Initiatives to Address Climate Change Issues
Basic Policy
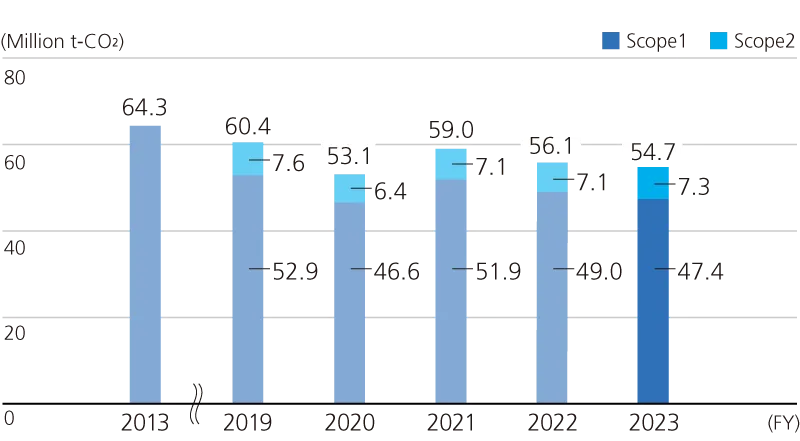
Climate change is a critical business concern for the JFE Group from the perspective of business continuity. Our steel business, which emits 99.9% of the Group’s total CO2 emissions, has been developing various technologies for saving energy and reducing these emissions. We have applied these technologies to steel manufacturing processes to enable production with low levels of CO2 emission intensity.
Furthermore, the JFE Group has developed and maintains a variety of products and technologies that contribute to reducing GHG emissions, including high-performance steel materials that save energy when customers use them, as well as renewable energy power generation. We will continue to develop and promote the widespread use of these processes and products. We consider this an opportunity to apply the technologies we have fostered across the globe and at the same time contribute to tackling climate change.
JFE announced its endorsement for the TCFD recommendations in May 2019 and has identified climate change-related issues based on the scenario analysis advocated in the TCFD to formulate strategies for sustainable growth. The JFE Group will be a top runner for the development of carbon neutral technologies and formulated the JFE Group Environmental Vision for 2050 toward achieving carbon neutrality in 2050. We will actively work on reducing GHG emissions and contributing to GHG reductions.
JFE Group Environmental Vision for 2050
The JFE Group intends to strengthen sustainability through solutions that address global climate change issues while restructuring its business in response to changes in the environment surrounding the steel business.
In 2021, we positioned climate change as a top-priority issue in the Seventh Medium-term Business Plan (FY2021-FY2024) and formulated the JFE Group Environmental Vision for 2050 toward achieving carbon neutrality by that year. We will continue to regard it as a top priority under the Eighth Medium-term Business Plan (FY2025-FY2027) and will implement related initiatives.
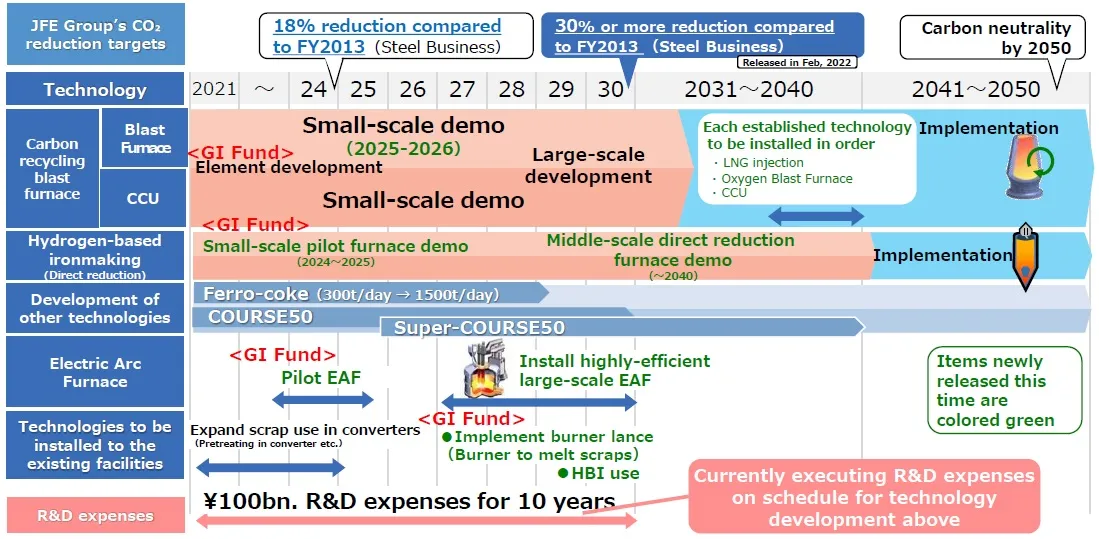
We will systematically address climate change by reflecting the TCFD’s principles in the business strategies of our JFE Group Environmental Vision for 2050. In the steel business, we will reduce GHG emissions by 18% from FY2013 levels by the end of FY2024. In addition, we have announced targets for our steel business of reducing GHG emissions by FY2027 by 24% and by FY2030 by 30% or more, compared to FY2013.
To explore all possibilities for realizing carbon neutrality in 2050, we will take on the challenge of developing ultra-innovative technologies such as carbon-recycling blast furnaces developed with our proprietary technology while also adopting a multitrack approach for pursuing other technologies. In our engineering business, we will widen our contribution to the reduction of GHG in society as a whole by expanding and advancing renewable power generation and carbon-recycling technologies, supplying high-performance steel products, and other initiatives. Furthermore, we will apply Group strengths to accelerate the commercialization of our offshore wind-power business.
The development of process technologies that minimize GHG emissions while enabling the mass production of high-quality, high-performance steel products is essential for the sustainable development of society. Efforts for achieving carbon neutrality will inevitably entail substantial costs for research and development and renewed facilities. We believe it will be necessary to consider how society will bear these costs and what support can be provided by the government and other sources.
Given the ambitious target of achieving carbon neutrality by 2050, we hope to lead the way in establishing the necessary decarbonization technologies at the earliest possible stage, based on developing a decarbonization infrastructure and realizing a global equal footing.
JFE Group Environmental Vision for 2050
- Climate change is a critical business concern for JFE, and we are aiming to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050.
- We will accelerate our research and development of new technologies and pursue ultra-innovative technologies.
- We will seek business opportunities that allow us to enhance corporate value by contributing to CO2 emissions reduction across society.
- The principles of TCFD will be reflected in our business strategies and systematically deployed.
The Target of Reducing GHG Emissions in FY2027 (Eighth Medium-term Business Plan Initiatives)
- Reduce steel-business GHG emissions in FY2027 by 24%, compared to FY2013 (steel business).
The Target of Reducing GHG Emissions in FY2030
- Reduce steel-business GHG emissions in FY2030 by 30% or more, compared to FY2013 (steel business).
Initiatives for Carbon Neutrality by 2050
-
Reduce steel-business GHG emissions
- Pursue ultra-innovative technology for carbon-recycling blast furnaces and CCU.
- Develop hydrogen-based ironmaking direct reduction technology.
- Leverage top-class electric arc furnace technology for high-quality, high-performance steel manufacturing and for high efficiency, ensure early implementation, etc.
- Develop transitional technologies for carbon neutrality, including increased use of steel scrap in converters, energy savings, and low-carbon energy transformations.
-
Expand contributions to GHG emissions reduction in society
- Engineering business: Expand and develop renewable energy power generation and carbon-recycling technologies. (Reduce GHG emissions by 13.5 million tonnes in FY2027, 20 million tonnes in FY2030, and 30 million tonnes in FY2035.)
- Steel business: Develop and market eco-products and eco-solutions.
- Trading business: Increase trading in biomass fuels, steel scrap, etc., and strengthen business in supply chain management for eco-products.
-
Offshore wind-power generation business (Groupwide effort to accelerate commercialization of the offshore wind-power business)
- Engineering business: Manufacture monopiles and other seabed-fixed structures for offshore wind-power generation.
- Steel business: Produce large, heavy plates using the No. 7 continuous casting machine at the Kurashiki District of the West Japan Works.
- Trading business: Carry out supply chain management for steel materials and processed products.
- Shipbuilding business: Manufacture offshore wind power generation floating structures and construct work vessels.
- Groupwide: Operation and maintenance (O&M) making maximum use of Group resources.
| Notes. | 1. Carbon-recycling blast furnace: A technology that converts CO2 from the blast furnace into methane, which is then used as reducing material in the blast furnace |
| 2. CCU: Carbon dioxide capture and utilization | |
| 3. Transitional technologies: Technologies that advance the transition to carbon neutrality |
- Eighth Medium-term Business Plan
- JFE Group Environmental Vision for 2050, Presentation Material
- JFE Group Environmental Management Strategy, Presentation Material
Information Disclosure Based on TCFD Recommendations

On May 27, 2019, JFE Holdings announced its endorsement for the final report of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD)*.
- *The TCFD was established by the Financial Stability Board (FSB) at the request of G20 finance ministers and central bank governors.
Climate-related risks and opportunities may have a significant impact on medium- to long-term corporate finance. The TCFD was established by the Financial Stability Board at the request of the G20 for reducing the risk of instability in the financial market. The TCFD considers disclosure frameworks that enable the financial markets to appropriately assess climate-related risks and opportunities and releases its findings as a final recommendations report.
Recognizing the importance of investors’ and others’ accurate understanding of how climate-related risks and opportunities may affect the financial condition of investee companies when making financial decisions, the TCFD recommends disclosure of information regarding the four core elements of organizational management: governance, strategy, risk management, and metrics and targets.
The JFE Group promotes the disclosure of climate-related information in line with international frameworks such as the TCFD, thereby enhancing the reliability and transparency of its initiatives for stakeholders, including investors, customers, employees, and local communities.
In addition, the International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB), established by the IFRS Foundation*, has succeeded in the achievements of the TCFD and formulated international standards for the integrated disclosure of financial and non-financial information. In Japan, the Sustainability Standards Board of Japan (SSBJ) has formulated disclosure standards based on the ISSB standards, which were published in March 2025. The application of these standards is scheduled to be phased in from 2027, and the JFE Group is also preparing to comply.
- *A private, nonprofit organization responsible for developing International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)
For the TCFD content index, please refer to:
Governance (Management Structure: JFE Group)
In the process of identifying material issues, the perspective of financial impact taking into account recent social and economic trends has become a key factor in addition to the conventional perspective of management through smooth PDCA cycles. In particular, initiatives such as reducing GHG emissions in the steelmaking process and developing and providing products that contribute to reducing GHG emissions are now recognized as being directly linked to corporate value and sustainable growth.
Accordingly, in formulating the Eighth Medium-term Business Plan, we reviewed material issues by selecting items of greater managerial importance, considering economic aspects, including financial impact. In this process, we emphasize the impact of responses to climate change on the Company’s medium- to long-term competitiveness, and we have positioned reducing the JFE Group’s GHG emissions and contributing to reducing GHG emissions in society as a whole as material issues, continuing from the Seventh Medium-term Business Plan, as initiatives for achieving carbon neutrality by 2050.
As the framework overseeing initiatives to address climate change, the JFE Group has established a cross-sectional JFE Group Environmental Committee under the JFE Group Sustainability Council, chaired by the president of JFE Holdings. This committee discusses setting goals for environmental protection, monitors the progress of these initiatives, and works to improve the Group’s overall environmental performance as well as risk assessment and responses.
Particularly important management themes requiring deliberation are discussed at the Group Management Strategy Committee, and the content of these discussions is reported to the Board of Directors, which fulfills its supervisory function through discussions on environmental issues, including climate change.
Examples of climate change-related agenda items involving Board of Directors decisions and reports
- Declaration of endorsement for the final TCFD recommendation report
- Information disclosure consistent with TCFD recommendations (scenario analysis, financial impact, and other information)
- Formulation of the Seventh Medium-term Business Plan, JFE Group Environmental Vision for 2050
- Review the CO2 emissions reduction target for FY2030.
- Use of climate-related metrics to determine executive remuneration
- Formulation of GHG emissions reduction targets and contribution targets under the Eighth Medium-term Business Plan
- Decision-making on capital investment for GHG emissions reduction
Risk Management
JFE Holdings is responsible for comprehensive risk management in accordance with its Basic Policy for Building Internal Control Systems.
Climate-related risks and opportunities are identified, assessed, and reviewed at the corporate level through scenario analysis in line with the framework recommended by the TCFD. The results of these analyses are appropriately reported in accordance with the aforementioned governance framework.
Furthermore, key factors affecting business are selected, and the results of a detailed analysis of their impacts are used in formulating business strategies, including the Medium-term Business Plan.
Monitoring Method for Risks
The JFE Group monitors risks that could affect management at the JFE Group Sustainability Council, Group Management Strategy Committee, and Management Committee. Measures are implemented based on a quarterly report on climate change-related risks deliberated by the specialized committees of each Group company (e.g., the Environmental Committee). In addition, the JFE Group Environmental Committee consolidates information related to risks, strengthens management systems, and strives to reduce the frequency and impact of risks. Moreover, the JFE Group promotes initiatives to maximize climate-related opportunities.
Countermeasures Based on Monitoring
- 1. Groupwide deliberations
- 2. Monitoring penetration of policies within the Group
- 3. Monitoring deployment of policies throughout the Group
JFE Group’s Strategy for Addressing Climate Change Issues
The JFE Group integrates climate change-related risks and opportunities as follows. The JFE Group formulated the Seventh Medium-term Business Plan (FY2021-FY2024) and positioned responses to climate change as top-priority issues for achieving the Group’s medium-to long-term sustainable growth and enhancing corporate value. In the Eighth Medium-term Business Plan (FY2025-FY2027), the Group continues to identify responses to climate change as a top priority and is pursuing related initiatives.
In addition, the Group formulated the JFE Group Environmental Vision for 2050toward achieving carbon neutrality by 2050, as a key initiative for environmental and social sustainability. Through this vision, we have incorporated climate change initiatives into our business strategies and reflected the TCFD philosophy in our environmental management strategy. JFE Vision 2035, the JFE Group’s long-term vision, sets forth the goal of systematically addressing climate change issues and becoming a top runner in carbon neutral technology development. Consistent with TCFD recommendations, we conduct scenario analysis as part of our information disclosure to identify and evaluate key factors affecting the business. These risks and opportunities are reflected in management strategies and used for decision-making. The JFE Group Environmental Vision for 2050 identifies three strategic pillars for achieving carbon neutrality:“reducing GHG emissions in the steel business,” “expanding contributions to reducing GHG emissions throughout society,”and“initiatives for the offshore wind power generation business.”
We also communicate our climate change initiatives through briefings and other channels to strengthen relationships of trust with our stakeholders.
For related materials, please refer to:
- Scenario Analysis in Line With the TCFD Recommendations
- JFE Group Environmental Vision for 2050, Presentation Material
- JFE Group Long-Term Vision “JFE Vision 2035”, Eighth Medium-term Business Plan (FY2025-FY2027)
- JFE Group Environmental Management Strategy, Presentation
Initiatives for Achieving Carbon Neutrality in the Steel Business
Promotion Structure
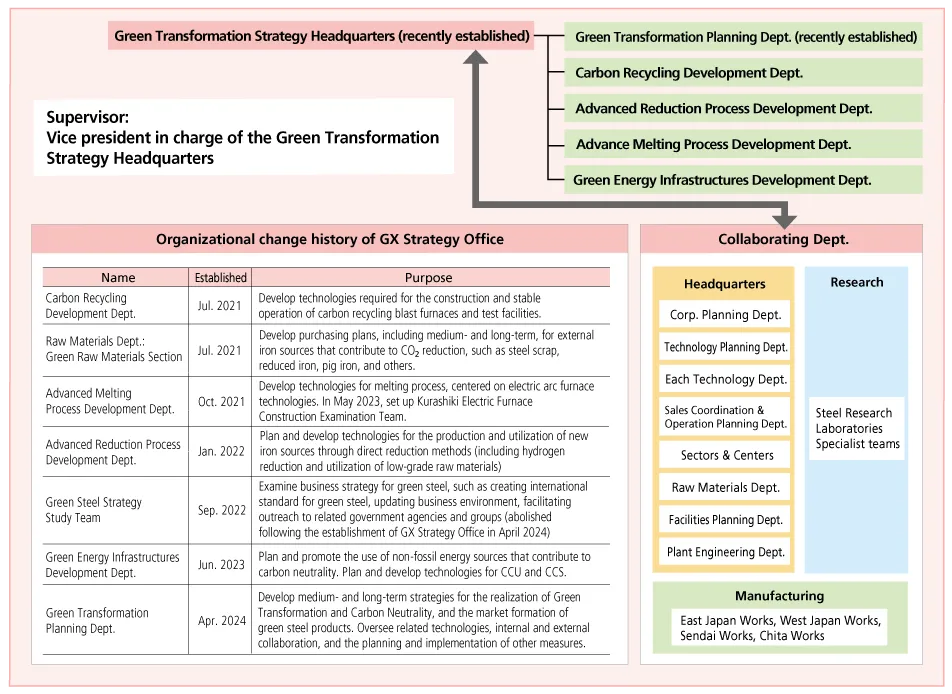
The key for ensuring JFE Steel’s sustainable growth is to develop and implement a medium- to long-term strategy for realizing Green Transformation (GX). In April 2024, the Green Transformation Strategy Headquarters was established to formulate and promote a Companywide strategy to realize GX. The office is comprised of the Green Transformation Planning Department and departments responsible for developing technologies, specifically the Carbon Recycling Development Department, the Advanced Reduction Process Development Department, the Advanced Melting Process Development Department, and the Green Energy Infrastructures Development Department. Under this structure, JFE Steel will conduct and manage carbon neutrality technology development and investment as well as address issues such as market development for expanding sales of green steel and strengthening cooperation with government authorities.
JFE Steel’s Management Structure to Promote Carbon Neutrality
Steel Business Initiatives for Achieving GHG Emissions Reduction Targets
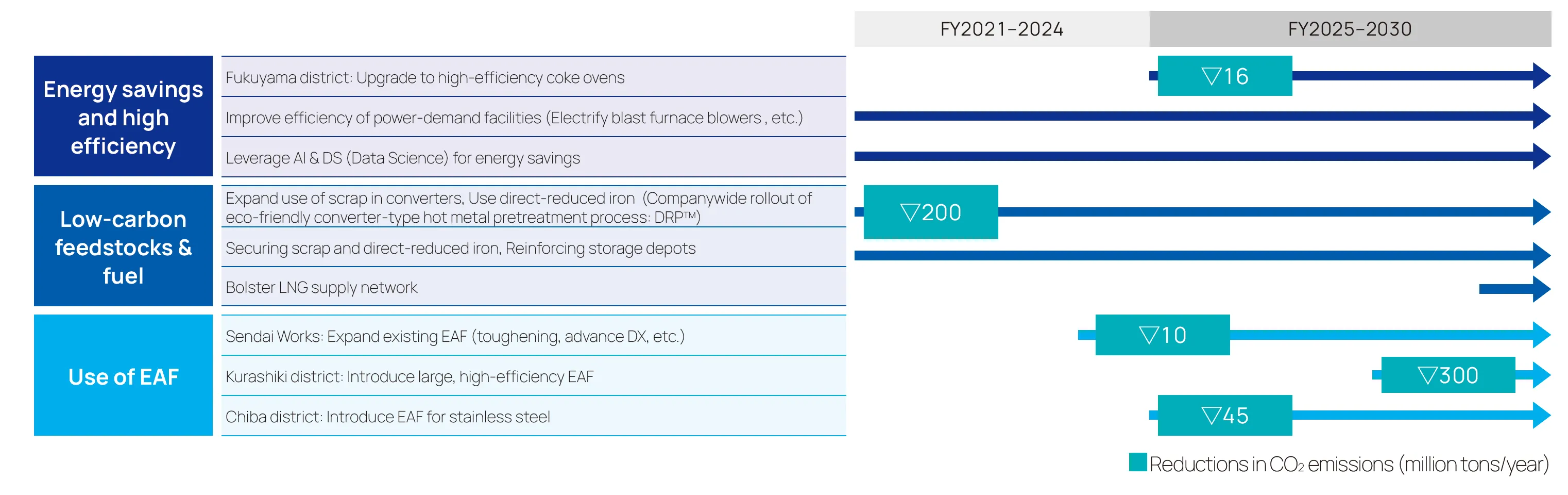
The JFE Group has adopted a multi-pronged approach to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050, including the development of ultra-innovative technologies. We have set a target in the steel business for reducing GHG emissions by 24% by FY2027 and by at least 30% by FY2030, compared to FY2013. We regard the period through 2030 as a transition phase, during which we will steadfastly implement plans to achieve our GHG reduction targets, mainly by expanding the application of low-carbon technologies focused on “reducing,” while accelerating research and development of ultra-innovative technologies in preparation for the innovation phase after 2030. In the innovation phase, we will advance initiatives for the wise use of resources, including the commercialization of carbon-recycling blast furnaces that leverage our proprietary carbon-recycling technology and direct reduction steelmaking, as well as the expansion of CCU applications. Furthermore, we will undertake CO2 sequestration through CCS to create a carbon-neutral society together with local communities and industrial complexes. We will achieve carbon neutrality through initiatives under these three themes.
Roadmap to Carbon Neutrality
JFE Steel announced its GHG reduction plan through FY2030 at the JFE Group Environmental Management Strategy Briefing on May 29, 2025. We have targeted a 24% reduction by FY2027 as an interim milestone toward a reduction of at least 30% by FY2030. GX investments that are expected to contribute significantly to achieving the FY2030 target, such as the Kurashiki innovative electric arc furnace and investments in the use of direct reduced iron in a blast furnace, have, for the most part, already been formally approved.
We are advancing phased and strategic initiatives to achieve carbon neutrality in our steel business by 2050. First, we are working on research and development of innovative low-carbon technologies utilizing public support such as the Green Innovation Fund . Targeted for completion around 2035, these efforts are intended to establish ultra-innovative technologies, such as carbon recycling blast furnaces, the use of hydrogen in the direct reduced iron method, and the development of production methods for high-quality, high-performance products using electric arc furnaces, that fundamentally reimagine conventional manufacturing processes.
The state of energy infrastructure will be a crucial factor in addition to the development of ultra-innovative technology for achieving carbon neutrality. Just as essential will be our response to external changes, such as the development of hydrogen supply networks and the stable securing of decarbonized electric power. Furthermore, market demand for green steel and the rising environmental awareness of customers will also be key indicators for the transformation of the steelmaking process. We will pursue this transformation with optimal timing by comprehensively taking these factors into account.
Roadmap to Carbon Neutrality in 2050
JFE Group’s Strategy and Alignment with the Paris Agreement
Transition Finance toward decarbonization in the iron and steel sector, published by the Japanese Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry (METI), is consistent with Japan’s emissions reduction targets based on and therefore aligned with the Paris Agreement. The roadmap sets out a pathway to achieve carbon neutrality by accelerating decarbonization through the introduction of innovative technologies starting in the 2040s, assuming the development of a hydrogen supply infrastructure and CCUS.
In 2022, the JFE Group issued transition bonds through a public offering. During the evaluation process for this issuance, the Group’s initiatives were certified by a third party as being aligned with METI’s roadmap and, by extension, the Paris Agreement.
- METI: Technology Roadmap for Transition Finance in the Iron and Steel Sector
- METI: Transition Finance Case Study
Metrics and Targets (Plans and Results for GHG Reduction in the Steel Business)
The JFE Group is promoting the JISF’s Commitment to a Low Carbon Society, which focuses on the Three Ecos initiatives and the development of innovative new iron and steelmaking processes. Phase I of the plan was completed in 2020. It was rebranded as the JISF’s Carbon Neutrality Action Plan, and the Phase II target (FY2030 target) was revised to a 30% reduction in energy-derived CO2 emissions in FY2030, compared to FY2013. JFE Steel is aggressively pursuing the achievement of this goal.
In addition, JISF formulated and announced the Long-term Vision for Climate Change Mitigation, which looks ahead to 2030 and beyond, in 2018, which is intended to realize zero-carbon steel. JFE Steel played a key role in formulating this vision. Furthermore, in 2021, the JISF announced the Basic Policy of the Japan Steel Industry on 2050 Carbon Neutrality sought by the Japanese government, declaring that the Japanese iron and steel industry will boldly take on the challenge of realizing zero-carbon steel.
As the JFE Group, we have declared our intention to reduce GHG emissions in the steel business in FY2030 by at least 30% compared to FY2013 and to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050.
Major Group companies of JFE Steel have formulated GHG reduction targets at the same level as JFE Steel. In May 2025, we formulated our long-term vision, JFE Vision 2035, expressing our aspirations for the future, and the Eighth Medium-term Business Plan (FY2025-FY2027) to drive growth strategies toward JFE Group’s aspiration. To achieve these plans, we will install an innovative electric arc furnace at the Kurashiki District of the West Japan Works to build a system for the mass supply of green steel. In addition, we will steadily reduce GHG emissions in the steel business by developing ultra-innovative carbon neutral technologies. By uniting all Group companies in Japan and overseas to incorporate efforts to address climate change into our business strategies, the Group will systematically reduce GHG emissions by reflecting the TCFD’s principles in its management strategies.
Domestic Steel Business: GHG Emissions Reduction Plan
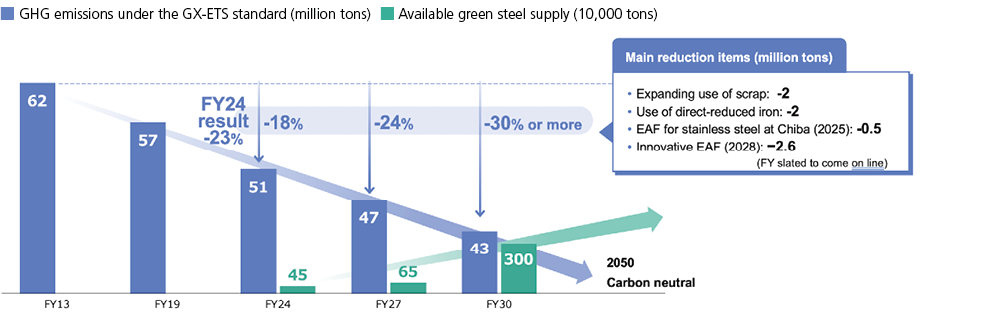
Steel Business GHG Emissions
GHG Emissions from Energy Sources and Unit GHG Emissions of JFE Steel
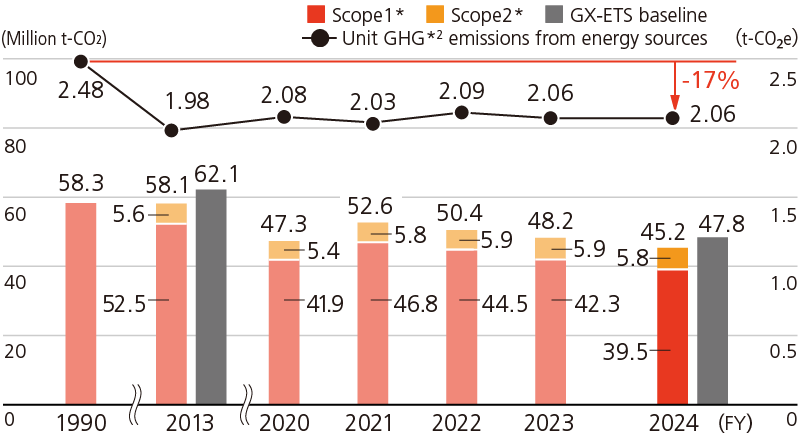
- *1FY2013 figure includes data for JFE Bars & Shapes Corporation’s Sendai Works.
- *2Under the JISF Carbon Neutrality Action Plan standards, emissions are limited to CO2 only.
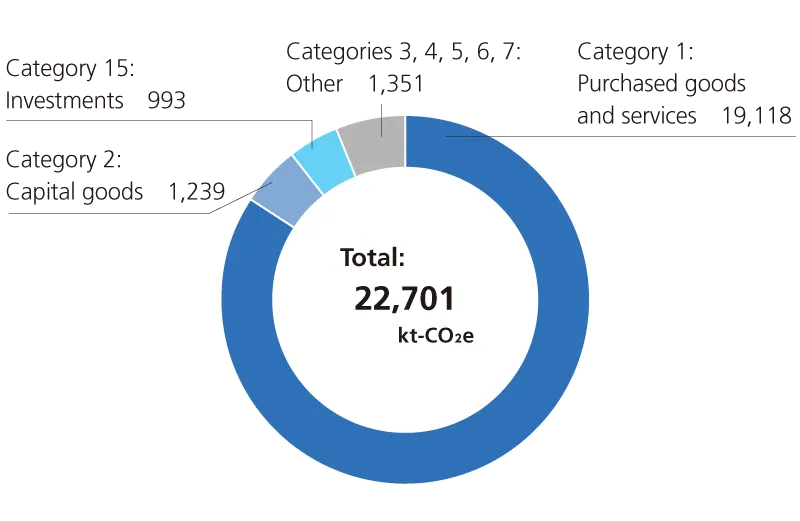
For quantitative data for the JFE Group’s GHG emissions, please refer to:
FY2030 Initiatives for Achieving GHG Emissions Reduction Targets
Our multi-pronged approach for achieving carbon neutrality by 2050 includes developing ultra-innovative technologies. We have defined the period up to 2030 as a transition phase, to be followed by an innovation phase. In the transition phase, the steel business is promoting energy-saving and high-efficiency improvements in existing processes and the use of electric arc furnace technology. By FY2024, we had authorized investments of approximately 0.4 trillion yen for reducing GHG, and in terms of achieving the FY2030 targets, investments have, for the most part, already been institutionally approved for delivering substantial emission reductions, such as the innovative electric arc furnace at the Kurashiki District of the West Japan Works and the use of direct reduced iron in the blast furnace at the Chiba District of the East Japan Works. We will continue to steadily promote the authorization and execution of necessary financing and investments toward achieving the reduction targets.
Development of Electric Arc Furnace Process Technology
The electric arc furnace is one of JFE Steel’s technology development efforts for carbon neutral steelmaking in which products are manufactured by melting steel scrap and direct-reduced iron in an electric arc furnace. So far, we have managed to reduce GHG emissions from this steelmaking process to one-quarter of the blast furnace-converter method. We are also striving to eliminate GHG emissions generated by the electric arc furnace process in the future by using the aforementioned hydrogendirect reduced iron as the raw material and non-fossil electricity.
Although the electric arc furnace process has the advantage of reducing GHG emissions, there are two major problems compared to the blast furnace-converter method: the productivity of the electric arc furnace process in general is about 30% lower than that of the blast furnace-converter method, and the use of scrap as the raw material inevitably increases the concentration of impurities, which limits the production of high-quality, high-performance steel products. JFE Steel has also been developing technologies to address these issues. We have theoretically established high-quality and high-efficiency technologies using existing electric arc furnaces and laboratory tests. Consequently, in April 2025, we decided to convert the No. 2 blast furnace at the West Japan Works (Kurashiki District), scheduled for refurbishment in FY2027, into an innovative electric arc furnace. This innovative electric arc furnace will be the largest in the world, enabling us to establish a mass supply system for high-quality, high-performance steel products not possible with conventional large-scale electric arc furnaces. We want to be the first in the industry to do so and secure the top share in the domestic green steel market.
Conceptual image of the innovative electric arc furnace and related facilities at the Kurashiki District

Using Electric Arc Furnaces to Increase the Use of Scrap
JFE Steel completed upgrading electric arc furnace production capacity at the Sendai Works in FY2024 by reinforcing the electric arc furnace, boosting capacity through DX, upgrading cargo handling facilities, and improving the load handling equipment by approximately 140,000 tonnes per year. This is expected to result in a reduction of approximately 0.10 million tonnes of GHG emissions per year.
Furthermore, we will install a new electric arc furnace in the Chiba district for stainless steel production. This will allow the facility to replace part of the feedstock from molten iron from blast furnaces with scrap and thus reduce GHG emissions. This could increase by up to six times the volume of scrap used, and we expect to reduce GHG emissions by a maximum of about 450,000 tonnes per year.
As mentioned above, we will suspend one blast furnace at the Kurashiki District and convert it into an innovative electric arc furnace to further expand the use of scrap.
Overview of Demonstration Tests for Developing Manufacturing Methods of High-Quality Steel Products in Electric Arc Furnaces
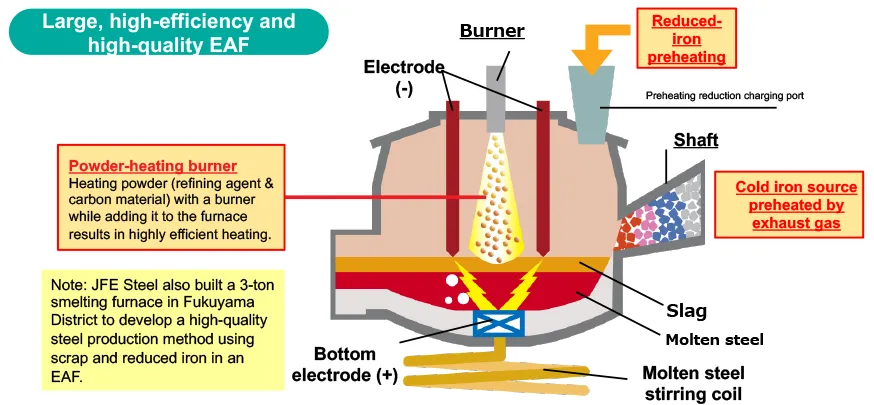
We are developing a process that reduces the electric arc furnace’s melting power consumption and also enables high-speed melting of cold iron sources (scrap and direct reduced iron). We will verify the following during demonstration tests.
- Optimal methods for preheating and feeding direct reduced iron
- Methods for using heating burners
- Optimal methods for molten steel stirring
Research and Development for Electric Arc Furnaces
Manufacturing Higher-Grade Steel Using the Electric Arc Furnace Process
The electric arc furnace process uses scrap and direct reduced iron as raw materials. The higher concentration of impurities in these materials, such as copper, causes material degradation, including surface defects and reduced workability in steel sheets and deterioration of properties in electrical steel sheets. We are working on two technologies to address the issue, one to remove impurities and another to detoxify impurities, so that we can use the electric arc furnace process to produce high-quality steel products such as steel sheets for automobiles and electrical steel sheets.
Increased Use of Scrap Iron in Steelmaking
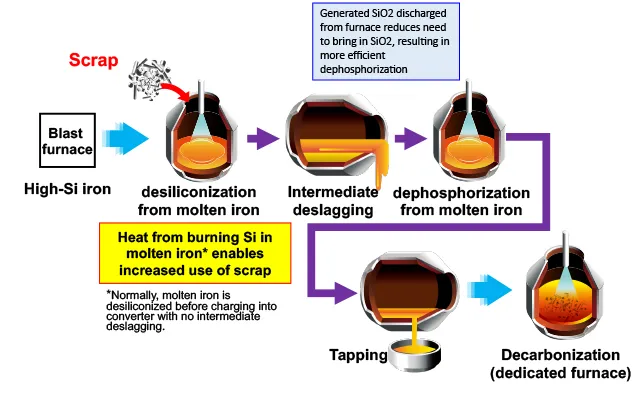
JFE Steel introduced the Double-slag Refining Process (DRP™), an eco-friendly converter-type molten-iron pretreatment process, at all of its sites in 2021, thereby increasing the amount of scrap iron to be used in converters and reducing GHG emissions.
DRP makes full use of silicon in molten iron as a heat source, thereby increasing the amount of scrap iron to be used in converters. It allows reducing the molten-iron blending ratio (molten iron vs. scrap charged into the converter) to 82%, down from 90% through conventional methods. The Company introduced this process in all of its steelmaking facilities, and the increased use of scrap iron in converters enabled us to reduce annual GHG emissions by approximately 1.15 million tonnes in FY2023. We will continue to develop technologies to further expand the use of scrap.
Eco-friendly converter-type molten iron pretreatment process DRP™: Double-slag Refining Process
East Japan Works (Chiba District) to Produce Stainless Steel with Electric Arc Furnace
JFE Steel has decided to install a new electric arc furnace at the No. 4 steelmaking shop at the East Japan Works (Chiba district) in the second half of FY2025 (planned). Scrap melting capacity is expected to increase to approximately 300 kilotonnes per year (planned), up to six times the amount compared to conventional processes, with GHG emissions expected to be reduced by up to about 450 kilotonnes per year. We have defined the period up to 2030 as a transition phase toward carbon neutrality and view the electric arc furnace process as an effective means for reducing GHG emissions. Looking ahead, we will continue our multi-pronged development of ultra-innovative technologies and steadily advance toward realizing carbon neutrality.
Feasibility Study on New Venture Business to Secure Direct Reduced Iron Supply
In the transition phase up to 2030, we expect a shortage in domestic scrap supply. The use of direct-reduced iron is considered an effective way to supplement this in the production of high-quality steel using electric arc furnaces and in the reduction of GHG emissions from blast furnaces.
JFE Steel is conducting detailed feasibility studies with EMSTEEL, the largest steel producer in the UAE, and ITOCHU Corporation to establish a supply chain of direct reduced iron with low carbon emissions. After the business scheme is finalized, we will begin producing direct-reduced iron (approximately 2.5 million tonnes per year) under a joint venture to be established in the UAE. As the largest off-taker, we will secure a long-term and stable supply of direct-reduced iron, mainly for the innovative electric arc furnace at the West Japan Works (Kurashiki District), which is scheduled to begin operation in FY2028.
- Overview of EMSTEEL
Company name: EMSTEEL
Representative: HE Engineer Saeed Ghumran Al Remeithi (Group CEO)
Business: Steel
The memorandum exchange ceremony held in Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, in the presence of then Prime Minister Fumio Kishida (July 17, 2023)


Adoption status of green steel products

Name origin: JFE + Green + GX
We invited the relevant departments to propose names and selected this name from the suggestions because it clearly expresses being a green steel product provided by JFE Steel.
Logo design:
The logo combines the letter X with an arrow to express our intention to move forward toward carbon neutrality.
In the first half of FY2023, JFE Steel began supplying JGreeX™, a brand of green steel products that significantly reduce GHG emissions in the steelmaking process compared to conventional products. With the current technology, it is difficult to quickly supply green steel products with significantly lower or zero emissions, so the reductions associated with our technologies are allocated to steel products by applying the mass balance approach* and then supplied as green steel products. With regard to the volume of GHG emission reductions and the emission intensity of each product, we have obtained a third-party certification from Nippon Kaiji Kyokai (ClassNK), which verified 1.15 million tonnes of GHG emission reductions in FY2023.In FY2024, public-private initiatives to stimulate demand for green steel products contributed to expanded adoption of JGreeX™ across all sectors.
Reduction of GHG emissions throughout the supply chain is rapidly progressing, and with steadfast efforts, we hope to achieve a reduction of at least 30% in FY2030, while further reducing GHG emissions through the wider application of low-carbon, energy-saving, and high-efficiency technologies. At the same time, we will contribute to the decarbonization of society as a whole by expanding the supply capacity of JGreeX™ to 3 million tonnes per year.
- *Consolidate the environmental value of GHG emission reductions from the entire product manufacturing process, allocate the value to some steel products, and regard them as having low GHG emission intensity.
Overview of the steel mass balance approach
STEP 1
Calculate the emissions intensity of any steel product to apply this approach
STEP 2
Identify emissions reduction projects and determine their emissions reduction levels
STEP 3
Issue a reduction certificate based on the determined reduction level, grant the certificate, and supply steel materials.
- *This certificate and the GHG emission reductions listed in this certificate do not represent carbon credits and cannot be transferred or sold to third parties.
- *The scope of GHG emissions calculation is within the scope of Scope 1, Scope 2 and Scope 3.
- *Reduction allocations are within the scope of Scope 1 and Scope 2.
Overview of green steel JGreeX™
| Supply start | First half of FY2023 |
|---|---|
| Supply capacity | |
| Target products | |
| Certification body | Nippon Kaiji Kyokai (ClassNK) |
Overview of green steel JGreeX™ adoption
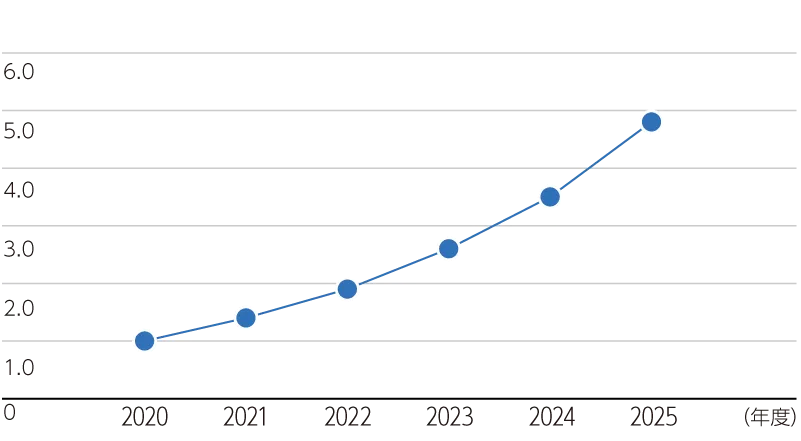
JGreeX™ Sales Performance (September 2024 Onward)
Initiatives for Achieving Carbon Neutrality by 2050
We engage in a multi-pronged approach to developing ultra-innovative technologies, such as carbon-recycling blast furnaces (CR blast furnaces), hydrogen steelmaking (direct reduction), and electric arc furnace process (high-efficiency, large-scale electric arc furnaces), to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050, as announced in the JFE Group Environmental Vision for 2050. We are particularly focused on a technology that combines a CR blast furnace and CCU, which allows us to efficiently mass-produce high-grade steel and reuse the GHG in the blast furnace. This technology is focused on achieving net zero emissions by using the remaining GHG, which cannot be fully reused to manufacture basic chemicals such as methanol.
Demonstration Tests for NEDO Project (GREINS) for Hydrogen Utilization in Iron and Steelmaking Processes
JFE Steel formed a consortium with Nippon Steel Corporation, Kobe Steel, Ltd ., and the Japan Research and Development Center for Metals and jointly commissioned the Green Innovation Fund Project (GREINS) of the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO) for Hydrogen Utilization in Iron and Steelmaking Processes, and work toward achieving carbon neutrality by 2050.
In order to further advance the development of ultra-innovative technologies to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050, JFE Steel has decided to construct all the necessary facilities for the demonstration tests for the project centrally in the East Japan Works (Chiba district) to increase the efficiency of the development effort. We will work together with consortium members to accelerate the development of ultra-innovative technologies.
Details of the Planned Demonstration Tests
- Carbon-recycling pilot blast furnace (150 m3)
Start construction in 2023, initiate demonstration tests in May 2025, complete demonstration tests by FY2026. - Direct reduction compact bench pilot furnace
Start construction in 2023, initiate demonstration tests in December 2024, complete demonstration tests by FY2026. - Pilot electric arc furnace (10 t pilot furnace)
Start construction in 2023, initiate demonstration tests in February 2025, complete demonstration tests by FY2025.
Details for each are as follows.
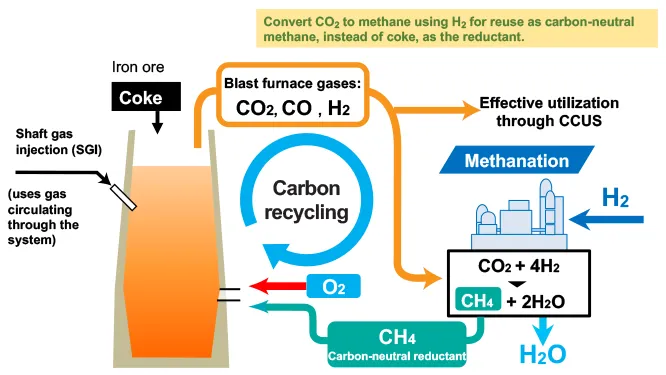
Carbon-recycling blast furnaces
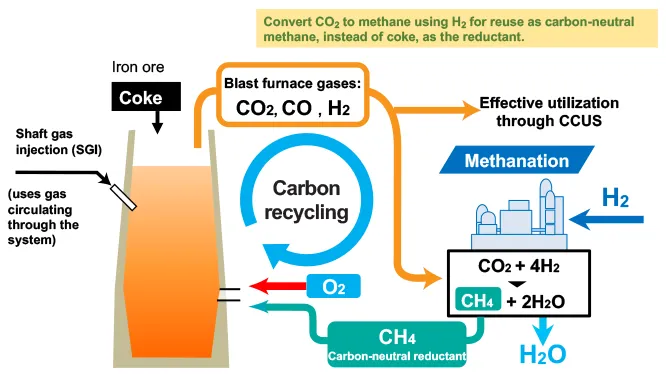
Technical Features of a CR Blast Furnace
The CR blast furnace incorporates an ultra-innovative technology that converts CO2 gas through methanation in the furnace exhaust gas into carbon neutral methane, which is then reused as reducing material in the furnace. The technology is expected to reduce CO2 emissions by 50% compared to conventional blast furnaces and to ultimately help achieve carbon neutrality by leveraging CCU/CCUS. The thermal efficiency of the process can be further enhanced by replacing the air blown into the blast furnace with pure oxygen, allowing the energy used to heat the nitrogen in the air to then be used to heat methane. In addition, the lack of nitrogen facilitates the separation of CO2, so the equipment necessary to separate CO2 for methanation can be more compact and efficient while effectively using gas at CCUS.
Overview of the Demonstration Tests
We are planning to develop a process that converts the CO2 produced in the blast furnace into methane using hydrogen, allowing the carbon to be repeatedly used in the furnace as a reducing agent and thus reducing CO2 emissions. We will verify the following during demonstration tests. We will verify the following during demonstration tests.
- Methods for blowing a large volume of methane along with oxygen into the furnace
- Applications for the heating burner that uses the circulation gas
- Methods for linking the operations of the furnace and the methanation facility that converts CO2 from the blast furnace gases to methane
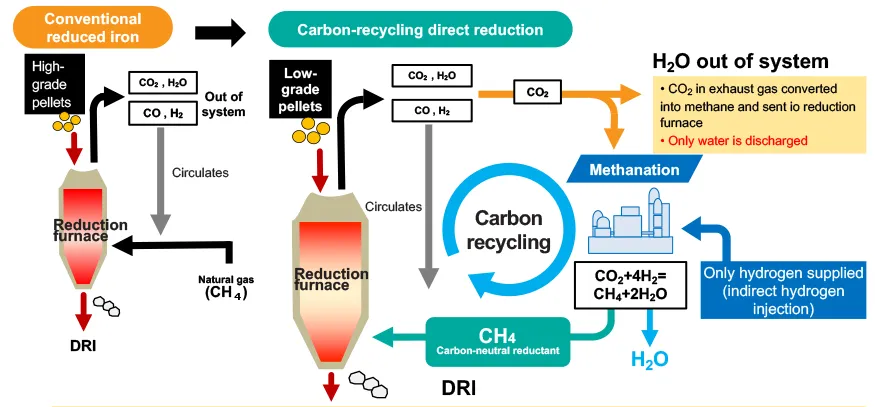
Overview of Carbon-Recycling Direct Furnaces
Development of Direct Hydrogen Reduction Technology (Carbon-Recycling Direct Reduction Process)
Hydrogen reduction ironmaking technology is another steelmaking process that the JFE Group is working on to achieve carbon neutrality. With this technology, the natural gas currently used in direct reduction ironmaking is replaced by 100% hydrogen to eliminate CO2 emissions when iron ore is reduced.
Technology for Processing Raw Materials
Currently, the only raw material that can be used for direct reduction ironmaking is high-grade iron ore. Its production volume, however, is limited, and we expect it will become even more difficult to obtain in the future if direct reduction ironmaking were to expand worldwide.
To address this, JFE and one of its iron ore suppliers, BHP, are collaborating in the development of a new raw material processing technology for low- and medium-grade ores, which are currently used as raw materials for blast furnaces due to their large production volume. We are hoping that this new technology will allow us to use low- and medium-grade ores as raw materials for direct reduction ironmaking, thus expanding the raw material sourcing for direct reduction ironmaking.
Technology for Pre-Heating Raw Materials, Technology for Heating Hydrogen Gas
One challenge of hydrogen reduction is that the reduction of iron ore by hydrogen is an endothermic reaction, which means that heat must be applied externally for the reaction to proceed. A sufficient reduction reaction may not take place if there is not enough heat. Thus, technologies for heating raw materials and hydrogen gas must be developed.
Overview of the Demonstration Tests
We are developing a process to convert the CO2 produced in the direct-reduction furnace into methane using hydrogen, allowing the carbon to be repeatedly used in the furnace as the reducing agent and thus reducing CO2 emissions. We will verify the following during demonstration tests.
- Optimal methods for recycling CO2 through methanation
- Methods for using low-grade ores
Carbon-Recycling Direct Reduction Process
CCUS Initiatives
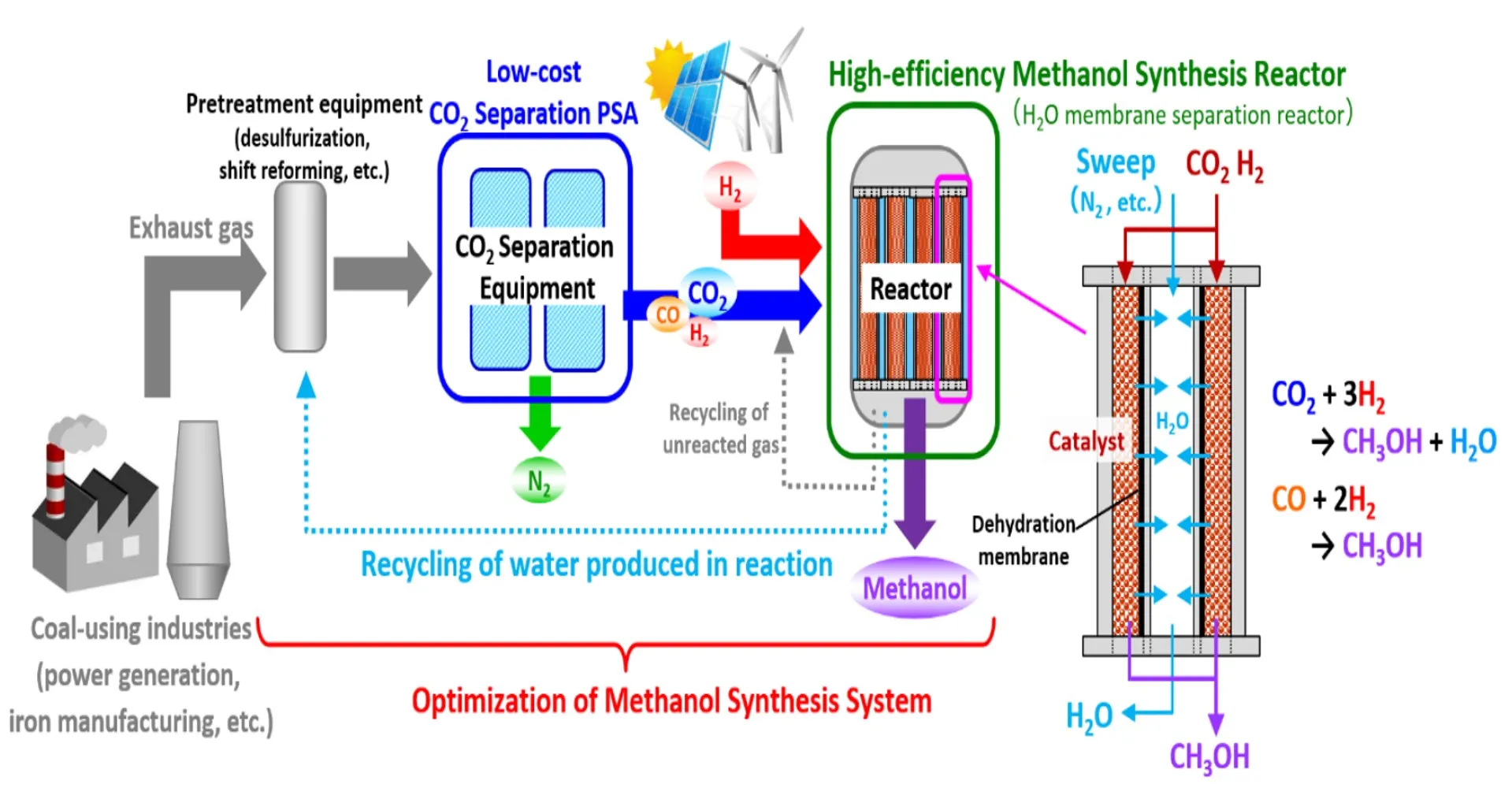
Development of an Optimal System for Methanol Synthesis Using CO2
JFE Steel is working on the Optimum System for Methanol Synthesis Using CO2, an R&D project, in collaboration with the Research Institute of Innovative Technology for the Earth (RITE) (see figure). On-site construction of a test facility commenced in FY2022 in the Fukuyama district of the West Japan Works, with operations scheduled to start in FY2023 and integrated practical application tests to be completed by the end of FY2025. The project focuses on establishing an optimal overall methanol synthetic system, mainly by developing technologies for low-cost CO2 separation and high-efficiency methanol synthesis. The ultimate goal is to combine this newly established system with carbon-recycling blast furnaces and other ironmaking processes to achieve large-scale CCU process.
Methanol Synthesis Flow Using CO2
Innovative CO2 Sequestration Technology through Quick, Large-Quantity Carbonation of Steel Slag
JFE Steel is also collaborating with Ehime University to promote the NEDO project: Innovative CO2 Sequestration Technology through Quick, Large-quantity Carbonation of Steel Slag. We have already confirmed the process principle, constructed facilities for demonstration testing at the Chiba District of the East Japan Works, and commenced tests in FY2025. Through this research and development, we will sequester the CO2 generated from ironmaking processes, such as carbon-recycling blast furnaces, and from nearby thermal power plants in slag, while at the same time verifying technologies for recovering sensible heat from high-temperature slag and converting the steel slag to roadbed materials and other products.
Quick, Large-Quantity Carbonation Flow of Steel Slag

Studies Toward Realizing CCS
In its public solicitation for FY2024, concerning Engineering Design Work for Advanced CCS Projects, the Japan Organization for Metals and Energy Security (JOGMEC) selected the Offshore Sarawak CCS Project (for the Kurashiki District of the West Japan Works) and the Northern Offshore of Peninsular Malaysia CCS Project (for the Chiba District of the East Japan Works), in which JFE Steel participates, and we are promoting studies aimed at realizing CCS. In addition, we are conducting our own study at the Fukuyama District of the West Japan Works. In FY2024, we examined optimal facility configurations and costs for each advanced CCS project, and JFE Steel conducted feasibility studies on CO2 separation and capture, liquefaction, temporary storage, and shipping facilities (Chiba District: separation and capture only). Going forward, we will advance studies for project implementation at the EPC (Engineering, Procurement, and Construction) phase, on the assumption that government support will be secured.
Overview of CCS Projects under Consideration at Each District
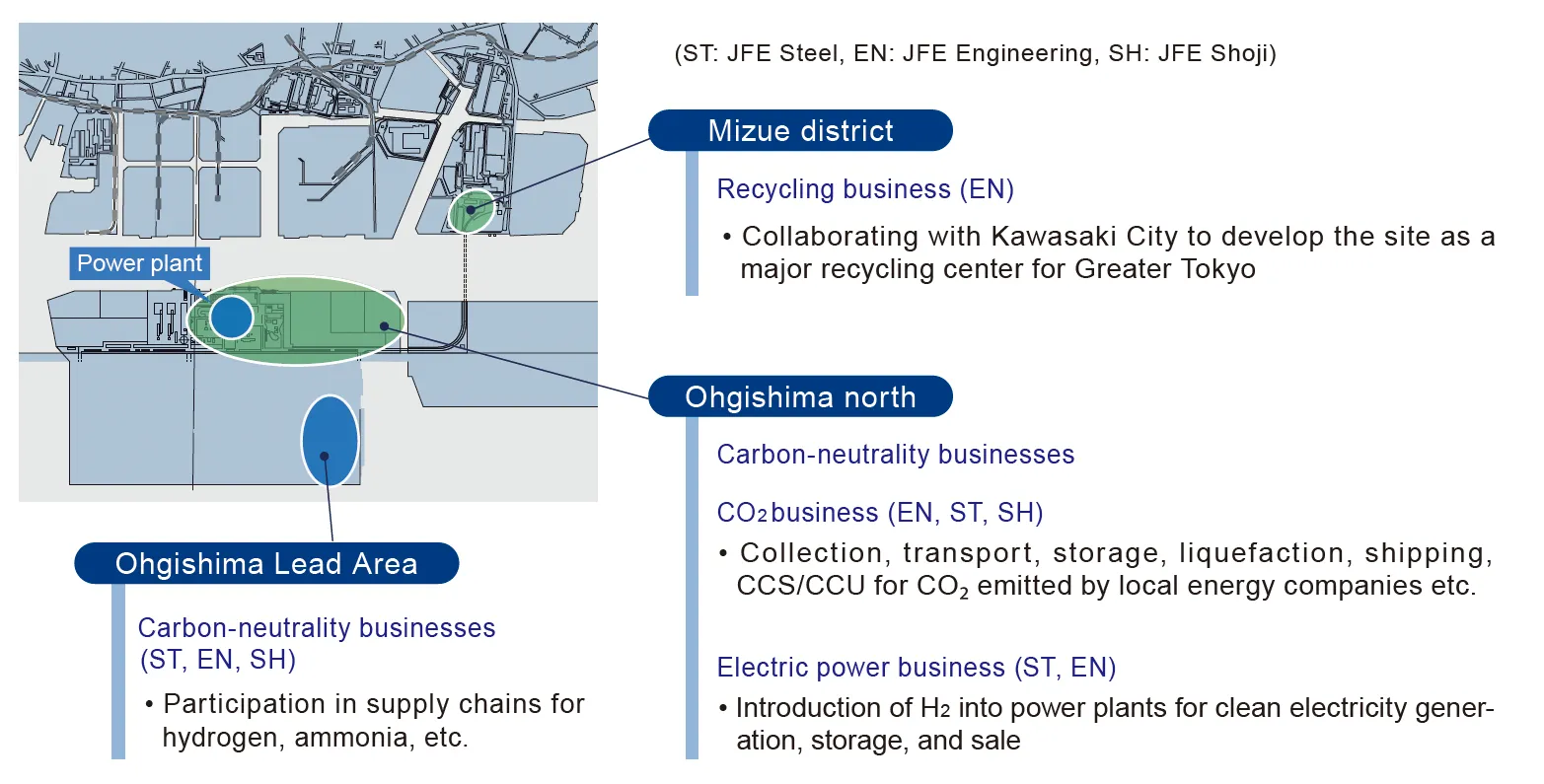
- JFE Group Environmental Management Strategy, Presentation Material, P.25
- JFE Steel Carbon Neutrality Strategy Briefing Presentation Material P.19
Initiatives for Inter-Company Collaboration at the Mizushima Complex
ENEOS Corporation and JFE Steel are advancing the materialization of joint studies on the utilization of CO2-free hydrogen at the Mizushima Complex (Kurashiki City, Okayama Prefecture) as a hydrogen procurement initiative.
In addition, JFE Steel Corporation, Mitsubishi Gas Chemical Company, Inc. (Mitsubishi Gas Chemical), and Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation (Mitsubishi Chemical) have signed a memorandum of understanding concerning a demonstration project at the Mizushima Complex (Kurashiki City, Okayama Prefecture). A new initiative within the Mizushima Complex promotes collaboration among Hard-to-Abate industries (industries where GHG emissions are difficult to reduce). By utilizing CO2 contained in byproduct gases from steel manufacturing processes to produce valuable chemicals, the project provides a model for collaborative CO2 utilization, with the aim of launching the demonstration in FY2026. Looking ahead, the initiative intends to develop into a conceptual framework for carbon recycling through the collaboration of the steel and chemical industries. This approach is expected to reduce GHG emissions compared to traditional fossil resource-based methods for chemical production.
Inter-Company Collaboration at the Mizushima Complex
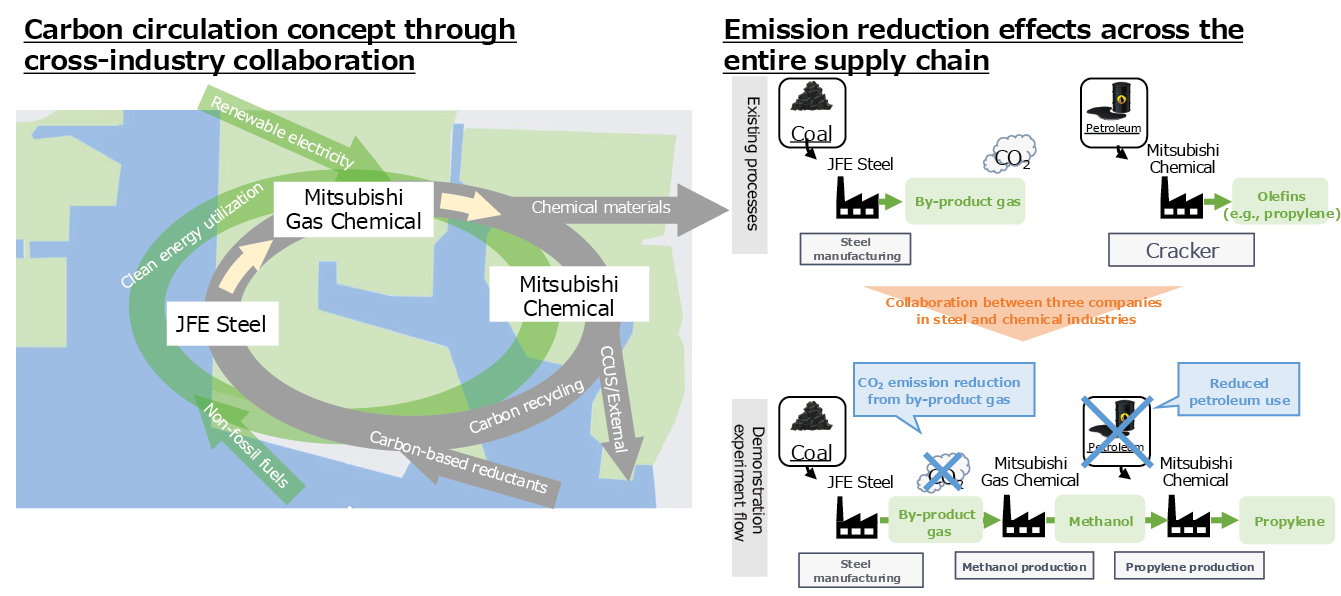
List of Related Initiatives
Initiatives for Greater Contribution to Reducing GHG in Society as a Whole
The JFE Group is promoting a variety of GHG reducing initiatives, such as offshore wind power generation projects and renewable energy-related fields, with a focus on the engineering business. In addition, in fields where demand is growing for eco-products such as electrical steel sheets and ultra-high-tensile steel sheets, we are collaborating with Group companies and others to maximize overall effectiveness.
Initiatives in the Engineering Business Contributing to GHG Reduction
Demand is expected to rise for power generation plants using renewable energy sources that do not emit carbon. Through the engineering business, the JFE Group is handling the design, procurement, construction, and operation of renewable energy generation plants, including biomass, geothermal, solar, and onshore wind power. We are also working to increase the amount of power generated at waste treatment facilities in order to promote recycling and the effective use of resources.
Furthermore, we are actively engaged in the retailing of electricity, which uses these renewable energies as the main power source, supporting the establishment and operation of new regional electricity companies that focus on local production and consumption of energy using renewable sources, and in expanding the Multisite Energy Total Service (JFE-METS), which optimizes energy use for multiple sites within the same corporate group through centralized management.
As new initiatives for carbon neutrality, we are developing a technology to safely and efficiently transport large amounts of hydrogen, ammonia, and CO2, and working on demonstrating a process that separates and collects CO2 for reuse from the exhaust gas of waste treatment facilities.
New initiatives for material recycling include bottle-to-bottle, an effort for recycling collected PET bottles for use as raw material for bottles; recycling waste plastics by directing unsorted post-use plastics to either material recycling or chemical recycling, depending on their properties; and recycling solar panels that are discarded due to age-related deterioration.
The following key initiatives contributed to reduced GHG.
Large-Scale Biomass Power Generation
Construction work for the Tahara Biomass Power Plant, one of the largest woody biomass combustion power plants in Japan, with an output of 112,000 kW
Tahara Biomass Power LLC, a joint venture between JFE Engineering Corporation, Chubu Electric Power Co., Inc., Toho Gas Co., Ltd. , and Tokyo Century Corporation, has started construction work on the Tahara Biomass Power Plant. The plant, to be constructed in Tahara, Aichi Prefecture, is one of the largest woody biomass power plants in Japan, with an output of 112,000 kW, and is scheduled to start operations in September 2025.
Food Waste Recycling Power Generation
Completion of Hokkaido’s largest food biogas power plant —Contributing to Sapporo city’s zero carbon goals through local “double recycling loop”
SAPPORO BIO FOOD RECYCLING CORPORATION, a subsidiary of J&T Recycling Corporation, of the JFE Engineering Group, constructed a new plant in Sapporo to update and expand the capacity of its food recycling power generation plant. The new plant accepts up to 100 tonnes of food waste per day and generates electricity using methane gas produced by microbial fermentation, with an output of 1,980 kW and an annual expected power generation of approximately 16,420 MWh. The electricity generated is sold through Urban Energy Corporation, a power retailing subsidiary of JFE Engineering, to promote local production and consumption of renewable energy. Furthermore, all fermentation residues generated during the treatment process are converted into fertilizer. These efforts are helping to realize a local production and consumption-based “double recycling loop” that converts food waste into clean electricity and fertilizer.
Multisite Energy Total Service (JFE-METS)
The House Foods Group has agreed to adopt the Multisite Energy Total Service at 18 sites across 8 group companies, driving CO2 reduction.
JFE Engineering has signed a basic agreement with House Foods Group Inc. to provide JFE-METS. JFE Engineering has signed a basic agreement with House Foods Group Inc. to provide JFE-METS. We will install a gas cogeneration system at the House Foods Shizuoka Plant and use JFE-METS to supply surplus electricity from the system and electricity provisioned by the JFE Group to 18 sites across 8 companies in the House Foods Group nationwide. The service is expected to reduce CO2 emissions by approximately 16.3% and energy consumption by approximately 21.5% (compared to FY2022) at these sites. Operations commenced in April 2024.
CCUS
Contract received for the construction of CO2 liquefaction, storage and loading/unloading facilities, a large-scale, long-distance, lower cost transportation system for liquid CO2 to realize a CCUS society.
JFE Engineering has received an order from Japan CCS Co., Ltd. to construct its CO2 liquefaction, storage, and loading/unloading facilities (EPC project). The EPC project is for constructing part of the facilities to be used in the NEDO project: Research, Development, and Demonstration of CCUS Technology / Large-scale CCUS demonstration testing at Tomakomai / Demonstration testing on CO2 Transportation. We will be involved in the design and construction of onshore facilities capable of liquefying and storing 10 kilotonnes per year of CO2 separated and recovered from coal combustion gas supplied by the Maizuru plant of The Kansai Electric Power Co., Inc.
PET Bottle Recycling (Bottle-to-Bottle)
Kyoei J&T Recycling Corporation ’s West Japan PET Bottle MR Center to start full commercial operation.
Kyoei J&T Recycling, a subsidiary of JFE Engineering, after starting the operations of the flake manufacturing plant in October 2021, has completed construction of the pellet production line in April 2022 and commenced full-scale commercial operations at the PET bottle recycling raw material manufacturing plant (West Japan PET Bottle MR center) in Tsu, Mie Prefecture. With an annual processing capacity of 60 kilotonnes (approximately 10 million bottles per day), the plant can recycle approximately 10% of the total number of PET bottles shipped nationwide.
By producing flakes and pellets from used PET bottles and supplying them to bottle manufacturers, we contribute to the production of plastic bottles using 100% recycled materials, which generates 63% less CO2 than the production of crude oil-derived pellets.
Metrics and Targets (Plans and Results for Contribution to GHG Reduction in the Engineering Business)
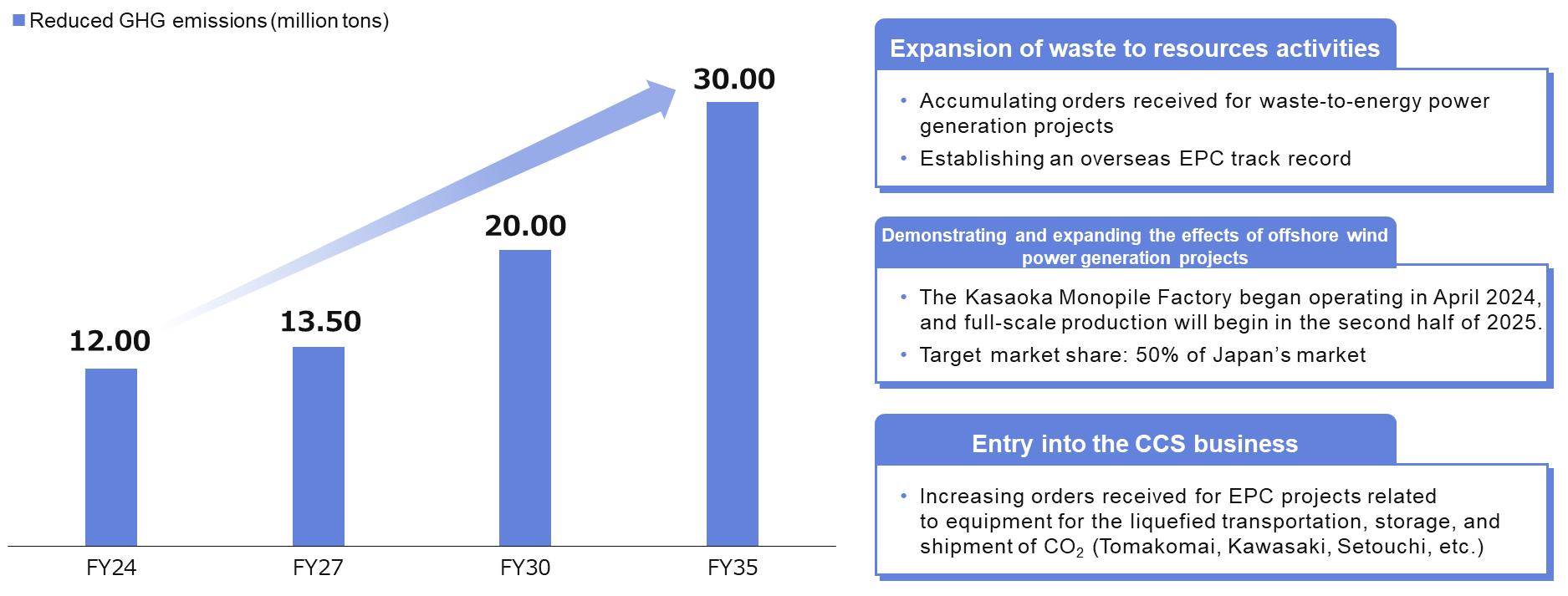
JFE Engineering contributes to GHG emissions reductions in society as a whole through its business operations, such as expanding renewable energy generation and constructing and operating plastic and food recycling plants. In FY2024, the Company contributed to reducing 12 million tonnes of GHG emissions (a 4% increase compared to FY2023) across society. JFE Engineering will further expand its business and contribute to GHG emissions reductions of 13.5 million tonnes in FY2027, 20 million tonnes in FY2030, and 30 million tonnes in FY2035.
With regard to JFE Engineering’s CO2 emissions, we set a KPI of reducing CO2 emissions at our plants and offices by 40% in FY2024 compared to FY2013. Since FY2021, we have introduced on-site solar power PPAs and zero-emission electricity plans at the Yokohama head office and low-emission electricity at the Tsu Works. We consequently achieved a 63% reduction in FY2024 compared to FY2013. At the same time, we are promoting energy-saving activities at our plants and offices. We will continue to steadfastly conduct business in ways that are environmentally sound, including expanding the use of renewable energy.
Engineering Business GHG Reduction Contribution Plan
- *1 Data cover:JFE Engineering
- *2 Data cover: JFE Engineering and Standardkessel Baumgarte GmbH (SBG), a German subsidiary of JFE Engineering Corporation
- *3 Data cover:J&T Recycling Corporation and JFE Urban Recycle Corporation
- *4 Others:Digestion gas, geothermal, solar, wind, waste heat recovery, fuel conversion, energy service, and logistics products
JFE Engineering’s Equivalent Contribution to CO2 Reduction (FY2024)
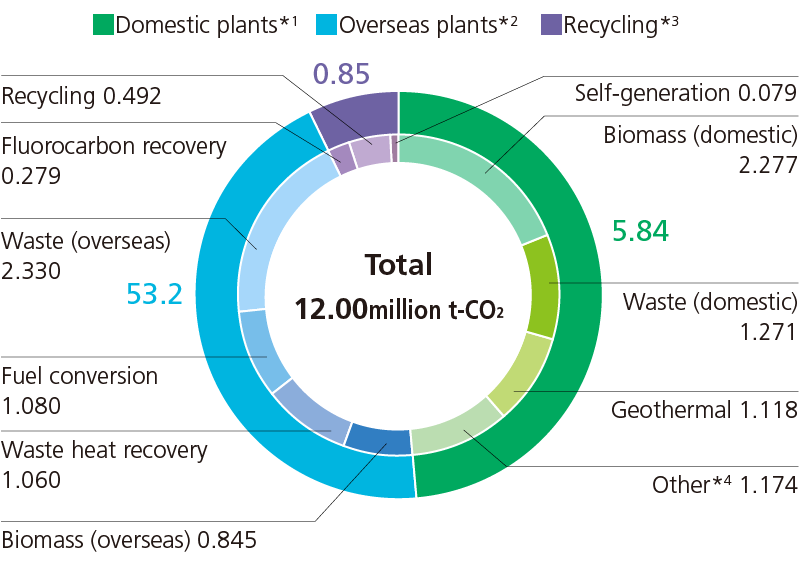
For quantitative data for the JFE Engineering Group’s CO2 emissions, please refer to:
EN JFE Engineering’s Commitment through Its Business
Under its corporate purpose to “Create, Care, Connect The Foundations of Life — Just For the Earth,” JFE Engineering is seeking to expand its contributions to GHG reductions, focusing on the key fields of waste to resource*1 and carbon neutrality*2. As part of our climate change initiatives, the following are some examples of carbon neutral business activities.
- *1Primarily promotes waste-to-energy power generation and recycling (food, plastics), etc.
- *2Primarily promotes renewable energy power generation and hydrogen/ammonia and CCUS, etc.
EN The Energy Forest Project (Demonstration Project for Creating Stable and Effective Supply Systems of Woody Biomass Fuel)
The town of Yuni, located in Hokkaido, and JFE Engineering are jointly carrying out an Energy Forest Project, which will continue until the end of FY2028. This project, named the JFE Forest NEXTGATE Project and drawn up by JFE Engineering, was selected by NEDO (New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization), a national research and development agency, for inclusion in the FY2023 Demonstration Project on Development of New Fuel Sources Such as Fast-growing Trees on August 3, 2023. JFE Engineering is specifically engaged in pioneering research for creating a large “energy forest,” involving the silviculture of trees that grow well and fast in a subarctic climate (clean larch and Sakhalin willow) on land owned by the town of Yuni.
The town of Yuni is seeking to nullify CO2 emissions by 2050 under the Yuni Zero Carbon City declaration. JFE Engineering is working with the town of Yuni to contribute to carbon neutrality and prevent global warming, thereby fulfilling its corporate purpose, “Foundation of Life—Just For the Earth.”
EN Aqua Connect Namie Corporation Launches Hydroelectric Power Generation Business at the Ukedogawa Hydro Power Plant
Aqua Connect Namie Corporation, a company established through the joint investment of JFE Engineering with The Tokyo Electric Generation Co., Ltd. and the Ukedogawa Land Improvement District (the town of Namie in the district of Futaba, Fukushima Prefecture), launched its power generation business at the Ukedogawa Hydro Power Station in May 2024, becoming the first hydrogen power generation business for JFE Engineering. The business was established to take advantage of the agricultural water supplied from the Ogaki Dam to the ward of Odaka in the city of Minamisoma and to the towns of Namie and Futaba in the district of Futaba.
The Ukedogawa Hydro Power Station, with its waterwheel and power generator located at the foot of the Ogaki Dam, generates power by using the energy produced from the difference in water levels. All the power generated at this station is sold through the Feed-in Tariff System. Aqua Connect Namie Corporation is committed to operating the station safely and stably while supporting farmers in the Ukedogawa area. The company will thereby contribute to carbon neutrality and a sustainable future.
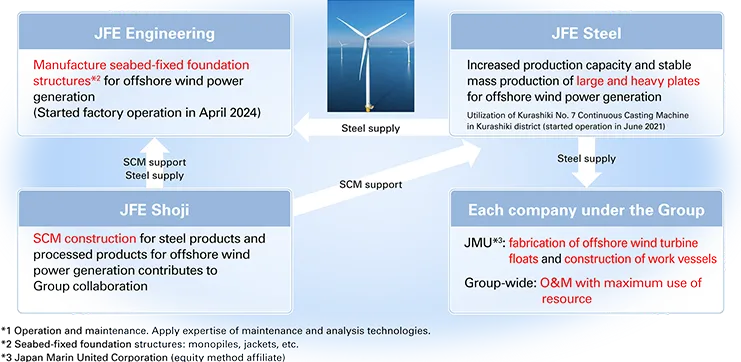
Offshore Wind Power Business Initiative
The JFE Group has positioned its offshore wind power business as a key initiative. With engineering as the core business, the Group is leveraging its diverse businesses to create synergies and deliver new added value. Specifically, we are commercializing the manufacture of offshore wind power generation foundations (monopiles, jackets) as well as O&M* services, establishing an integrated supply chain covering materials, foundation manufacturing, and O&M. We will continue to take advantage of the comprehensive strengths of the Group to commercialize this business, thereby significantly contributing to the JFE Group’s efforts to achieve carbon neutrality and make progress toward the government’s goal of realizing carbon neutrality.
- *Operation and maintenance. Applies repair and diagnostic technologies.
Commercialization of Offshore Wind Power Business

Technologies of Group Companies
| Category | Company | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Foundation structures | JFE Engineering | Seabed foundations (monopiles, jackets, etc.) |
| Japan Marine United | Floating foundations (semi-submersible) | |
| JFE Steel | High-quality, large and heavy steel plates, high-strength steel (reduced using HBL series steel plates) | |
| JFE Shoji | Manufacture and sale of scour protection materials for seabed-fixed foundations | |
| Construction | Japan Marine United | SEP vessels (self-elevating platform) |
| JFE Engineering | JFE-RAPID (cable laying method) | |
| Battery systems for power storage | ||
| GECOSS | Stands for large steel structures | |
| JFE Steel | Natural stone substitute materials (use of steel slags) | |
| O&M (operation and maintenance) | JFE Engineering | Technologies for remote monitoring and operation |
| JFE Advantech | Vibration measurement equipment and systems, sea monitoring tools (water quality, sea conditions) | |
| Japan Marine United | Offshore support vessels (work vessels) | |
| JFE Plant Engineering | Wind turbine maintenance (diagnosis and repair) | |
| JFE Technos | Technologies and expertise in planning, constructing, and maintaining onshore turbines | |
| JFE Techno-Research | Equipment evaluation and analysis for corrosion, fatigue, vibration, etc., diagnosis of remaining service life, strength and durability testing and evaluation techniques for large structures | |
| Supply chain | JFE Shoji | Contribution to optimizing offshore wind power generation project execution |
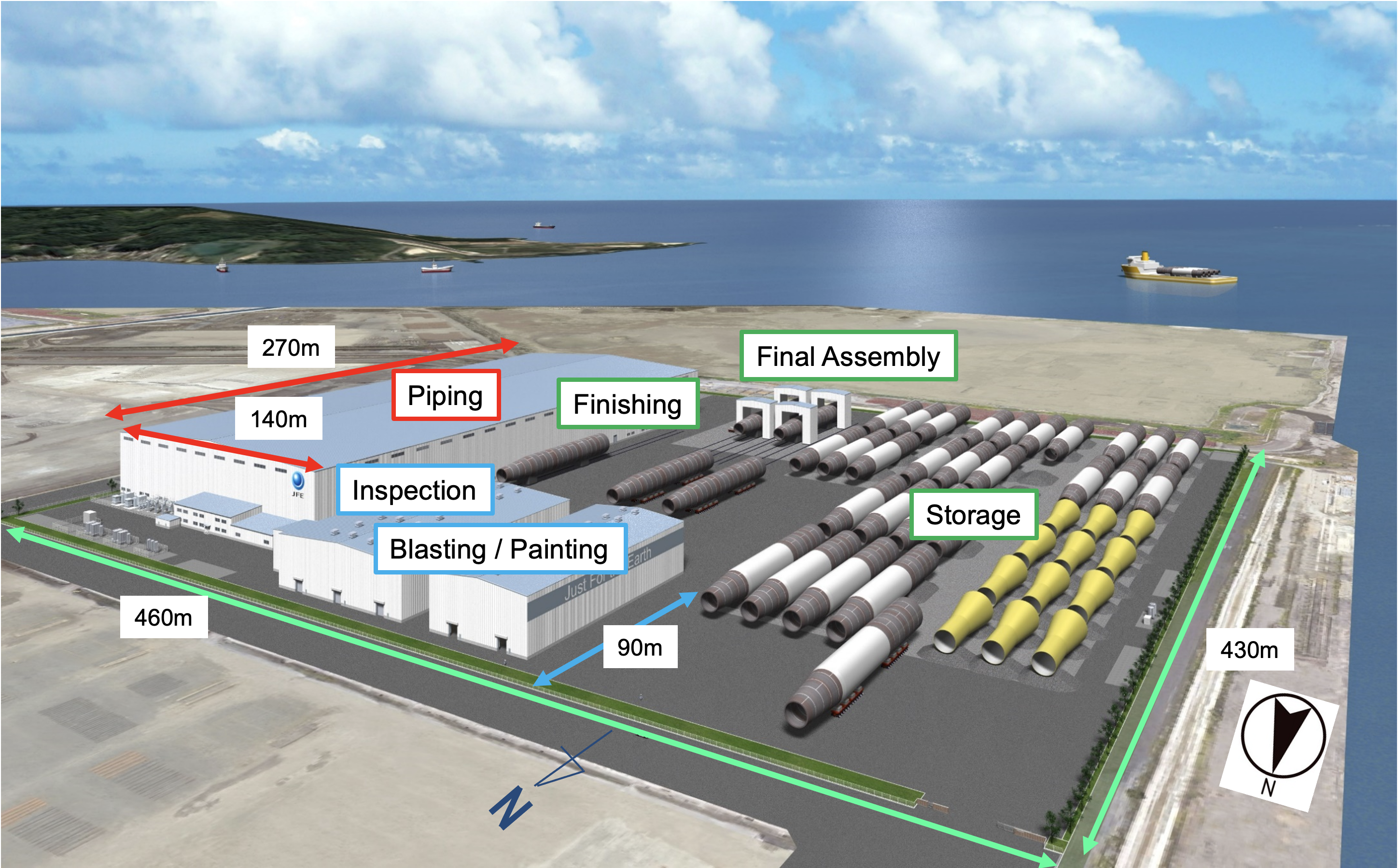
EN Operation of Monopile Manufacturing Base
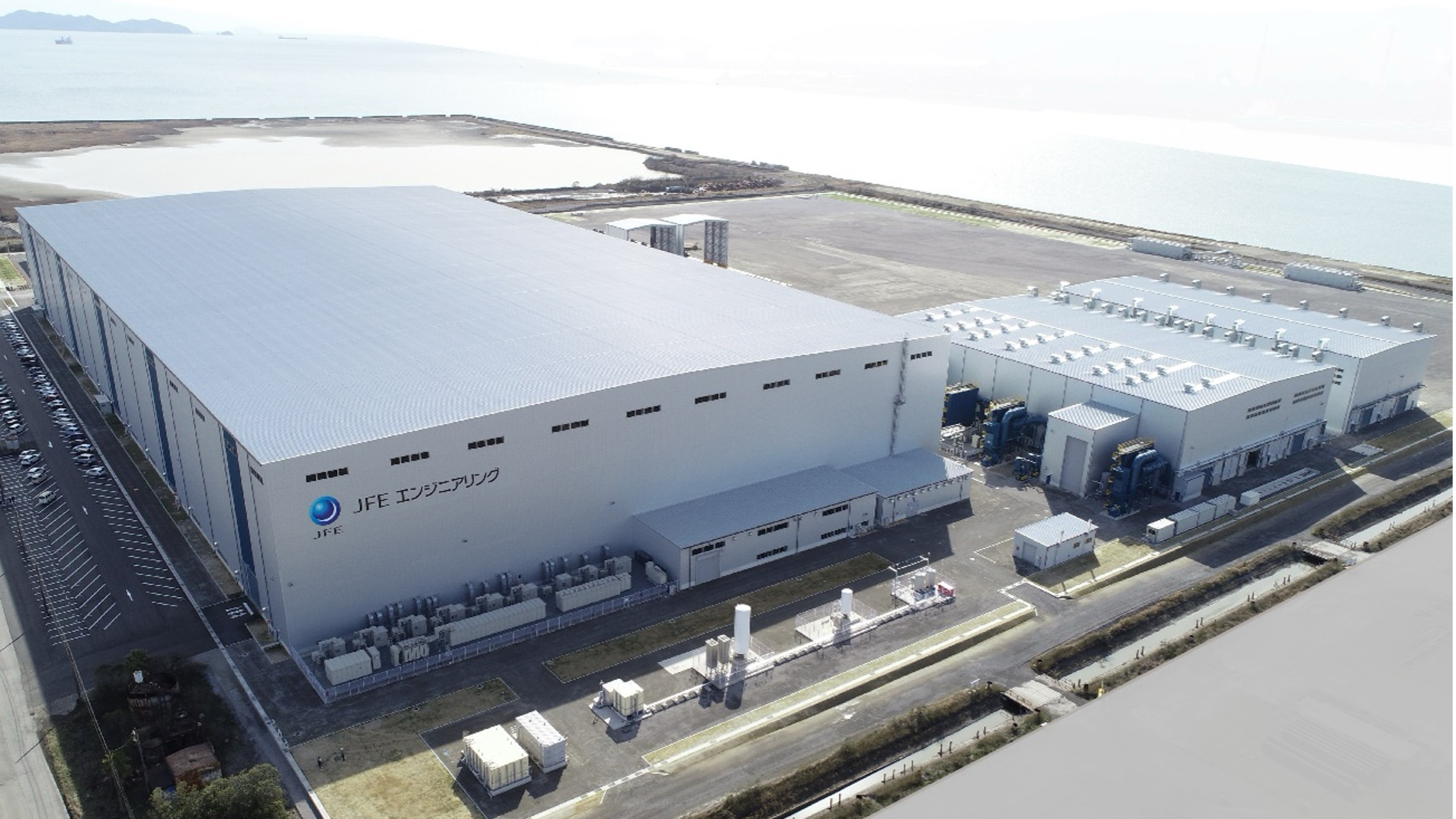
JFE Engineering has completed construction of the monopile manufacturing plant in Kasaoka, Okayama Prefecture and operations commenced in April 2024. Monopiles are the foundational structural components for offshore wind power generation and are extremely large steel structures, approximately 10 m in diameter, 100 mm thick, and 100 m long. The plant is the only one in Japan capable of manufacturing such large structures. It was designed for production efficiency, implementing manufacturing processes based on the experiences gained in the manufacturing of large steel structures at the Tsu Works. The plant site includes extensive grounds and a quay from which manufactured structures can be directly shipped, as well as state-of-the-art equipment such as large-diameter bending machines and welding machines for extra-thick plates. When operating at full capacity, the plant is capable of manufacturing up to 100,000 tonnes annually, and it is expected to significantly contribute to the establishment of a domestic supply chain in the offshore wind power generation business and to the realization of carbon neutrality.
Overview of the Kasaoka Monopile Factory
| Construction site | Kasaoka City, Okayama Prefecture (JFE Steel West Japan Works Fukuyama area) | Investment amount | Approximately 40 billion yen* (plant building, mechanical equipment, quay reinforcement)
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction start | Site area | Approximately 20 ha (includes storage area) | |
| Operation start | Production capacity | Approximately 80,000-100,000 tonnes per year (Approx. 50 sets) | |
| Length of shipping quay | 200 m (quay total length: 400 m) | Quay depth | -11 m |


EN Offshore Wind Power Generation, a Foray into O&M through a Remote Integrated Management System
For more than 25 years since 1996, JFE Engineering has been involved in EPC for onshore wind-power stations (131 generators at 25 sites) in addition to equipment supply and associated maintenance services. JFE Engineering will fully leverage its deep, extensive expertise in onshore wind power generation as well as technologies owned by other JFE Group companies to grow and advance its O&M services for offshore wind power plants.
In October 2023, JFE Engineering launched a 20-year O&M contract for offshore wind power facilities (three generators with the max output of 7,495 kW) off the coast of Nyuzen in Toyama Prefecture. These facilities were built under Japan’s first offshore wind energy project in a general sea area. JFE Engineering adopted a remote integrated management system for this project, the first of its kind in the nation for an offshore wind power project. The use of the system is allowing the company to provide systematic and preventive maintenance services and facilitate sensor management and data analysis for failure detection and diagnosis.
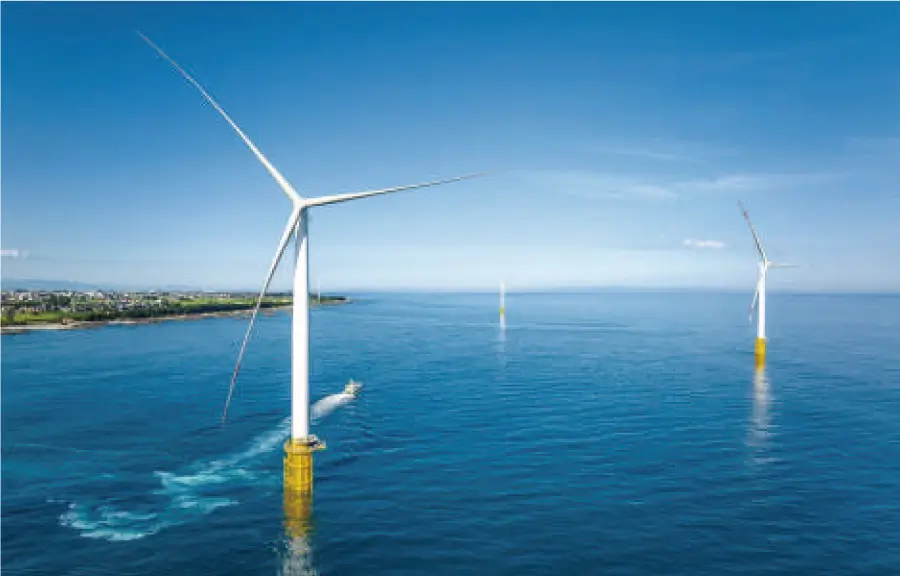

EN Demonstration Research on Cost Reduction for Floating Offshore Wind Power Generation
JFE Engineering through a consortium in which it participates, has been selected for the Southern Akita Floating Offshore Wind Demonstration Project Aimed at Overseas Expansion via Cost Reductions, proposed under under the Green Innovation Fund* Project/Cost Reductions for Offshore Wind Power Generation/Floating Offshore Wind Power Demonstration Project (Phase 2), publicly solicited by the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO).
The consortium consists of MOWD as the leading company; Akita Floating Offshore Wind Corporation, a special purpose company in which Marubeni has invested; Tohoku Electric Power Co., Inc.; Japan Marine United Corporation; TOA CORPORATION; TOKYO SEIKO ROPE MFG. CO., LTD.; Kanden Plant Corporation; JFE Engineering Corporation; and NAKANIHON AIR Co., Ltd.
Offshore wind is expected to become a major power source of renewable energy due to its potential for large-scale generation capacity, cost reductions, and positive contributions to the local economy. In particular, the use of floating offshore wind is expected to grow rapidly as its power generation facilities can be installed in a wider range of sea areas, allowing for cost reductions at an early stage. NEDO’s “Cost Reductions of Offshore Wind Power Generation” project aims to establish a technology to commercialize floating offshore wind power generation at an internationally competitive cost level by fiscal year 2030 under specific conditions.
The project plans to deploy two 15 MW wind turbine on-site approximately 400 meters offshore from the southern coast of Akita Prefecture. The project period will span July 2024 to March 2031, with commercial operation scheduled to begin in autumn 2029.
JFE Engineering will pursue cost reductions for floating offshore wind power generation to both expand introduction and develop the domestic industry by establishing a domestic supply chain and human resource development toward realizing carbon neutrality.
- *A fund established by NEDO under the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry to support companies committed to ambitious goals toward achieving carbon neutrality by 2050, providing continuous support for research, development, demonstration, and social implementation for up to ten years.
Project Overview (Planned)
| Project name | Southern Akita Floating Offshore Wind Demonstration Project Aimed at Overseas Expansion via Cost Reductions |
|---|---|
| Demonstration site | Southern coast of Akita Prefecture (approx. 25 km offshore, water depth approx. 400 m) |
| Turbine output | Over 15 MW |
| Number of turbines | 2 |
| Floating type | Semi-submersible |
| Project period | July 2024-March 2031 |
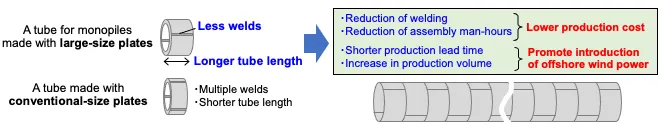
ST Manufacture and Supply of Large and Heavy Steel Plates for Offshore Wind Power Generation
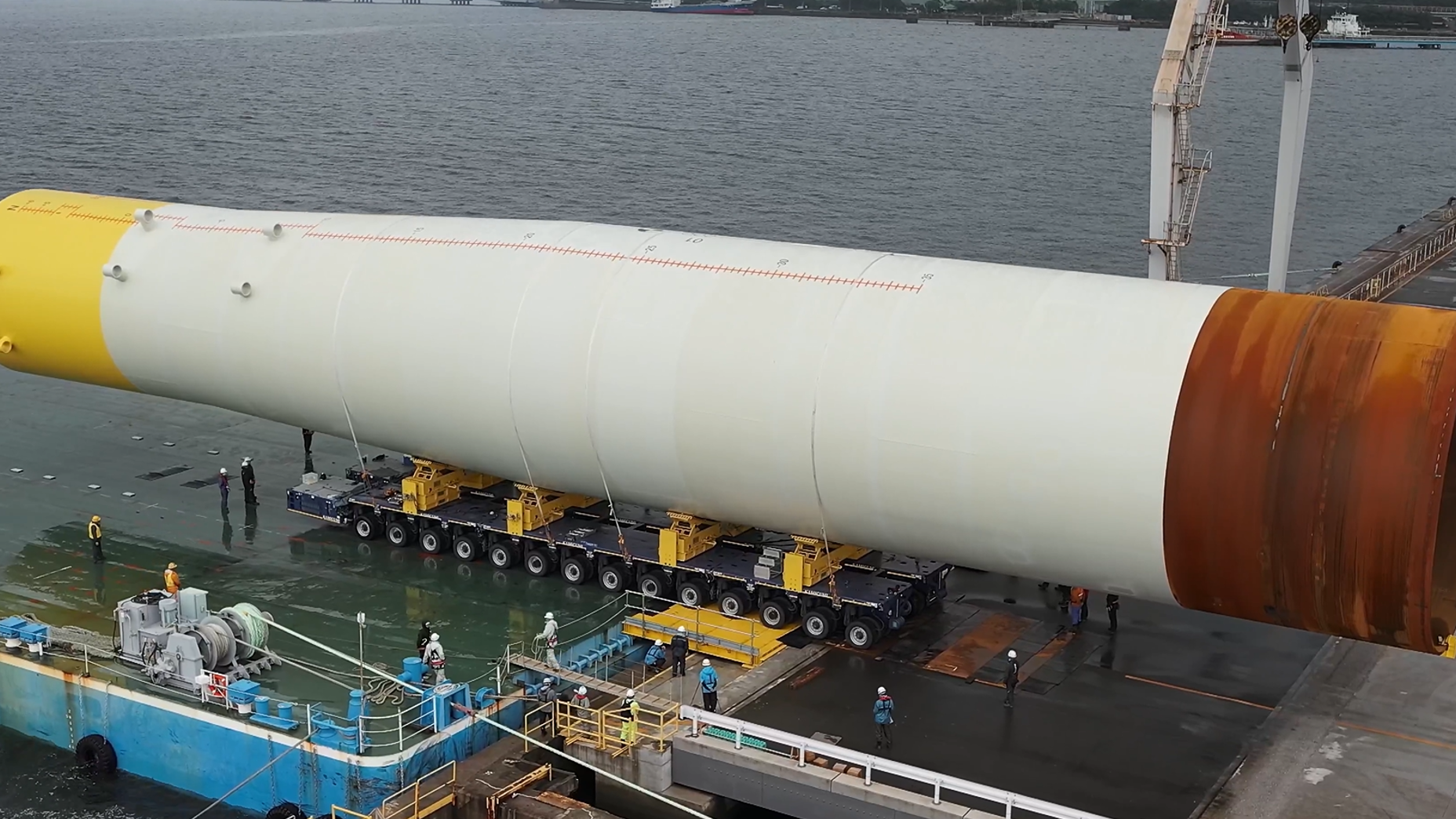
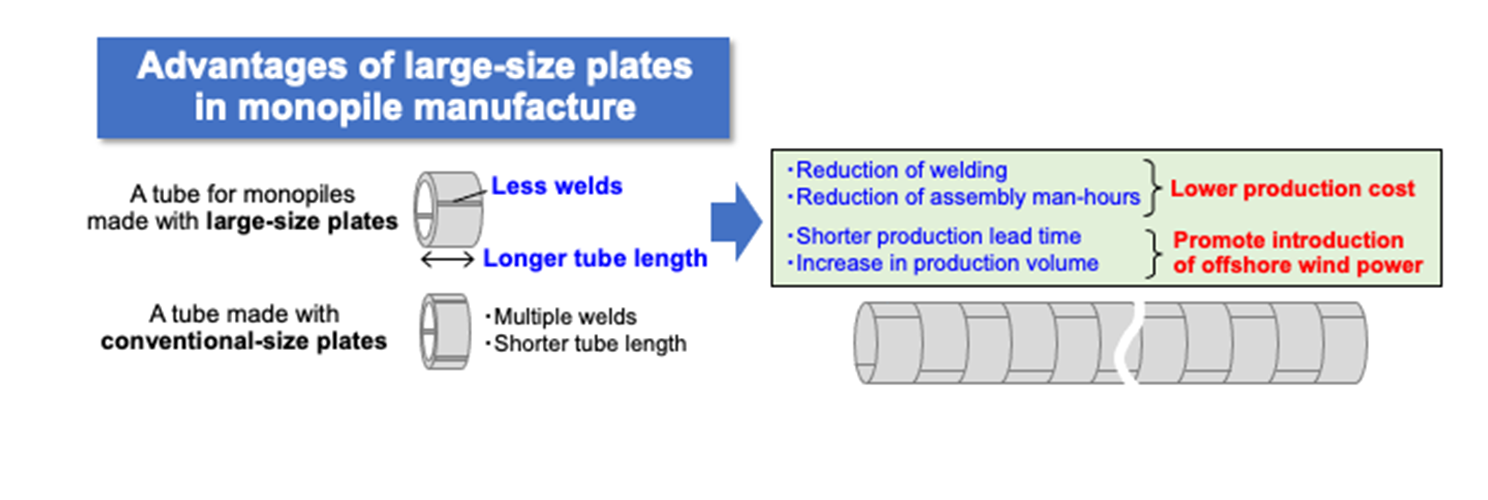
The large and heavy steel plate J-TerraPlate™, produced with the No. 7 continuous caster of the Kurashiki Plant at the JFE Steel’s West Japan Works, has been increasingly adopted for monopile foundations for offshore wind power generation.
Offshore wind turbines have recently grown in size, requiring larger monopiles and other foundational structures to support them. The monopiles are manufactured by welding ultra-thick steel plates, resulting in increased welding workloads that require monopile manufacturers to improve the efficiency of the operations. Using larger and heavier steel plates makes it possible to reduce the volume of welding operations, compared to conventional small-size plates, and also helps to raise process efficiency while lower manufacturing costs.
We have been investing in equipment at the plate mills and other facilities to manufacture and supply steel plates of up to 37 tonnes (previously limited to around 20 to 28 tonnes per plate in general), the largest in Asia and capable of supporting wind turbines in harsh offshore environments over the long term and in large quantities using the extra-large slabs produced with the state-of-the-art No. 7 continuous casting machine. As a result, we have established a production system for the growing global demand for large and heavy steel plates accompanying active offshore wind development worldwide.
Manufacturing Process of Large and Heavy Steel Plates for Offshore Wind Power Generation
Advantages of Using Large and Heavy Steel Plates for Monopiles
SH Manufacture and Sale of Scour Prevention Materials for Offshore Wind Power Generation
JFE Shoji established JFE Shoji Akita Offshore Materials, LTD. (JAOM), a joint venture with quarry operators, construction companies, and financial institutions in Akita Prefecture, in Oga City, Akita, to manufacture and sell scour prevention materials for offshore wind power generation.
When monopiles are driven into the seabed for offshore wind power generator projects, “scour” forms around the monopile due to waves and tidal currents, causing turbines to tilt. JAOM will base itself in Akita, where offshore wind power is expanding, to manufacture and stockpile scour prevention materials made from local natural stone and artificial stone* produced by JFE Steel, on a just-in-time basis within construction schedules.
Furthermore, the company will also pursue businesses through the expanded use of steel slag products and stone products for purposes such as forming fishing reefs and seaweed beds toward restoring the marine environment and mitigating global warming. JAOM hopes to contribute through this business to the development of Japan’s offshore wind power industry and the realization of carbon neutrality and a sustainable society.
- *Artificial stone manufactured by mixing steelmaking slag, a byproduct of the steelmaking process, with ground granulated blast furnace slag (a raw material for blast furnace cement) and water, then hydrating and solidifying. This artificial stone, produced by JFE Steel under the brand name Frontier Rock™, contains a high level of iron and has excellent properties for algae adhesion.
Conceptual Diagram of Scour Protection Material

SH Building a Supply Chain for the Offshore Wind Power Generation Industry
Carbon neutrality initiatives are expanding worldwide to address concerns over climate change. To achieve carbon neutrality by 2050, Japan approved the Seventh Strategic Energy Plan at a Cabinet meeting in 2025, which sets targets for FY2040: a 73% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, renewable energy accounting for 40-50% of the electricity mix, and wind power accounting for around 4.8% compared to 1.1% in FY2023.
As for offshore wind power generation, the industry is planning projects that will achieve 10 GW capacity by 2030 and 30-45 GW by 2040. Steadfast efforts are also being made to adopt a large number of internationally competitive technologies, such as the adoption of a demonstration project for a floating offshore wind power generation system under the Green Innovation Fund.
JFE Shoji is collaborating with a local enterprise that manufactures the windmill foundations in Taiwan, which is leading in the offshore wind power generation market, and have been achieving progress regarding supply chain of steel materials for foundation structures. Looking ahead, the company will capitalize on the knowledge acquired and contribute to the realization of carbon neutrality by establishing a supply chain that supports the domestic production of goods and the local economy while also meeting customer demand in the offshore wind power generation industry in Japan.
Eco-Products and Eco-Solutions Contributing to GHG Reduction
We provide a wide range of eco-products and eco-solutions for reducing GHG by efficiently using resources and optimizing energy use through environmentally sound technological innovations.
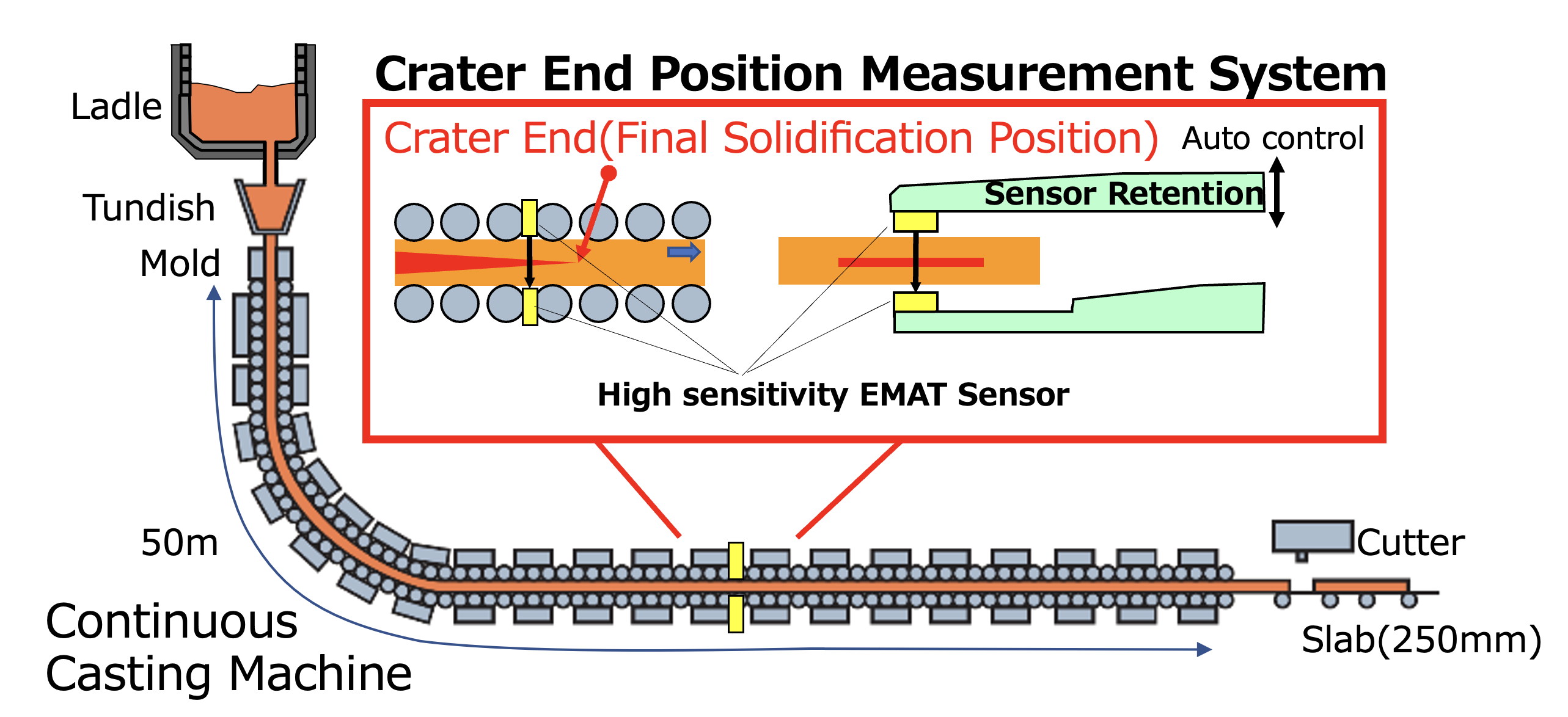
ST Automatic Measurement Device for Crater end position in Continuous Casting to Realize High-Quality Steel Plate
Our Crater end position Measurement Device for Continuous Casting, developed in-house, received the Minister of Economy, Trade and Industry Award at the 59th Machinery Promotion Award, organized by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Machine Industry (Chairman: Kazuaki Kama). The annual Machinery Promotion Award recognizes companies, universities, research institutions, and developers that are significantly advancing the progress and development of industrial machinery technology in Japan through outstanding R&D and the practical application of results, thereby further promoting technological development in the machinery industry. This marks our 13th Machinery Promotion Award and our third Minister of Economy, Trade and Industry Award.
1. Award-winning technology
Automatic Measurement Device for Crater end position in Continuous Casting to Realize a High-Quality Heavy Plate
2. Overview of development
We developed the Crater end position Measurement Device, which automatically measures the crater end position in the continuous casting process (see figure). Although the crater end position in continuous casting is an extremely important index in terms of productivity and quality, it had previously been difficult to ascertain continuously and accurately . By applying the electromagnetic ultrasonic method, which enables non-contact ultrasonic transmission and reception together with Halbach array (a special magnet arrangement) and digital signal processing, we significantly improved sensitivity, achieved non-contact ultrasonic measurement, and developed a measurement technology that combines longitudinal ultrasonic waves and transverse ultrasonic waves for the crater end position. In addition, we developed an automatic control mechanism that maintains a constant distance between the hot slab and the sensor, preventing sensor contact and damage. This made it possible to automatically measure the crater end position of continuously cast slabs with surface temperatures exceeding 900°C.
The device has already been introduced to improve operations at the steelmaking plant of the West Japan Works (Fukuyama District).
This technological development made it possible to grasp the crater end position in continuous casting and control it at the appropriate position, thereby suppressing center segregation and enabling the manufacture of steel materials with improved resistance to hydrogen-induced cracking. In addition, it allowed for the manufacture of high-grade steel plates, including steel products for pipelines used in harsh corrosive environments. Customers have adopted high-grade steel plates manufactured using this device as steel materials for natural gas development pipeline projects in Southeast Asia*. We will continue to contribute to reducing environmental impact through these high-grade steel materials.
Fig. Crater End Position Measurement System
ST Development of Steel Material for Sour Gas Transmission Line Pipe Containing High Concentrations of Hydrogen Sulfide
Steel material for natural gas transmission line pipe containing high concentrations of hydrogen sulfide, developed by JFE Steel, received the 71st (FY2024) Okochi Memorial Production Prize from the Okochi Memorial Foundation (Chairman: Hiroo Yamazaki, Professor Emeritus of The University of Tokyo). The Okochi Memorial Production Prize is awarded for achievements that significantly contribute to academic progress and industrial development by producing outstanding and original research results in the fields of production engineering and production technology. The award ceremony was held on March 25 at the Industry Club of Japan (Marunouchi, Tokyo).
1. Award-winning achievement
Development of Steel Material for Sour Gas Transmission Line Pipe Containing High Concentrations of Hydrogen Sulfide
2. Overview of development
Steel grade sour service pipe is suitable for pipelines that transport natural gas with high concentrations of hydrogen sulfide. It has recently become necessary to control and reduce the hardness of the pipe’s extreme surface to prevent sulfide stress cracking*1, which can develop in hardened micro layers at the pipe internal surface when transporting high H2S “sour” gas*2. In addition, complete inspection and full quantity assurance of extreme surface hardness are now required for the thick steel plates used to manufacture the pipes, a requirement that has been formalized in IOGP specifications*3. Finally, to improve material safety and conserve resources, development of new center segregation control technologies is required to avoid fracture accidents caused by hydrogen-induced cracking (HIC) originating from center-segregation in the steel plate.
In response, we have developed a surface hardness control technology for both high strength and low surface hardness with a low-alloy design through advanced cooling control and a surface hardness full-surface inspection technology that enables full-quantity quality assurance by a unique non-destructive inspection. These advances strengthen resistance to sulfide stress cracking under high hydrogen sulfide environments and contribute to stable manufacturing, including quality assurance in mass production. We also worked to develop a center segregation control technology by optimizing the light reduction position using a new sensor, called a crater end meter, during slab casting, thereby achieving stabilizing steel quality by improving resistance to hydrogen-induced cracking*4.
Going forward, we will continue to improve safety, economy, and reliability by providing high-performance, high-grade steel material for sour gas transmission line pipe containing high concentrations of hydrogen sulfide, while also protecting the global environment and responding to the diverse needs of our customers.
- *1Phenomenon in which hydrogen flows into steel in a sour gas environment, deteriorating the steel and creating cracks under stress. Higher hydrogen sulfide concentrations and stress increase the likelihood of cracks.
- *2Natural gas containing hydrogen sulfide.
- *3International Association of Oil & Gas Producers (an international gas producers association led by oil majors)
- *4Phenomenon in which hydrogen that has entered steel accumulates at inclusions such as MnS, and cracks occur; cracks propagate in hardened areas due to center segregation.
ST Development of Blast Furnace Automatic Operation Technology Contributing to Decarbonization of the Steel Industry
JFE Steel achievements in developing blast furnace automatic operation technology for advancing the decarbonization of the steel industry have been recognized with the Science and Technology Award (Development Category) of the Commendation for Science and Technology by the Minister of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology in FY2025.
1. Award-winning project
Development of Blast Furnace Automatic Operation Technology Contributing to Decarbonization of the Steel Industry
2. Project overview
This award-winning project features a technology for automating blast furnace operation using a cyber-physical system (CPS). In the steel industry, high efficiency and stable operation are extremely important for reducing CO2 emissions and improving labor productivity. On the other hand, manual operation drawing upon the knowledge and experience of skilled operators has been necessary in light of the inability to directly observe or measure the internal state of the blast furnace and the significant variation in operating conditions due to fluctuations in the properties of raw materials charged into the blast furnace. We therefore constructed a digital twin based on our own model using sensor data collected from the actual process. The system uses a CPS for real-time monitoring and future prediction of equipment conditions and automatically executes optimal operating actions for controlling hot metal temperature and permeability, which are important in blast furnace operation. In this system, the physical model representing furnace reactions and heat transfer phenomena enables real-time prediction of hot metal temperature up to 12 hours into the future. We also established a permeability control method using anomaly prediction technology based on statistical methods applied to furnace pressure measurement data. This system has been put into use at blast furnace sites, leading to improved labor productivity and reduced CO2 emissions.
The technology has also received the Sawamura Award of The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan (FY2020), the Technology Award of the Society of Instrument and Control Engineer (FY2020), the Outstanding Technological Development Award of The Society of Chemical Engineers, Japan (FY2020), and the Okochi Memorial Production Award (FY2023). Going forward, we will promote the CPS for the BF process and other processes and aspire to implement the system across the entire steelmaking process to realize innovative productivity improvements and stable operation.
ST Hot Repair Technology for Coke Batteries
JFE Steel and its partner MEGATECH Corporation have received an order for the Hot Repair Engineering Service of Coke Battery from Ouro Branco/Minas Gerais Works, Gerdau S. A., which is one of our Solution Business products and technologies. This is JFE’s first opportunity to apply this technology as a Solution Business for domestic and overseas customers.
The effective repair and replacement of old coke batteries is important in the use of blast furnaces for producing steel. We have long been developing various coke battery repair technologies to extend battery life, based on our experience in operating multiple coke batteries. Gerdau’s favorable impression of the more than 200 applications of the Hot Repair of Coke Battery technology in our steelworks led to this order.
We will actively provide its technologies and expertise for improving operation under the JFE Resolus™ brand of products and technologies under its Solution Business and develop sound customer relationships for the future.
-
*
Features of Hot Repair Technology for Coke Batteries
1) Partial and selective repair of required ovens, either full rebuilding of batteries or green field projects, which require large investment.
2) JFE has developed a measurement and visualization technology for oven walls using a laser scanner that can quantitatively evaluate and visualize wall damage such as deformation and erosion to precisely identify the area to repair.
3) Large pre-casted zero-expansion blocks achieve shorter repair periods and stronger walls.
4) This technology can minimize production loss during repair work since ovens outside the repair area can continue coke production.
5) High-performance insulation material can provide a safer work environment for repair personnel.
Outline of Coke Hot Repair Technology
Overview of GERDAU
Company Name: Gerdau S.A.
Head Office: Belo Horizonte, Minas Gerais, Brazil
Chairman: Guilherme Chagas Gerdau Johanpeter
Business: Steel production, sales, and scrap collection
Established: 1901
Overview of MEGATECH
Company Name: MEGATECH Corporation
Head Office: Chiba Port Side Tower 26F, 1-35, Tonyacho, Chuo-ku, Chiba City, 260-0025, Japan
Chairman and Representative Director: Nagao Shigeru
Business: Coke oven repair, plant design, fabrication, and construction
Established: Established as Sanyo Industry Ltd., in 1971, and renamed as MEGATECH Co., Ltd in 2000

Initiatives for Achieving Carbon Neutrality in the Keihin Waterfront Areas
JFE Holdings has released OHGISHIMA 2025 , the JFE Group’s conceptual plan for the reuse of land currently occupied by JFE Steel’s East Japan Works (Keihin District), following the suspension of blast furnace operations and other upstream processes there, and in accordance with Kawasaki City’s land use policy. The concept is to create fields of innovation and enterprise that will address the complex challenges involved in the pursuit of carbon neutrality. Through implementation of its OHGISHIMA 2050 plan, the JFE Group aims to convert the land for use on projects that will offer significant public benefit and help address some of the key challenges Japan faces. By attracting new industries and creating jobs that will benefit the country over the next 100 years, the JFE Group hopes to contribute to the sustainable development of local communities and society as a whole.

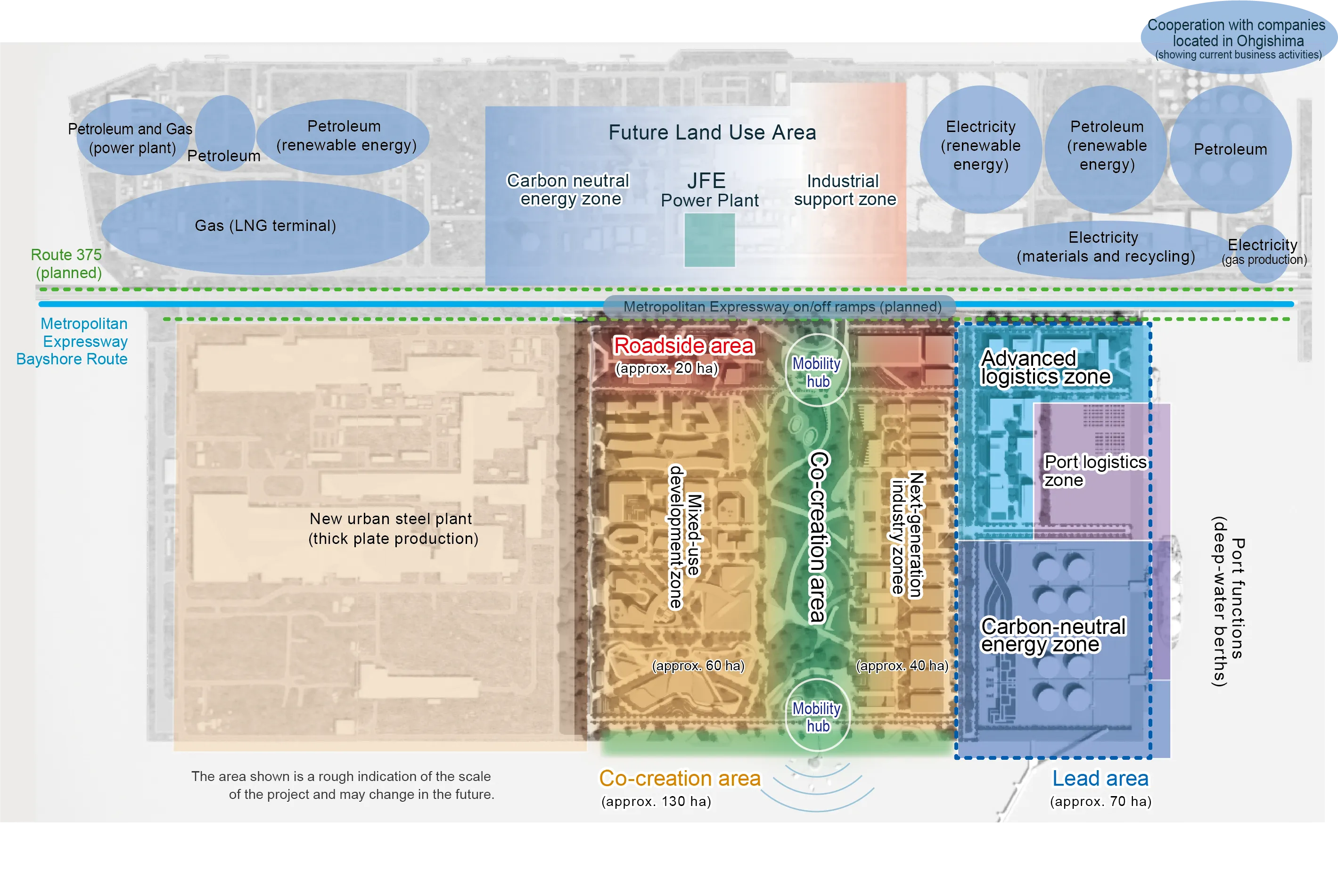
Initiatives for Developing a Hydrogen Supply Hub in the Carbon-Neutral Energy Zone
The Lead Area of the Ohgishima district has been designated as a Carbon-neutral Energy Zone, where hydrogen supply facilities will be deployed. Dramatically improved access to these facilities will support carbon neutrality and innovation across the entire district. The location has been selected as the construction site for a liquefied hydrogen receiving terminal under the “Commercial demonstration of Liquefied Hydrogen Supply Chain,” under the Green Innovation Fund Project of NEDO, being undertaken by Japan Suiso Energy, Ltd. (JSE) . A land lease agreement between JFE Steel and JSE was concluded in July 2024, the transfer of the land commenced in April 2025, and construction of the hydrogen receiving terminal began in May 2025. Preparations are steadily underway toward starting commercial demonstration operations in FY2028.
The hydrogen to be supplied in the future to Ohgishima will be used to generate green electricity at JFE’s in-house power plant, which will in turn be supplied to ongoing factory operations. Surplus power will also be supplied to JSE in the leading area, advanced logistics operators, and a data center in the northern part of Ohgishima that is under consideration for joint commercialization with Mitsubishi Corporation. In addition, we envision using hydrogen also as a green fuel in the reheating furnaces of the plate mill.
Starting from Ohgishima, the JFE Group plans to play a role in building a stable, economical supply chain for hydrogen and other decarbonized fuels and to contribute to realizing carbon neutrality throughout society, including the Keihin waterfront area.


Adapting to Climate Change (Contribution to Achieving Societal Resilience)
Contributions to Disaster Prevention and Mitigation and Increased National Resilience
The JFE Group is not only focused on reducing CO2 emissions (climate change mitigation); we also intend to contribute to the resilience of society in general by adapting to climate change. With infrastructure such as hybrid tide embankments and permeable steel slit dams, the Group will contribute to preventing and mitigating disaster-related damage to infrastructure that is critical to daily life and economic activities and to strengthening their resilience.
Hybrid Tide Embankments
Hybrid tide embankments are made of steel and concrete. Because of their hybrid structure, they require shorter construction time and less space.
Concrete blocks for hybrid tide embankments are precast at a JFE Group factory, while steel pipe piles for foundations are installed at the construction site, thereby reducing the time required for on-site construction by about 60%. This arrangement does not require large amounts of materials, equipment, or workers on site, so it does not interfere with other construction work. Furthermore, compared to a conventional embankment structure, the land area occupied by the embankment can be reduced by about 80%, saving considerable space. We will continue to apply and advance our technology to further contribute to disaster prevention in the region.

Permeable Steel Slit Dams
A permeable steel slit dam is a steel pipe structure installed in a river to trap debris flows.
Made of strong steel pipes to withstand the impact of driftwood and huge debris, it has large openings to let water and sediment to pass through, which prevents the water level from rising upstream during floods and also ensuring that debris does not flow downstream. Since it does not block the flow of water, unlike a dam, it can be shaped to the slope of a riverbed to protect the ecosystem. The JFE Group is working to expand the use of permeable steel slit dams by reducing installation costs and shortening the construction period through structural innovations.

Terre Armée Method
The Terre Armée method involves reinforced soil wall construction in which layers of steel reinforcements are laid within an embankment to create a vertically strong structure with excellent earthquake resistance.
The robust yet flexible structure formed by interaction between the embankment and the reinforcements helps suppress sediment-related disasters from increasingly severe natural hazards (heavy rainfall and major earthquakes) and supports the maintenance of critical lifelines.
JFE Shoji Terre One Corporation, a subsidiary of JFE Shoji, is working to commercialize low-carbon facing panels that use blast furnace slag generated by JFE Steel as facing materials for the Terre Armée method. This is expected to reduce CO2 emissions by 70% compared to ordinary concrete, differentiating the product as an environmentally friendly solution.
Going forward, we will contribute to building disaster-resistant roads and communities by promoting the Terre Armée method and expanding sales of other products that contribute to disaster prevention and mitigation and strengthen national resilience.

Internal structure of the Terre Armée method

Initiatives to Reduce Energy Consumption
Reducing energy consumption is a core initiative of our response to climate change. The JFE Group is working to improve energy efficiency in our business activities and reduce GHG emissions by introducing renewable energy and optimizing facilities.
Initiatives in the Steel Business
In addition to introducing high-efficiency facilities, we have been working to reduce energy consumption in the steelmaking process by actively applying digital solutions (DS) and IoT technologies. These initiatives improve production efficiency and optimize energy use, representing important steps toward building a sustainable manufacturing framework. Going forward, we will continue pursuing technological innovation and on-site improvement to further enhance energy efficiency.
Energy Consumption and Unit Energy Consumption of JFE Steel
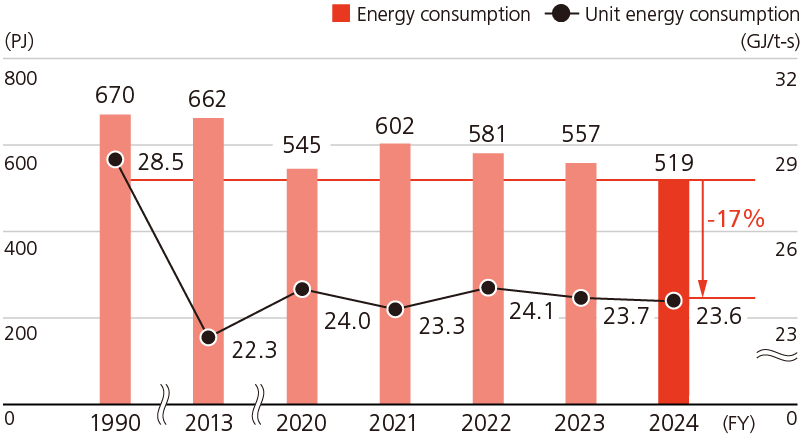
- Note:FY2013 figure includes data for the Sendai Works of JFE Bars & Shapes Corporation.
ST Fuel and Power Operation Guidance System for Steelworks
JFE Steel developed a fuel and power operation guidance system for steelworks and succeeded in saving energy and reducing CO2 as well as fuel and power by optimizing the fuel, steam, and electric power used in the steelmaking process.
Previously, operators determined various factors such as the distribution of byproduct gas to each process, amount of fuel (heavy oil, city gas, etc.) and electricity to purchase, and the amount of byproduct gas stored, taking into account energy demand and supply (amount generated and used) as well as the operating conditions of power generation facilities, to minimize cost and energy loss. However, it was difficult to use this method to accurately estimate the change in energy demand and supply. The guidance system (diagram 1) developed by JFE Steel uses voluminous real-time measurement data (1) obtained through a cyber physical system (CPS)* and the precise production plans of each factory to predict future demand and supply with high accuracy (2), and by taking into account information such as in-house power generation capacity (3), fuel and power simulation allows for the calculation of the optimal operating conditions with the lowest possible purchase from external sources (4), and the results are fed back to guide the operator (5). The system’s development was awarded the Academic Award (Technical Division) of the 2022 Japan Institute of Energy Award. JFE Steel established the JFE Digital Transformation Center (JDXC™) to promote CPS within the manufacturing process and other digital transformation initiatives to achieve innovative production improvements as well as stable operations. We remain committed to realizing a sustainable society by adopting digital transformation to address the various issues identified at production sites.
- *A system that brings together a vast amount of sensor information about physical space as big data in cyberspace and generates value by feeding back in real time the results analyzed by various measures for application in the physical space.
Guidance System Overview
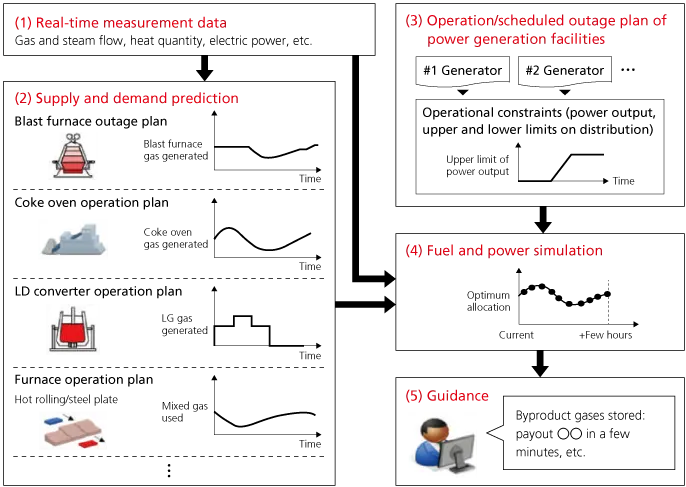
Initiatives in the Trading Business
Under the environmental strategies formulated in 2001, JFE Shoji is continuously implementing initiatives to reduce paper and electricity consumption and strictly manage waste separation as part of its energy reduction efforts.
In terms of reducing paper consumption, the company continues to use recycled paper to conserve natural resources, and we also ensure that documents are printed in black and white using both sides of the paper. We are also promoting paperless meetings through the use of large monitors and web conferencing systems. Consequently, the amount of paper used per employee is on a downward trend. As for electricity consumption, JFE Shoji is reducing its environmental impact by introducing motion-sensor lighting and energy-saving equipment through office renovations, implementing leave-on-time days, improving operational efficiencies through robotic process automation (RPA), and other measures.
Furthermore, the company has established a new goal in the domestic operating companies to reduce CO2 emissions by installing solar panels and purchasing electricity derived from renewable energy sources. Going forward, in addition to procuring renewable energy-derived electricity through solar panel installation, we will begin procuring non-fossil certificates derived from additional renewable energy by introducing off-site PPAs. Domestic group companies reduced CO2 emissions in FY2024 by 32.4% compared to FY2019 through ongoing efforts to reduce electricity usage and a decline in emission factors.
Electric Power Consumption by JFE Shoji
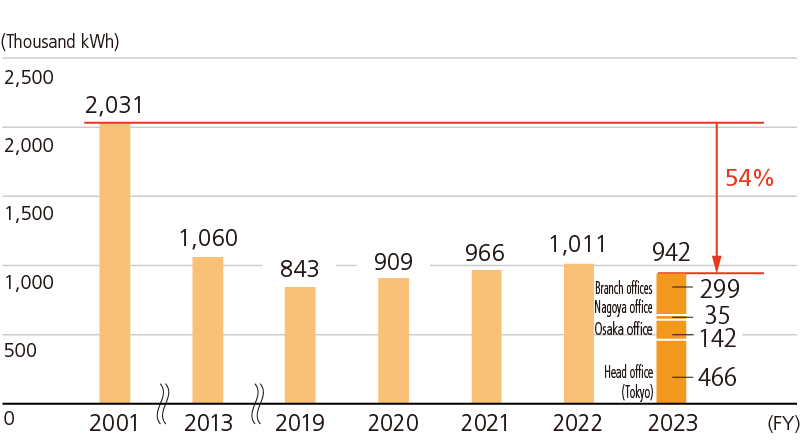
For quantitative data for the JFE Shoji Group’s CO2 emissions, please refer to: