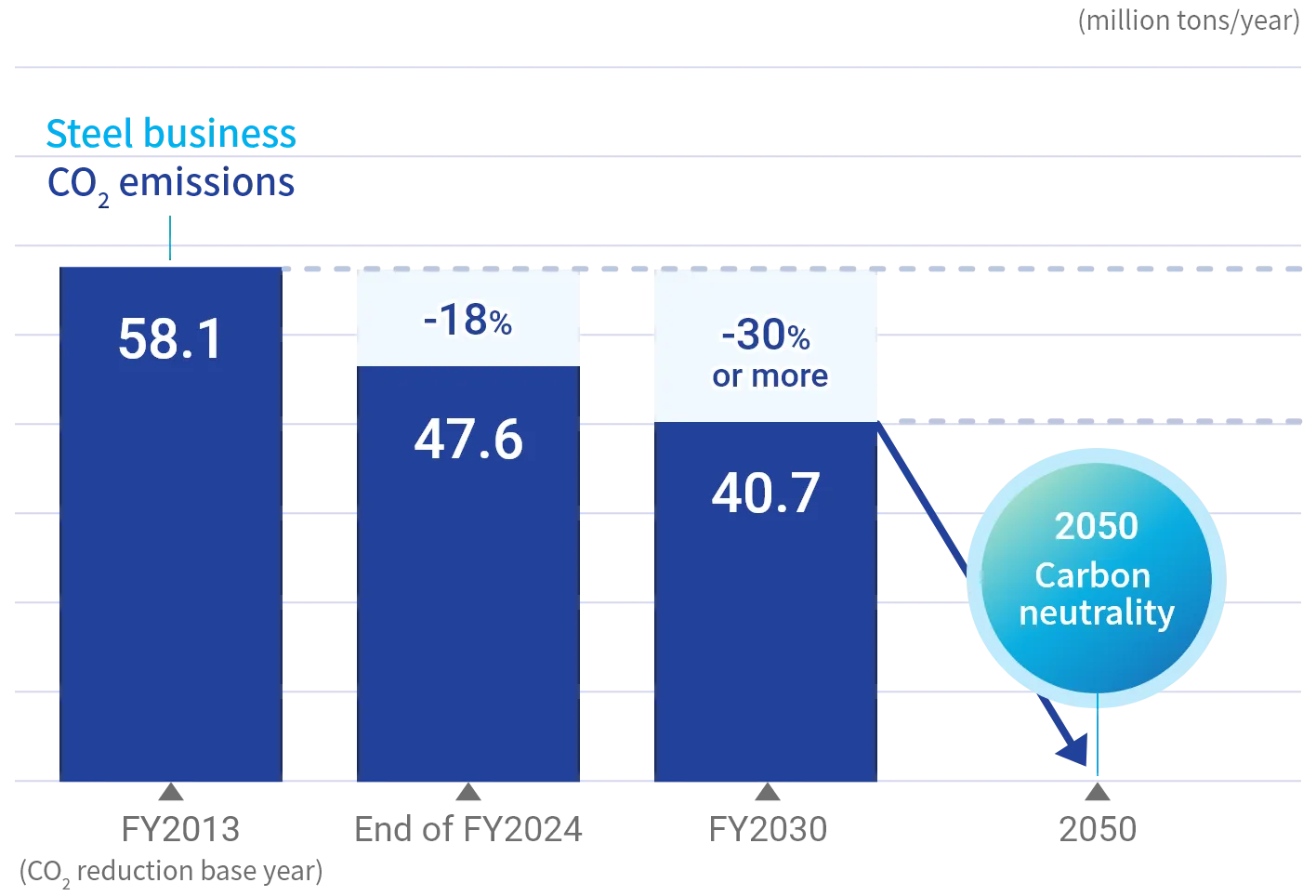
Specifically, in the steel business, we aim to reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by 24% as of fiscal 2027 and by more than 30% as of fiscal 2030 compared to fiscal 2013 levels. To achieve carbon neutrality by 2050, we are striving to develop ultra-innovative technologies, such as a proprietary carbon-recycling blast furnace, and pursuing other promising technological pathways in parallel.
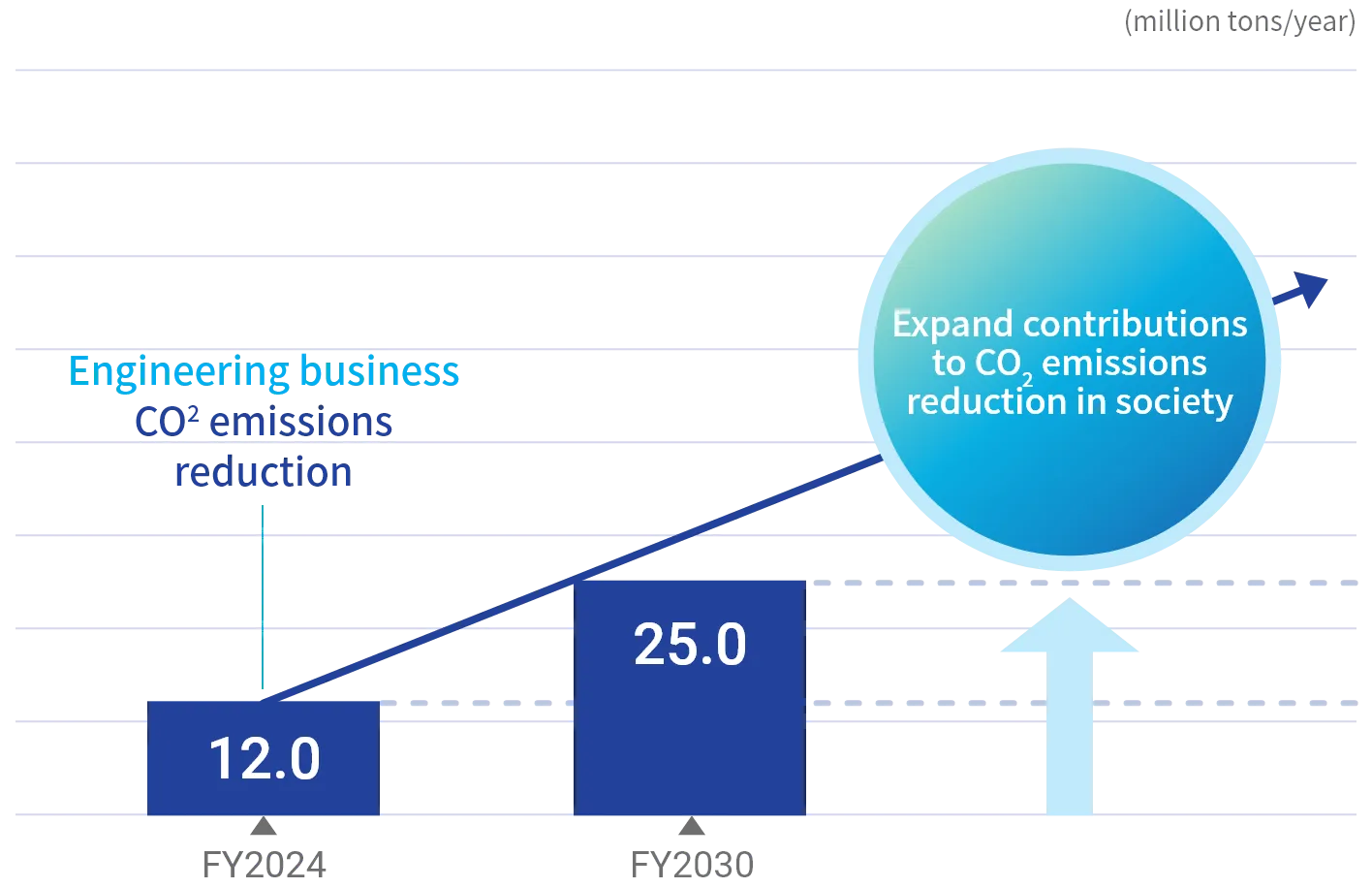
In addition, we are expanding our contributions to GHG emissions reduction across society through various initiatives, such as expanding and developing offshore wind power and other renewable-energy projects in our engineering business, advancing carbon-recycling technologies, and providing high-performance steel products in our steel business.
We are also promoting initiatives for the transition to a circular economy and for the conservation of biodiversity.

JFE Group Environmental Management Strategy

Briefing session on JFE Group Environmental Vision for 2050
Steel Business
Carbon neutrality by 2050
Engineering Business
Expand contribution to GHG emissions reduction across society
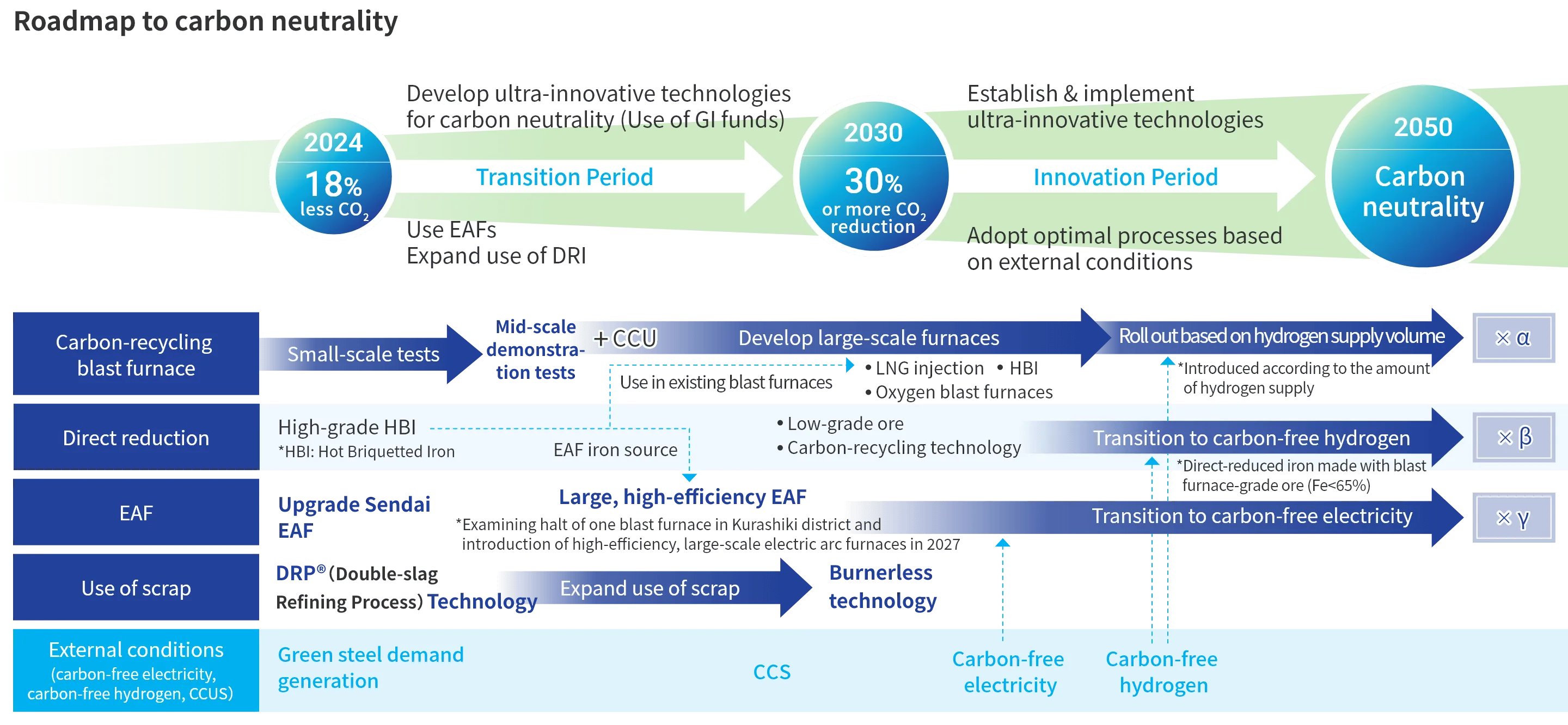
Efforts to Achieve Carbon Neutrality in Steel Business by 2050
JFE is advancing multifaceted efforts, including the development of ultra-innovative technologies, toward achieving carbon neutrality by 2050. In the steel business, we have defined the period up to 2030 as the transition phase, and the period thereafter as the innovation phase. During the transition phase, JFE is working on energy conservation and efficiency improvements in existing processes, as well as the utilization of electric arc furnace technology.
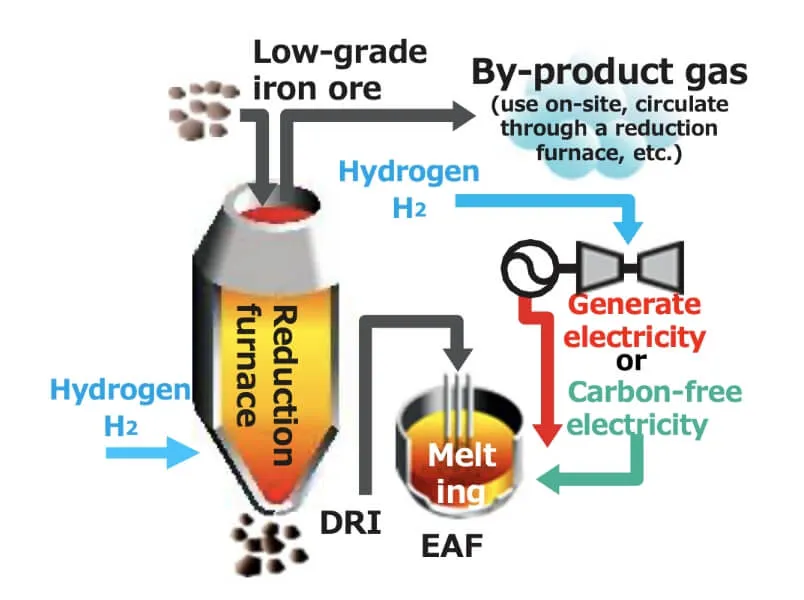
During the innovation phase, we will challenge ourselves with the research and development of ultra-innovative technologies such as carbon-recycling blast furnaces and hydrogen steelmaking (direct reduction), aiming to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050.

JFE Steel Corporation Carbon Neutrality Strategy Briefing
Advantages and disadvantages on the path to carbon-neutral steelmaking
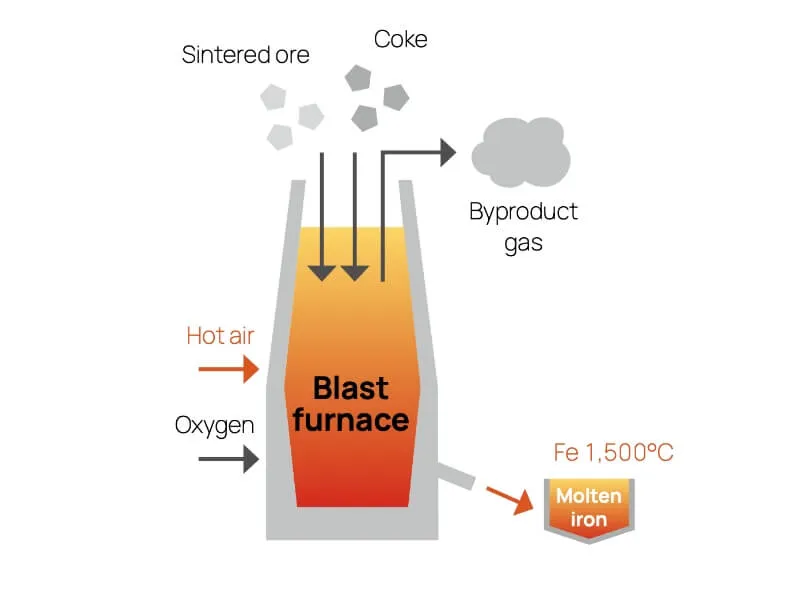
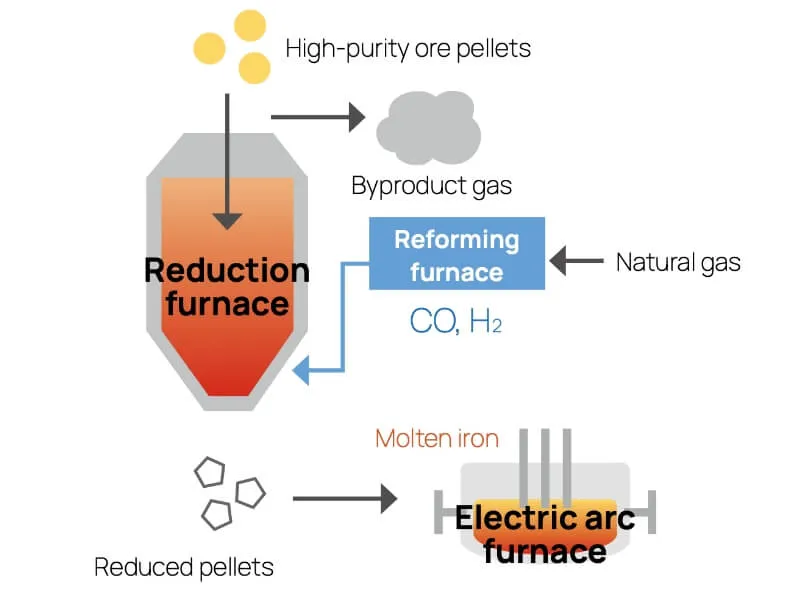
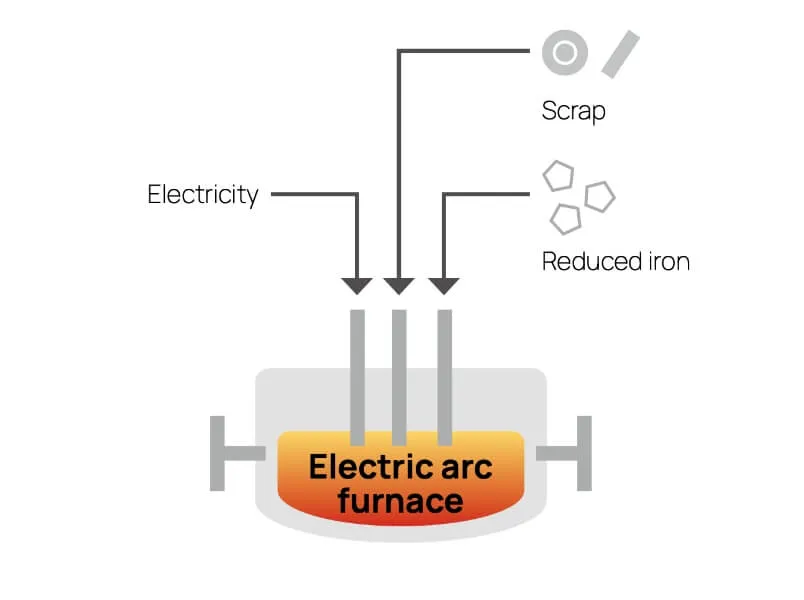
Steel is an essential material that is key to an abundant planet in the future, and demand for steel will never go away. Achieving a carbon-neutral process for steelmaking is necessary for the future of the planet, but the technologies for this have not yet been established. Steelmaking processes currently include blast furnace steelmaking, electric furnace steelmaking, and direct reduction steelmaking methods. Each process has advantages and disadvantages with respect to the objective of attaining carbon neutrality. We believe it will be important to take a multitrack approach to innovation for overcoming these disadvantages.
| Blast furnace | Direct reduction | Electric arc furnace | |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
|
| Advantages |
|
|
|
| Disadvantages |
|
|
|
- *CCCUS: Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage
Development of Ultra-innovative Technologies
| Ultra-innovative blast furnace (Carbon-recycling blast furnace) |
Direct-reduction steelmaking | Large, high-efficiency EAF | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Development project | 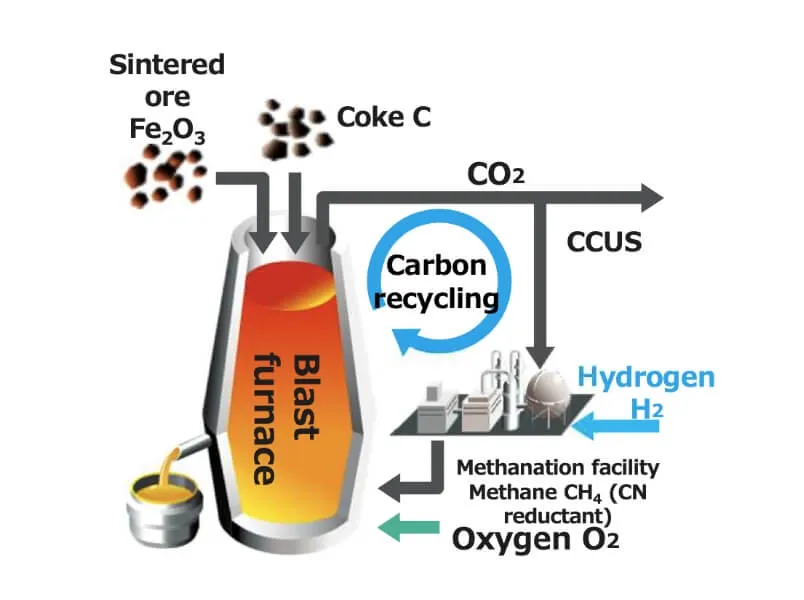 |
 |
 |
| Target | Reduce CO₂ emissions by 50% or more (compared to conventional blast furnaces) |
Reduce CO₂ emissions by 50% or more (compared to conventional blast furnaces) |
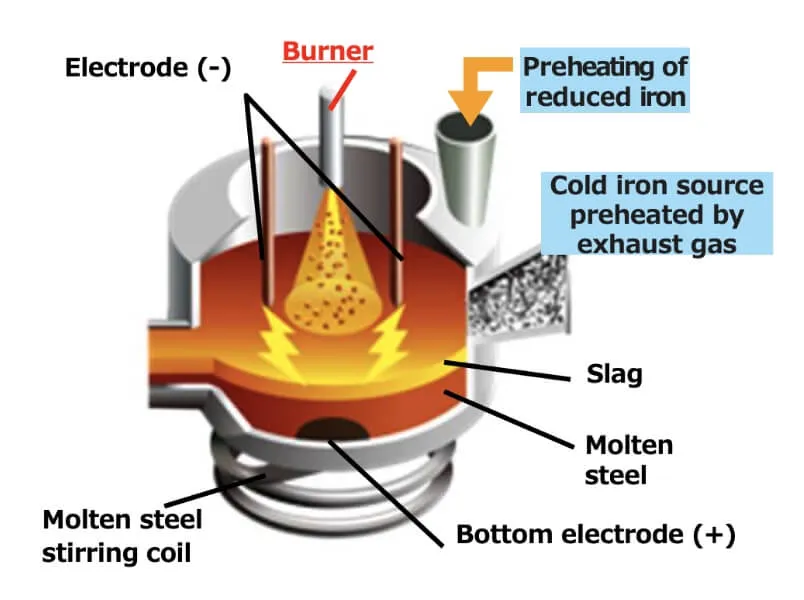
Establish high-quality and high-efficiency melting technologies |
| Description |
|
|
|
| Period | Test scheduled for FY2025-2026 | Test scheduled for FY2024-2026 | Test scheduled for FY2024-2025 |
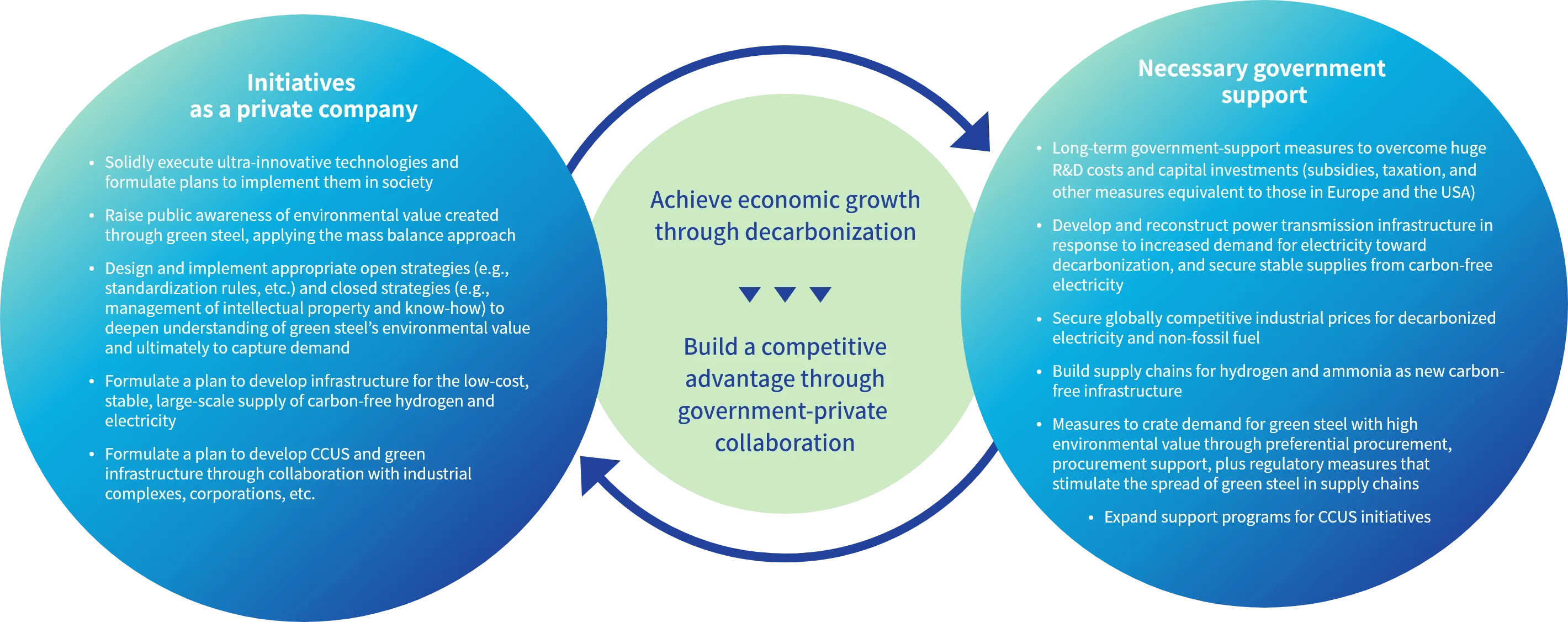
Collaborating with Society on Carbon Neutrality
While achieving carbon neutrality is a top management priority for JFE Steel, generating environmental value involves large investments and cost increases associated with transitioning, requiring efforts beyond the private company level.
In order to maintain and strengthen Japan's overall industrial competitiveness, long-term and continuous government support for R&D and facility implementation of discontinuous innovation is essential.
We will make various recommendations on climate change measures and energy policies in Japan, and promote activities through industry associations.